12 Lead Ecg Interpretation Part 1 Authorstream

Ecg 12 Lead Explained Leads i, ii, and iii. two electrodes ( and ) equidistant from heart. records electricity flow from negative to positive electrode. a wave of depolarization moving toward a positive electrode produces a positive deflection on the ecg. depolarization moving away from a positive electrode records a negative deflection. A 12 lead ecg is one of them. the goal of this study guide is to lay the foundation for how you interpret each 12 lead ecg you run on your patients. this is by n o means the end all, be all guide for 12 leads. reading and interpreting a 12 lead ecg takes hundreds of repetitions and lots of study time. as always, follow your local protocols.
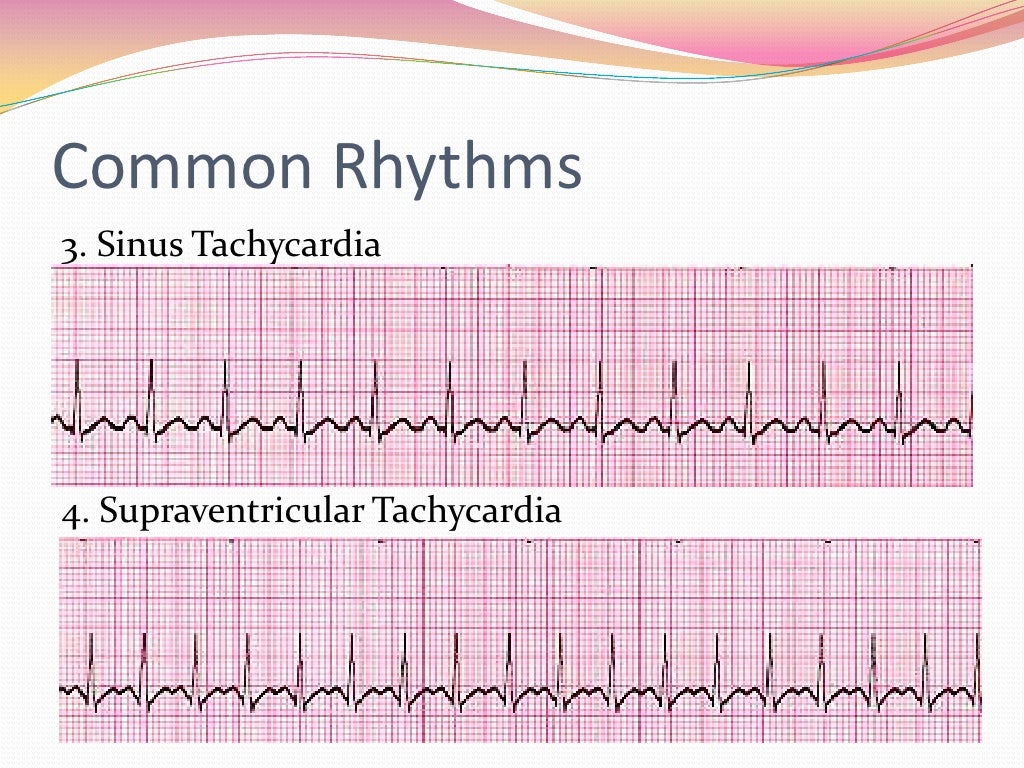
12 Lead Ekg Interpretation 12 lead ecgs, part i: recognizing normal findings. genteral purpose: to provide information about basic 12 lead ecg interpretation. learning objectives: after reading this article and taking this test, you should be able to: 1. describe the normal cardiac conduction system. 2. differentiate between normal and abnormal ecgs. Numerous ecg lead systems and constellations of leads have been tested but the standard 12 lead ecg is still the most used and the most important lead system to master. the 12 lead ecg offers outstanding possibilities to diagnose abnormalities. importantly, the vast majority of recommended ecg criteria (e.g. criteria for acute myocardial. An ecg electrode is a conductive pad attached to the skin to record electrical activity. the data gathered from these electrodes allows the 12 leads of the ecg to be calculated (e.g. lead i is calculated using data from the electrodes on both the right and left arm ). the electrodes used to generate a 12 lead ecg are described below. Step 1. draw a cross on a section of the ecg paper that will not interfere with subsequent interpretation of the ecg in the north to south and east to west configuration. label the 4 ends with “i” or “avf,” and mark whether each is at the positive or negative pole for that lead ( figure 3 ).

Comments are closed.