3 Binomial Theorem Example 1 A Basic Binomial Expansion Question To Get Used To The Formula
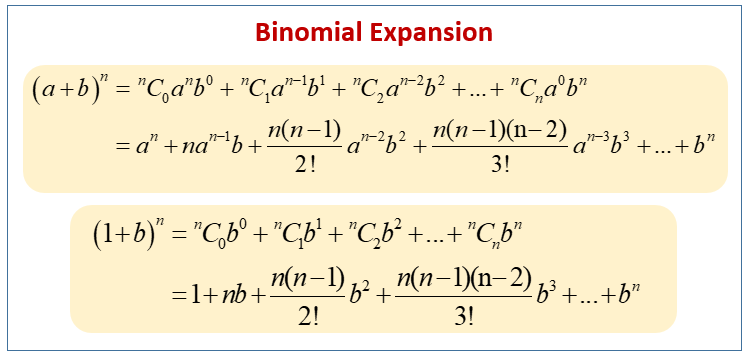
Binomial Expansion Formula Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos A typical binomial expansion question in exams with a hence part.find the first four terms of the expansions (1 3x)^6 and (1 4x)^5. hence find the coefficien. The formula to find the n th term in the binomial expansion of (x y) n is t r 1 = n c r x n r y r. applying this to (2x 3) 9 , t 5 = t 4 1 = 9 c 4 (2x) 9 4 3 4. thus the 5th term is = 9 c 4 (2x) 5 3 4. term independent of x: the steps to find the term independent of x is similar to finding a particular term in the binomial expansion.

3 Binomial Theorem Example 1 A Basic Binomial Expansion The binomial theorem is a formula for expanding binomial expressions of the form (x y) n, where ‘x’ and ‘y’ are real numbers and n is a positive integer. the simplest binomial expression x y with two unlike terms, ‘x’ and ‘y’, has its exponent 0, which gives a value of 1. (x y) 0 = 1. if the exponent is increased by 1, (x. Now take that result and multiply by a b again: (a 2 2ab b 2 ) (a b) = a3 3a2b 3ab2 b3. and again: (a 3 3a 2 b 3ab 2 b 3 ) (a b) = a4 4a3b 6a2b2 4ab3 b4. the calculations get longer and longer as we go, but there is some kind of pattern developing. that pattern is summed up by the binomial theorem:. Let’s use binomial theorem on certain expressions to practically understand the theorem. example 1. expand (a b) 5. solution. (a b) 5 = a n (5 1) a 5– 1 b 1 (5 2) a 5 – 2 b 2 (5 3) a 5– 3 b 3 (5 4) a 5– 4 b 4 b 5 = a 5 5a 4 b 10a 3 b 2 10a 2 b 3 5ab 4 b 5. example 2. expand (x 2) 6 using the binomial theorem. Using the binomial theorem, we can also expand more general powers of sums or differences. example 25.2.1 25.2. 1. expand the expression. (x2 2y3)5 ( x 2 2 y 3) 5. (2xy2 − 4 y2)3 ( 2 x y 2 − 4 y 2) 3. ( 2–√ 1)6 ( 2 1) 6. (i − 3)4 ( i − 3) 4. solution.
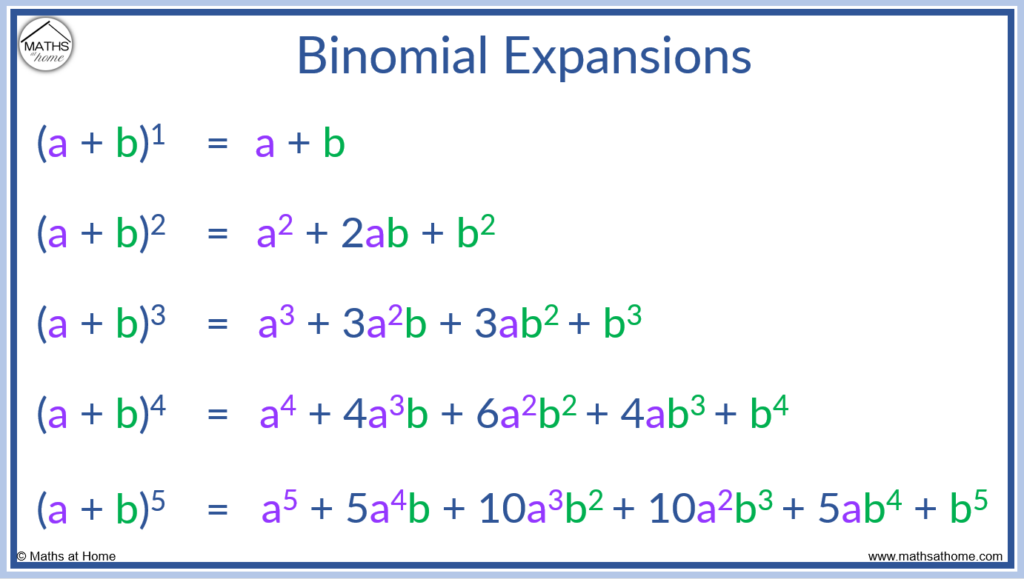
How To Do The Binomial Expansion вђ Mathsathome Let’s use binomial theorem on certain expressions to practically understand the theorem. example 1. expand (a b) 5. solution. (a b) 5 = a n (5 1) a 5– 1 b 1 (5 2) a 5 – 2 b 2 (5 3) a 5– 3 b 3 (5 4) a 5– 4 b 4 b 5 = a 5 5a 4 b 10a 3 b 2 10a 2 b 3 5ab 4 b 5. example 2. expand (x 2) 6 using the binomial theorem. Using the binomial theorem, we can also expand more general powers of sums or differences. example 25.2.1 25.2. 1. expand the expression. (x2 2y3)5 ( x 2 2 y 3) 5. (2xy2 − 4 y2)3 ( 2 x y 2 − 4 y 2) 3. ( 2–√ 1)6 ( 2 1) 6. (i − 3)4 ( i − 3) 4. solution. In the shortcut to finding (x y)n, we will need to use combinations to find the coefficients that will appear in the expansion of the binomial. in this case, we use the notation (n r) instead of c(n, r), but it can be calculated in the same way. so. (n r) = c(n, r) = n! r!(n − r)! the combination (n r) is called a binomial coefficient. Binomial theorem. the binomial theorem is used to expand polynomials of the form (x y) n into a sum of terms of the form ax b y c, where a is a positive integer coefficient and b and c are non negative integers that sum to n. it is useful for expanding binomials raised to larger powers without having to repeatedly multiply binomials.

Comments are closed.