Acute Kidney Injury A K A Acute Renal Failure Animation

Acute Kidney Injury A K A Acute Renal Failure Animation Youtube (usmle topics) pathology of aki, causes (prerenal, renal and postrenal), symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. purchase a license to download a non watermarked. Acute kidney injury. chris nickson. nov 3, 2020. home ccc. reviewed and revised 7 august 2015. overview. aki is the entire spectrum of disease (mild > severe), and can be defined as an abrupt (1 to 7 days) and sustained (more than 24 hours) decrease in kidney function. mortality of critically patients with acute renal failure is high (50%–60.

Acute Renal Failure Vs Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury (aki), previously called acute renal failure (arf), denotes a sudden and often reversible reduction in kidney function, as measured by glomerular filtration rate (gfr).[1][2][3] however, immediately after a renal insult, blood urea nitrogen (bun) or creatinine (cr) levels may be within the normal range, and the only sign of aki may be a decline in urine output. Acute kidney injury (aki) is an abrupt and usually reversible decline in the glomerular filtration rate (gfr). this results in an elevation of serum blood urea nitrogen (bun), creatinine, and other metabolic waste products that are normally excreted by the kidney. in addition, if urine output is also diminished, fluid retention and volume. Management of acute kidney injury is primarily supportive, with the goals of preventing further damage and promoting recovery of renal function. 7 figure 1 is a suggested approach to the. Acute kidney injury (aki) refers to an abrupt decrease in kidney function, resulting in the retention of urea and other nitrogenous waste products and in the dysregulation of extracellular volume and electrolytes. the term aki has largely replaced acute renal failure (arf), reflecting the recognition that smaller decrements in kidney function.

Acute Kidney Injury Aki Nursing Process Adpie Osmosis Management of acute kidney injury is primarily supportive, with the goals of preventing further damage and promoting recovery of renal function. 7 figure 1 is a suggested approach to the. Acute kidney injury (aki) refers to an abrupt decrease in kidney function, resulting in the retention of urea and other nitrogenous waste products and in the dysregulation of extracellular volume and electrolytes. the term aki has largely replaced acute renal failure (arf), reflecting the recognition that smaller decrements in kidney function. Acute kidney injury (aki) describes a range of conditions in which nephrons are damaged, impairing their function and reducing the efficiency of filtration through the glomerulus. infographic. Renal ultrasonography should be performed in most patients with acute kidney injury to rule out obstruction. adequate fluid balance should be maintained in patients with acute kidney injury by.
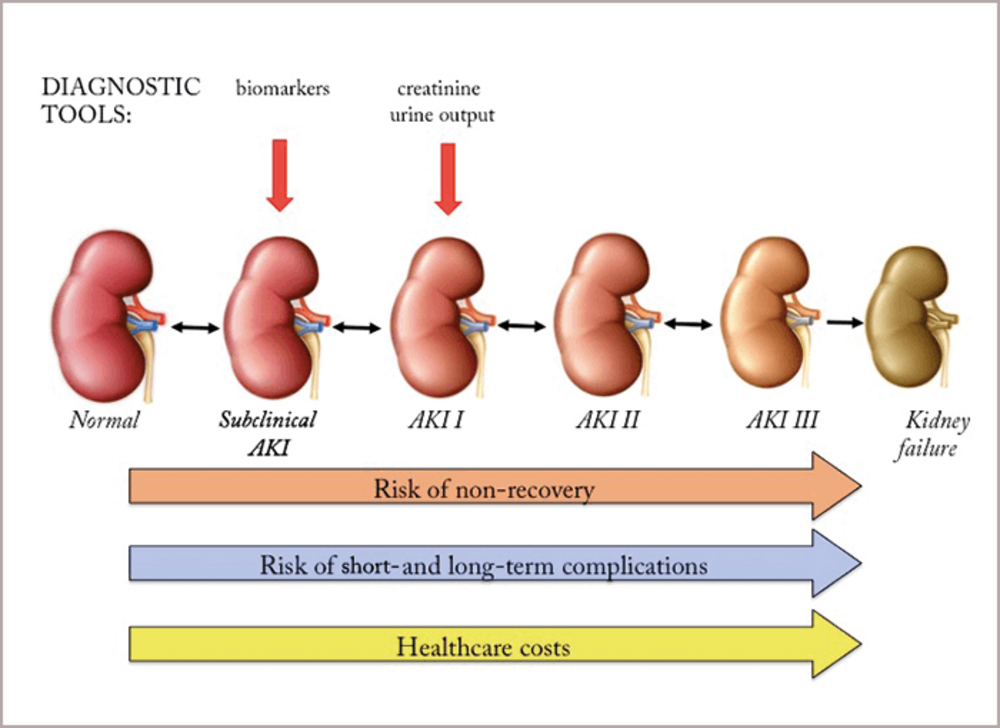
A Renal Failure Acute kidney injury (aki) describes a range of conditions in which nephrons are damaged, impairing their function and reducing the efficiency of filtration through the glomerulus. infographic. Renal ultrasonography should be performed in most patients with acute kidney injury to rule out obstruction. adequate fluid balance should be maintained in patients with acute kidney injury by.

Comments are closed.