Algebra Algebra Formulas Definitions Examples Cuemath
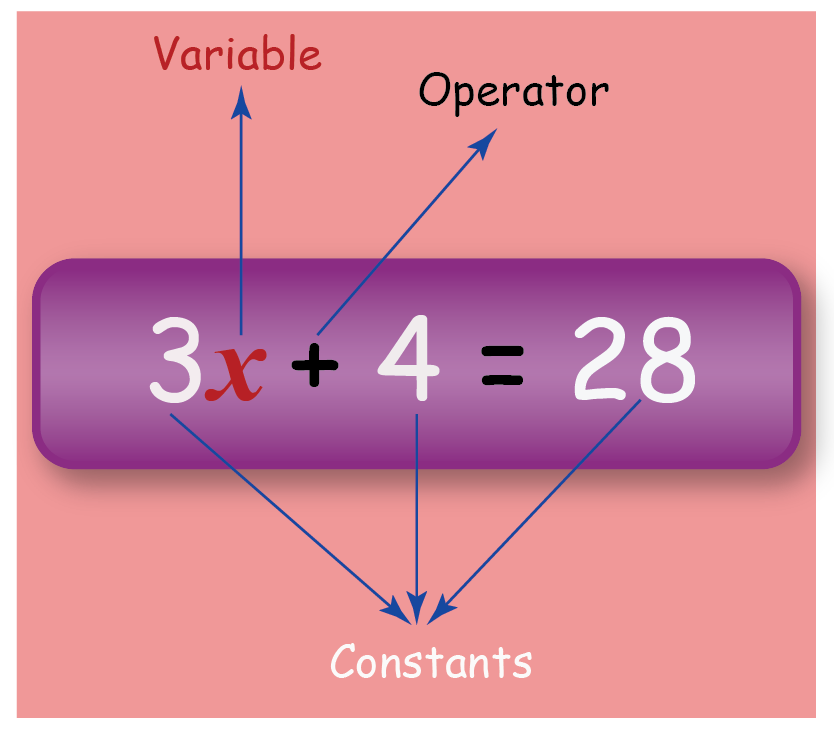
Algebra Algebra Formulas Definitions Examples Cuemath A linear algebraic equation is one in which the degree of the polynomial is 1. the general form of a linear equation is given as a 1 x 1 a 2 x 2 a n x n = 0 where at least one coefficient is a non zero number. these linear equations are used to represent and solve linear programming problems. example: 3x 5 = 5 is a linear equation in. An algebraic expression in algebra is formed using integer constants, variables, and basic arithmetic operations of addition ( ), subtraction ( ), multiplication (×), and division ( ). an example of an algebraic expression is 5x 6. here 5 and 6 are fixed numbers and x is a variable. further, the variables can be simple variables using.

Algebra Algebra Formulas Definitions Examples Cuemath Vector algebra helps for numerous applications in physics, and engineering to perform addition and multiplication operations across physical quantities, represented as vectors in three dimensional space. let us learn more about vector algebra, operations in vector algebra, vector types, with the help of solved examples, and practice questions. Algebraic expressions (definition, basics, formulas &. Basic algebra operations. the general arithmetic operations performed in the case of algebra are: addition: x y. subtraction: x – y. multiplication: xy. division: x y or x ÷ y. where x and y are the variables. the order of these operations will follow the bodmas rule, which means the terms inside the brackets are considered first. Square of the sum: (a b)2 = a2 2ab b2. square of the difference: (a– b)2 = a2– 2ab b2. difference of squares: a2–b2 = (a b)(a– b) this quick example of the square of the sum formula, will help you see how this formula works in practice. the following formulas are useful when expanding and simplifying binomials.
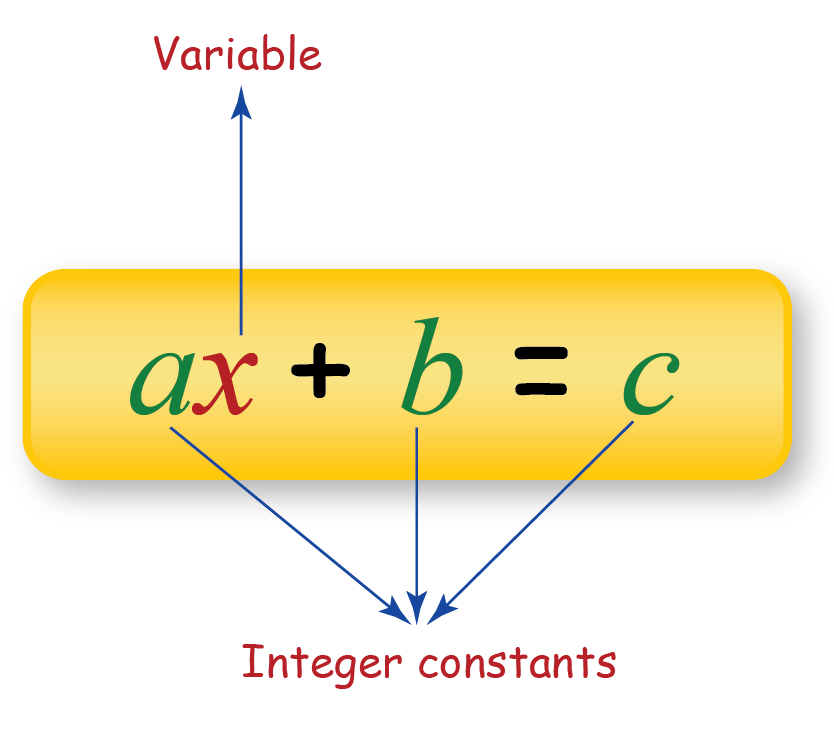
Algebra Algebra Formulas Definitions Examples Cuemath Basic algebra operations. the general arithmetic operations performed in the case of algebra are: addition: x y. subtraction: x – y. multiplication: xy. division: x y or x ÷ y. where x and y are the variables. the order of these operations will follow the bodmas rule, which means the terms inside the brackets are considered first. Square of the sum: (a b)2 = a2 2ab b2. square of the difference: (a– b)2 = a2– 2ab b2. difference of squares: a2–b2 = (a b)(a– b) this quick example of the square of the sum formula, will help you see how this formula works in practice. the following formulas are useful when expanding and simplifying binomials. Solved examples on formula in math. example 1: find the perimeter of a square with a side of 5 units. solution: perimeter of a square = 4 × side = 4 × 5 = 20 units. example 2: find the value of n, when 3 7 × 3n = 32. solution: using the laws of exponents, we get. Example . let us take an example of the algebraic expression 2x 6. here, x is a variable and can take any value. if x = 1, the value of this algebraic expression will be 2 (1) 6 i.e. 8 and. if x = 2, the value of the algebraic expression changes to 10. hence, we can say that the value of the algebraic expression varies as the x varies.

Algebra Algebra Formulas Definitions Examples Cuemath Solved examples on formula in math. example 1: find the perimeter of a square with a side of 5 units. solution: perimeter of a square = 4 × side = 4 × 5 = 20 units. example 2: find the value of n, when 3 7 × 3n = 32. solution: using the laws of exponents, we get. Example . let us take an example of the algebraic expression 2x 6. here, x is a variable and can take any value. if x = 1, the value of this algebraic expression will be 2 (1) 6 i.e. 8 and. if x = 2, the value of the algebraic expression changes to 10. hence, we can say that the value of the algebraic expression varies as the x varies.

Comments are closed.