Amino Acids Types Structure And Function

Compound Interest A Brief Guide To The Twenty Common Amino Acids Amino acids are a crucial, yet basic unit of protein, and they contain an amino group and a carboxylic group. they play an extensive role in gene expression process, which includes an adjustment of protein functions that facilitate messenger rna (mrna) translation. there are over 700 types of amino acids that have been discovered in nature. Proline is a non essential amino acid and is coded by ccu, ccc, cca, and ccg. it is the least flexible of the protein amino acids and thus gives conformational rigidity when present in a protein. proline’s presence in a protein affects its secondary structure. it is a disrupter of α helices and β strands.
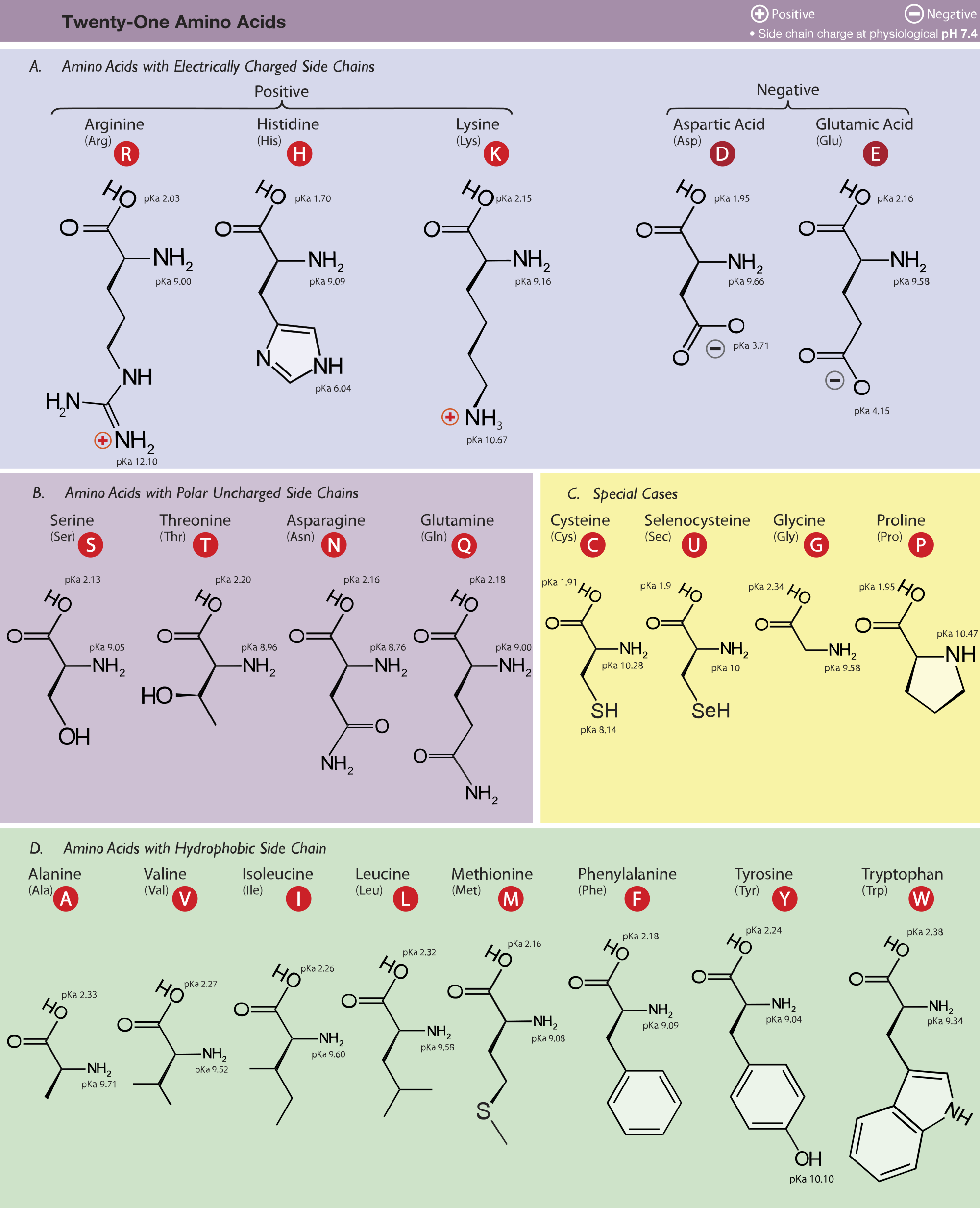
Amino Acid Study Guide Structure And Function Albert Io Definition. amino acids are the building blocks of polypeptides and proteins and play important roles in metabolic pathway, gene expression, and cell signal transduction regulation. a single organic amino acid molecule contains two functional groups – amine and carboxyl – and a unique side chain. humans require twenty different amino acids. Each of these polypeptide chains is made up of amino acids, linked together in a specific order. a polypeptide is kind of like a long word that is "spelled out" in amino acid letters 4 . the chemical properties and order of the amino acids are key in determining the structure and function of the polypeptide, and the protein it's part of. All amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in figure 2.1. at the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it are four groups – a hydrogen, a carboxylic acid group, an amine group, and an r group, sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. the α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino. Structure of a typical l alpha amino acid in the "neutral" form. amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. [1] although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α amino acids incorporated into proteins. [2] only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life.
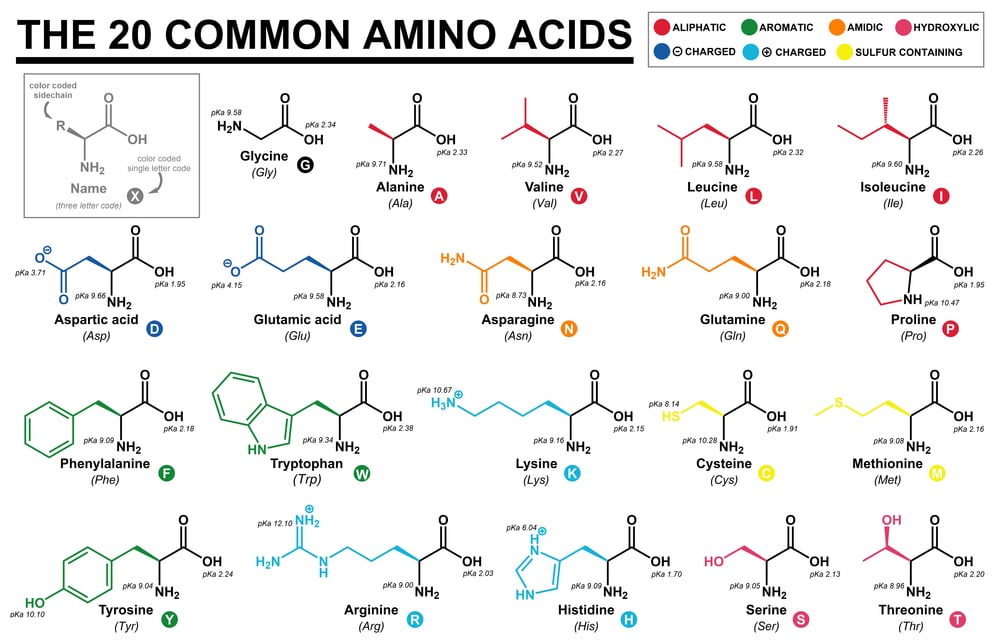
What Are The Two Rare Amino Acids в Scienceabc All amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in figure 2.1. at the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it are four groups – a hydrogen, a carboxylic acid group, an amine group, and an r group, sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. the α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino. Structure of a typical l alpha amino acid in the "neutral" form. amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. [1] although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α amino acids incorporated into proteins. [2] only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (―nh 2 ), an acidic carboxyl group (―cooh), and an organic r group (or side chain) that is unique to each amino acid. the term amino acid is short for α amino [alpha amino] carboxylic acid. each molecule contains a central carbon (c) atom, called the α. Glycine (gly g) is the amino acid with the shortest side chain, having an r group consistent only of a single hydrogen. as a result, glycine is the only amino acid that is not chiral. its small side chain allows it to readily fit into both hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments. figure 2.3 non polar amino acids.

Comments are closed.