Amplitude Period And Phase Shift Of Sine And Cosine Functions

How To Find Phase Shift Of Cosine Function Amplitude a = 2. period 2π b = 2π 4 = π 2. phase shift = −0.5 (or 0.5 to the right) vertical shift d = 3. in words: the 2 tells us it will be 2 times taller than usual, so amplitude = 2. the usual period is 2 π, but in our case that is "sped up" (made shorter) by the 4 in 4x, so period = π 2. and the −0.5 means it will be shifted to. Peak if the coefficient before the function is positive; or. trough if the coefficient is negative. calculate the distance from the vertical line to that point. if the function was a sine, subtractπ 2 or 3π 2 from that distance for a peak or a trough, respectively. enjoy having found the phase shift from a graph.

Amplitude Period Phase Shift And Vertical Shift Of Trigonometric Learn how to graph the sine and cosine functions using their amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift. explore the relationship between these functions and the unit circle. openstax offers free online textbooks and resources for precalculus and other math courses. In this simplified example, we really have only one transformation to worry about the phase shift. notice that the amplitude, period and vertical shift have all been left out. when considering a sine or cosine graph that has a phase shift, a good way to start the graph of the function is to determine the new starting point of the graph. Periodic functions repeat after a given value. the smallest such value is the period. the basic sine and cosine functions have a period of \(2\pi\). the function \(\sin x\) is odd, so its graph is symmetric about the origin. the function \(\cos x\) is even, so its graph is symmetric about the y axis. As discussed below, given any generalized sine or cosine curve, you should be able to determine its amplitude, period, and phase shift. sample question: state the amplitude, period, and phase shift of $\,y = 5\sin(3x 1)\,.$.

Phase Shift Amplitude Frequency Period в Matter Of Math Periodic functions repeat after a given value. the smallest such value is the period. the basic sine and cosine functions have a period of \(2\pi\). the function \(\sin x\) is odd, so its graph is symmetric about the origin. the function \(\cos x\) is even, so its graph is symmetric about the y axis. As discussed below, given any generalized sine or cosine curve, you should be able to determine its amplitude, period, and phase shift. sample question: state the amplitude, period, and phase shift of $\,y = 5\sin(3x 1)\,.$. The final piece of the puzzle, the vertical shift works the same way, but measures how far up or down the y axis, or vertically, the wave has been shifted from the normal sine function. sinusoidal functions. sinusoidal functions are periodic, but also use a trigonometric function like sine or cosine. sin usoidal. you met one of them earlier. Transformations of sine and cosine (amplitude, period, phase shift and vertical shift) graph sine and cosine functions with the four basic transformations: amplitude, period, phase shift and vertical shift. graph y = asin(b(x d)) c and y = acos(b(x d)) c. show step by step solutions.

Graphing Sine And Cosine With Amplitude Period Phase Shift And V The final piece of the puzzle, the vertical shift works the same way, but measures how far up or down the y axis, or vertically, the wave has been shifted from the normal sine function. sinusoidal functions. sinusoidal functions are periodic, but also use a trigonometric function like sine or cosine. sin usoidal. you met one of them earlier. Transformations of sine and cosine (amplitude, period, phase shift and vertical shift) graph sine and cosine functions with the four basic transformations: amplitude, period, phase shift and vertical shift. graph y = asin(b(x d)) c and y = acos(b(x d)) c. show step by step solutions.
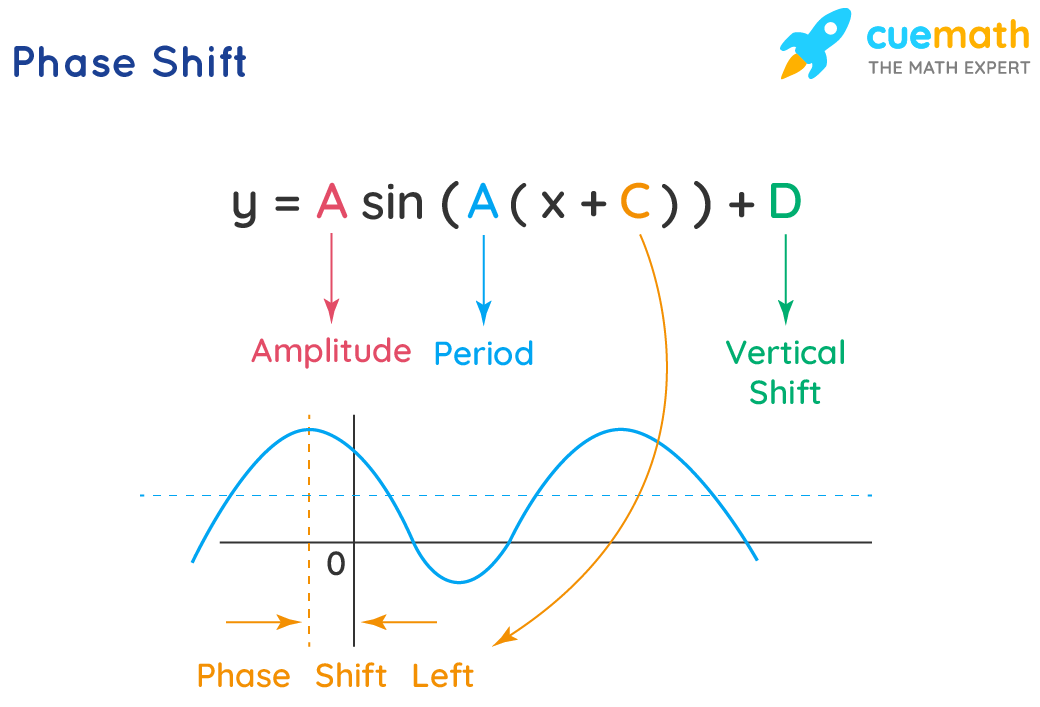
How To Find Phase Shift Of Cosine Function

Comments are closed.