Angles Formula What Is Angles Formula What Is Central Angle Formula
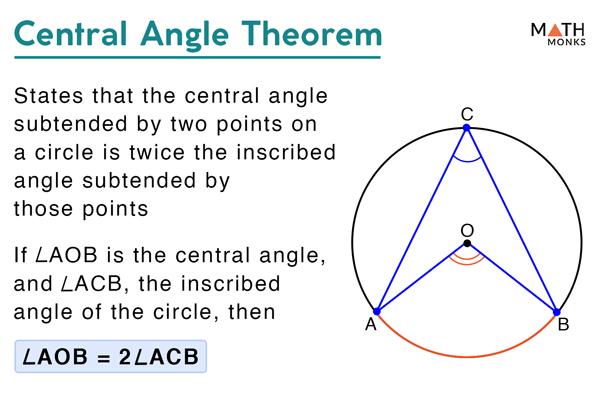
Central Angle вђ Definition Formula Theorem With Examples Examples using angle formulas. example 1: jill has a circular segment with an arc length is 7π and a radius is 9 units. find the angle of the segment using the angles formulas. solution: arc length = 7π (given) radius = 9 units (given) using angles formulas, angle = (arc length × 360 o) 2π r. angle = (7π × 360 o) 2π × 9}. The central angle of a circle formula is as follows. central angle= \(\frac{s \times 360^0}{2 \pi r}\) here "s" is the length of the arc and "r" is the radius of the circle. this is the formula for finding central angle in degrees. for finding the central angle in radians, we have to divide the arc length by the length of the radius of the circle.

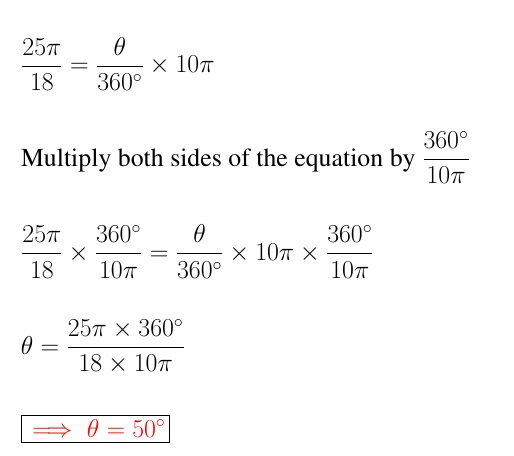
Angles Formula What Is Angles Formula What Is Central Angle Formula Solution: as we know, central angle = arc length x 360° 2πr, here central angle = 88°arc length = 28 cm. 88° = 28 x 360° 2 x 3.14 x r. r = 28 x 360° 2 x 3.14 x 88. = 10080° 552.64. = 18.23 cm. what is a central angle of a circle and how to find their measure– its definition in geometry, proof of theorem, formula & examples. We know that. central angle = s × 360 2 π r. where, “ s ” is the length of the arc, and “ r ” is the radius of the circle. central angle = 11 × 360 2 × 22 7 × 7 = 90 ∘. the angle will be 90 ∘. 4. in the circle below, find out the value of “a.”. solution: we know that the central angle = intercepted arc. Measuring central angles: the measure of a central angle is directly equal to the measure of the arc it intercepts. central angle theorem: states that the measure of a central angle is exactly equal to the measure of the arc that it intercepts. central angle formula: central angle (in degrees) = (arc length circumference) x 360. Angle aob is a central angle. a central angle is an angle whose apex (vertex) is the center o of a circle and whose legs (sides) are radii intersecting the circle in two distinct points a and b. central angles are subtended by an arc between those two points, and the arc length is the central angle of a circle of radius one (measured in radians). [1].
What Is A Central Angle Measuring central angles: the measure of a central angle is directly equal to the measure of the arc it intercepts. central angle theorem: states that the measure of a central angle is exactly equal to the measure of the arc that it intercepts. central angle formula: central angle (in degrees) = (arc length circumference) x 360. Angle aob is a central angle. a central angle is an angle whose apex (vertex) is the center o of a circle and whose legs (sides) are radii intersecting the circle in two distinct points a and b. central angles are subtended by an arc between those two points, and the arc length is the central angle of a circle of radius one (measured in radians). [1]. Because the polygon is regular, all central angles are equal. it does not matter which side you choose. all central angles would add up to 360° (a full circle), so the measure of the central angle is 360 divided by the number of sides. or, as a formula: where. the measure of the central angle thus depends only on the number of sides. The measure of an arc of a circle is congruent to the measure of the central angle that intercepts the arc. if a central angle and an inscribed angle subtended by the same arc, central angle is twice the inscribed angle. in a circle or in congruent circles, congruent central angles have congruent arcs.
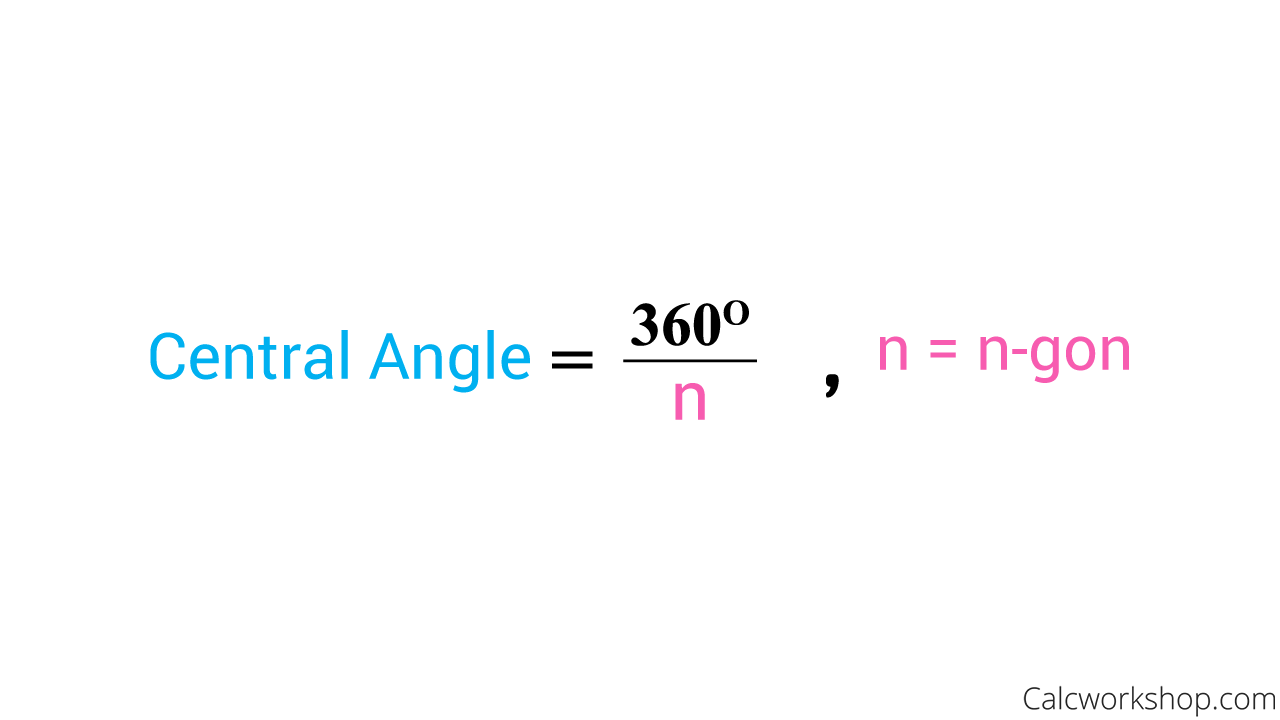
Area Of A Regular Polygon 17 Step By Step Examples Because the polygon is regular, all central angles are equal. it does not matter which side you choose. all central angles would add up to 360° (a full circle), so the measure of the central angle is 360 divided by the number of sides. or, as a formula: where. the measure of the central angle thus depends only on the number of sides. The measure of an arc of a circle is congruent to the measure of the central angle that intercepts the arc. if a central angle and an inscribed angle subtended by the same arc, central angle is twice the inscribed angle. in a circle or in congruent circles, congruent central angles have congruent arcs.

Comments are closed.