Aortic Aneurysm Cardiac Nursing School Pathophysiology Nursing
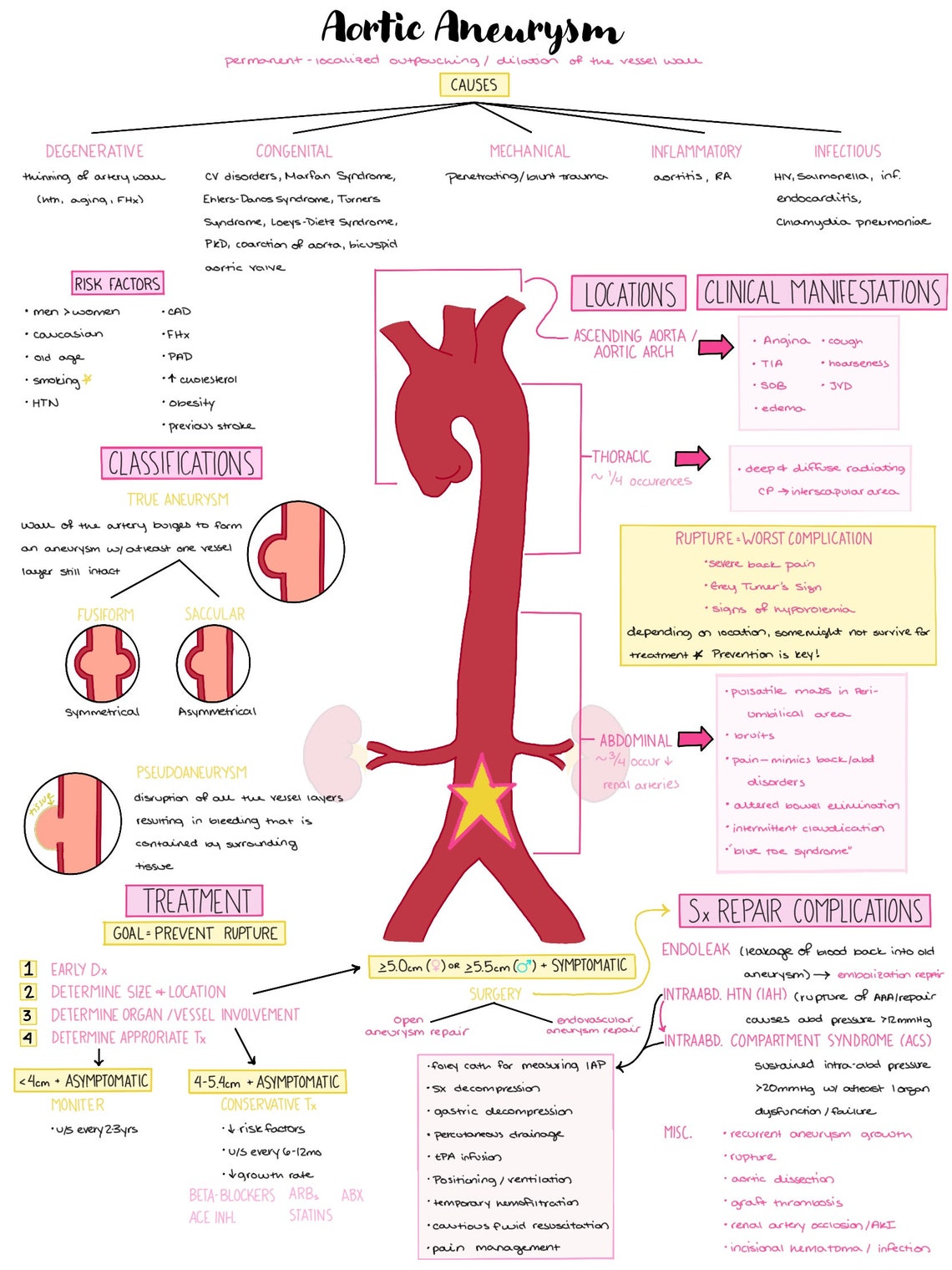
Aortic Aneurysm Nursing Notes Nclex Notes Pathophysiology Notes Nursingођ Gently palpate the abdomen for a midline mass or pulsation. an enlarging abdominal aortic aneurysm may present as a midline pulsatile abdominal mass. the pulsations may equal the apical heart rate. the technique for pulsation should be as gentle as possible to avoid trauma to the aneurysm. 7. Overview. dilation or outpouching of the aorta due to the weakened medial layer of the blood vessel. most commonly caused by hypertension. pathophysiology: this caused by a weakened medial layer of the vessel wall. the medical wall balloons out from the pressure. this forms the aneurysm. nursing points. general. classified by location.

Aortic Aneurysm Nursing Process Adpie Osmosis Pathophysiology. “a dilation or out pouching of the aorta due to weakened medial layer. it is a classified by location (thoracic, abdominal). there are four different types; dissection blood vessels separated by layer of blood; fusiform dilation that involve the entire circumference; saccular localized out pouching; false clot forms. Abdominal aortic aneurysm (aaa), abnormal focal dilation of the abdominal aorta, is a life threatening condition that requires monitoring or treatment depending upon the size of the aneurysm and or symptomatology. aaa may be detected incidentally or at the time of rupture. an arterial aneurysm is defined as a permanent localized dilatation of the vessel at least 150% compared to a relative. Pathophysiology when the aorta is under extreme high pressure from hypertension, the wall of the vessel can weaken, causing a dilation or outpouching of the vessel that is extremely weak, causes turbulent flow, and is at high risk for rupture. aortic aneurysms are classified by location: thoracic and abdominal. there are four types of aneurysms that […]. Lesson objective for aortic aneurysm nursing care. an aortic aneurysm is a serious condition involving the aorta, the largest blood vessel in the body that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. imagine the aorta like a major water pipe in a building. normally, this pipe is strong and can handle the high pressure of water flowing.
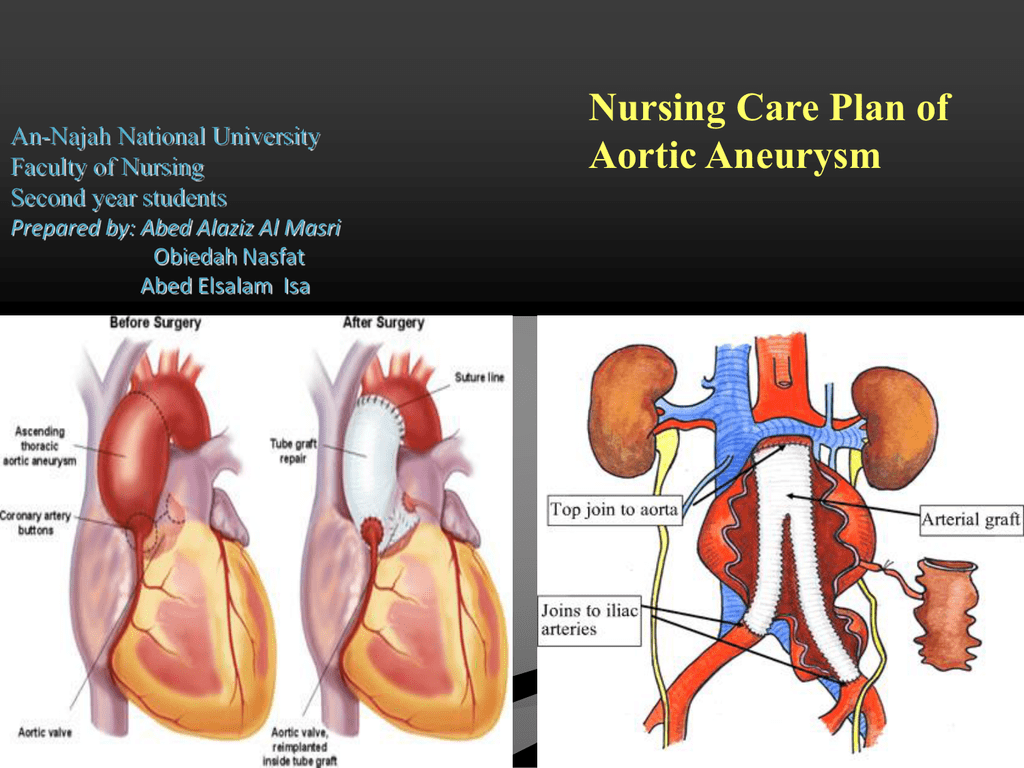
Nursing Care Plan Of Aortic Aneurysm An Pathophysiology when the aorta is under extreme high pressure from hypertension, the wall of the vessel can weaken, causing a dilation or outpouching of the vessel that is extremely weak, causes turbulent flow, and is at high risk for rupture. aortic aneurysms are classified by location: thoracic and abdominal. there are four types of aneurysms that […]. Lesson objective for aortic aneurysm nursing care. an aortic aneurysm is a serious condition involving the aorta, the largest blood vessel in the body that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. imagine the aorta like a major water pipe in a building. normally, this pipe is strong and can handle the high pressure of water flowing. The thoracic aorta consists of the aortic root, ascending aorta, aortic arch, and the descending aorta.[1] an aneurysm occurs when the typical diameter of the artery increases by 50%.[2] it occurs due to the intrinsic weakness of the aortic wall. thoracic aortic aneurysms (taa) rarely manifest with symptoms, and about 95% of the patients are asymptomatic.[3][4] these aneurysms can lead to. The need for intervention is based on the size of the aneurysm. 1 the overall goal is to prevent rupture. 2 the american heart association american college of cardiology (aha acc) guidelines recommend surgical referral when the aortic root, or the ascending aorta diameter, measures 5.5 cm or more. for aneurysms less than 4.0 cm in arch diameter.

Aortic Aneurysm Cardiac Nursing School Aortic Aneurysm Abd The thoracic aorta consists of the aortic root, ascending aorta, aortic arch, and the descending aorta.[1] an aneurysm occurs when the typical diameter of the artery increases by 50%.[2] it occurs due to the intrinsic weakness of the aortic wall. thoracic aortic aneurysms (taa) rarely manifest with symptoms, and about 95% of the patients are asymptomatic.[3][4] these aneurysms can lead to. The need for intervention is based on the size of the aneurysm. 1 the overall goal is to prevent rupture. 2 the american heart association american college of cardiology (aha acc) guidelines recommend surgical referral when the aortic root, or the ascending aorta diameter, measures 5.5 cm or more. for aneurysms less than 4.0 cm in arch diameter.

Aortic Aneurysms Cardiac Nursing Medical Knowledge Nursing Schoolођ

Comments are closed.