Arithmetic Progression Ap Formula Nth Term Sum Examples

Arithmetic Progression Ap Formula Nth Term Sum Examples The general term (or) n th term of an ap whose first term is 'a' and the common difference is 'd' is given by the formula a n = a (n 1) d. for example, to find the general term (or) n th term of the progression 6, 13, 20, 27, 34,. . . ., we substitute the first term, a 1 = 6, and the common difference, d = 7 in the formula for the n th term formula. Definition 1: a mathematical sequence in which the difference between two consecutive terms is always a constant and it is abbreviated as ap. definition 2: an arithmetic sequence or progression is defined as a sequence of numbers in which for every pair of consecutive terms, the second number is obtained by adding a fixed number to the first one.

Sum Of The First N Terms Of An Arithmetic Progression A Plus Topper Sum of the terms of an arithmetic progression. let an ap has the first term a and the common difference d. then the sum of the first n terms of the ap is given below: s n = n 2 [ 2 a ( n − 1) d] proof: note that the ap has the form a, a d, a 2 d, ⋯. its n th term a n = a ( n − 1) d. Nth term of arithmetic progression. the formula a n = a ( n – 1 ) d is used to get the general term (or) nth term of an arithmetic progression (ap) whose first term is a, and the common difference is d. for example, we have the sequence 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23, and 26. finding the general term or the nth term, we will substitute a =5 as. Problem: given the n th term of an arithmetic progression t n = 2 n 3, find the sum of the first n terms, s n, using the relationships p = 2 p and q = q − p derived from the general form of an arithmetic progression sum s n = p n 2 q n. solution: step 1: identify p and q from t n. from t n = 2 n 3, we identify:. The formula used to find the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is n 2 (2a (n−1)d). what is the sum of n terms of an ap when the last term is given? if a n is the n th term of an arithmetic progression, a is the first term, and n is the total number of terms, then we can use the following formula to find its sum: s n = n 2 (a 1 a n).
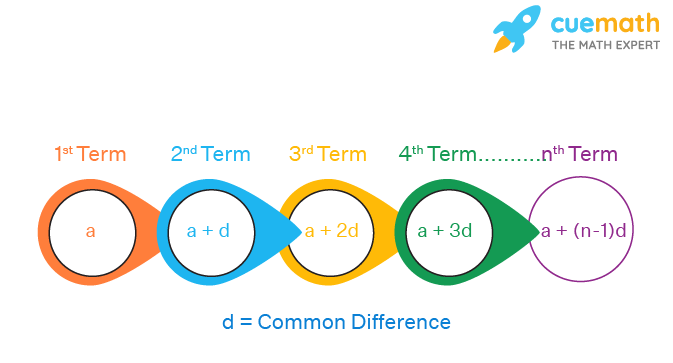
Arithmetic Progression Ap Formula Nth Term Sum Examples Problem: given the n th term of an arithmetic progression t n = 2 n 3, find the sum of the first n terms, s n, using the relationships p = 2 p and q = q − p derived from the general form of an arithmetic progression sum s n = p n 2 q n. solution: step 1: identify p and q from t n. from t n = 2 n 3, we identify:. The formula used to find the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is n 2 (2a (n−1)d). what is the sum of n terms of an ap when the last term is given? if a n is the n th term of an arithmetic progression, a is the first term, and n is the total number of terms, then we can use the following formula to find its sum: s n = n 2 (a 1 a n). First term = a = 2. common difference = d = 4. term to be found is 11 th term. so n = 11. hence, the 11 th term for the given progression is, t n = a (n 1)d. t 11 = 2 (11 1)4 = 2 40 = 42. thus, the 11 th term of given ap is 42. example 2: if the 5 th term of an ap is 40 with a common difference of 6. A n is called the general term of an ap. sum of n terms in an arithmetic progression. the sum of first n terms in arithmetic progressions can be calculated using the formula given below. s = [ (n 2) * (2a (n – 1) d)] here s is the sum, n is the number of terms in ap, a is the first term and d is the common difference.

Comments are closed.