Atrial Fibrillation Overview Ecg Types Pathophysiology Treatment Complications

Atrial Fibrillation Overview Ecg Types Pathophysiology Treatm Buy pdfs here: armandoh.org shop "atrial fibrillation (af) is the most popular arrhythmia and diagnosed by the finding of an irregularly irregular ven. Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of cardiac arrhythmia. it is due to abnormal electrical activity within the atria of the heart, causing them to fibrillate. it is characterized as a tachyarrhythmia, which means that the heart rate is often fast. this arrhythmia may be paroxysmal (less than seven days) or persistent (more than seven days). due to its rhythm irregularity, blood flow.

Atrial Fibrillation Overview Ecg Types Pathophysiology Treatm Atrial fibrillation (af), the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, is becoming progressively more prevalent with population aging. 1 enormous advances in the understanding of af pathophysiology have occurred over the past 20 years. 2,3 the present article, part of a thematic series in circulation on af, provides a broad overview of af pathophysiology and the potential implications for af. Atrial fibrillation (afib) is an irregular heart rhythm that begins in your heart’s upper chambers (atria). symptoms include fatigue, heart palpitations, trouble breathing and dizziness. afib is one of the most common arrhythmias. risk factors include high blood pressure, coronary artery disease and having obesity. During atrial fibrillation, the heart's upper chambers — called the atria — beat chaotically and irregularly. they beat out of sync with the lower heart chambers, called the ventricles. for many people, afib may have no symptoms. but afib may cause a fast, pounding heartbeat, shortness of breath or light headedness. Atrial fibrillation (af) is an ectopic rhythm originating in the atrium. an electrocardiogram (ecg) of af shows the normal sinus p waves are replaced by f waves (350 to 600 beats per min) and the ventricular rate is often irregular, which is characterised by an uneven r r interval. 1, 2 the prevalence of af is higher in men than in women and it.
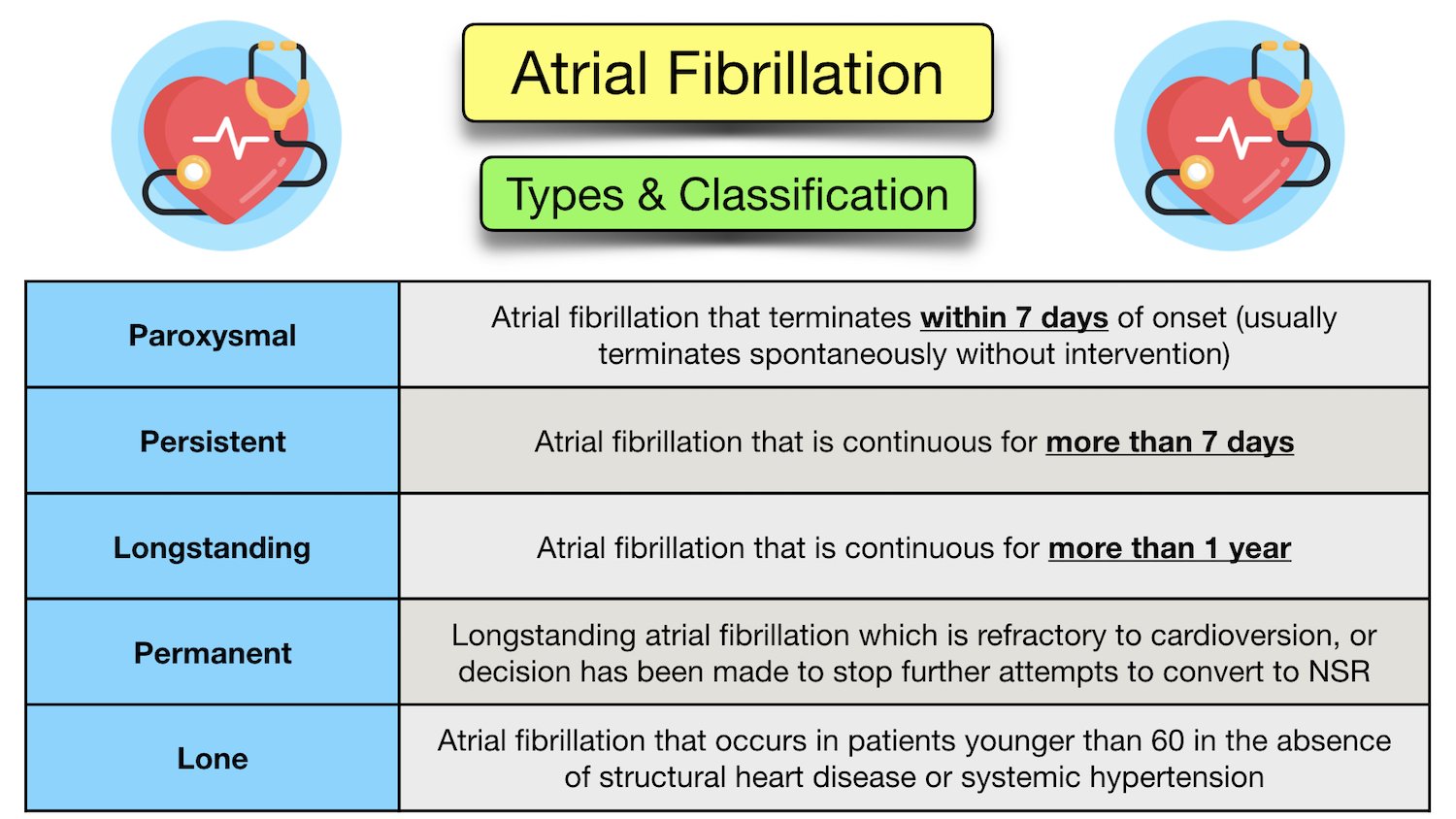
Learn Atrial Fibrillation Overview Ecg Types Pathophysiology During atrial fibrillation, the heart's upper chambers — called the atria — beat chaotically and irregularly. they beat out of sync with the lower heart chambers, called the ventricles. for many people, afib may have no symptoms. but afib may cause a fast, pounding heartbeat, shortness of breath or light headedness. Atrial fibrillation (af) is an ectopic rhythm originating in the atrium. an electrocardiogram (ecg) of af shows the normal sinus p waves are replaced by f waves (350 to 600 beats per min) and the ventricular rate is often irregular, which is characterised by an uneven r r interval. 1, 2 the prevalence of af is higher in men than in women and it. It is characterised by disorganised atrial electrical activity and contraction. the incidence and prevalence of af is increasing. lifetime risk over the age of 40 years is ~25%. complications of af include haemodynamic instability, cardiomyopathy, cardiac failure, and embolic events such as stroke. ecg features of atrial fibrillation. Treatment with ablation is only meaningful in paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation. treatment with anticoagulants, rate control or rhythm control should be considered in all types of atrial fibrillation. other types of atrial fibrillation. the term lone atrial fibrillation is used to describe a patient younger than 60 years of age, who.
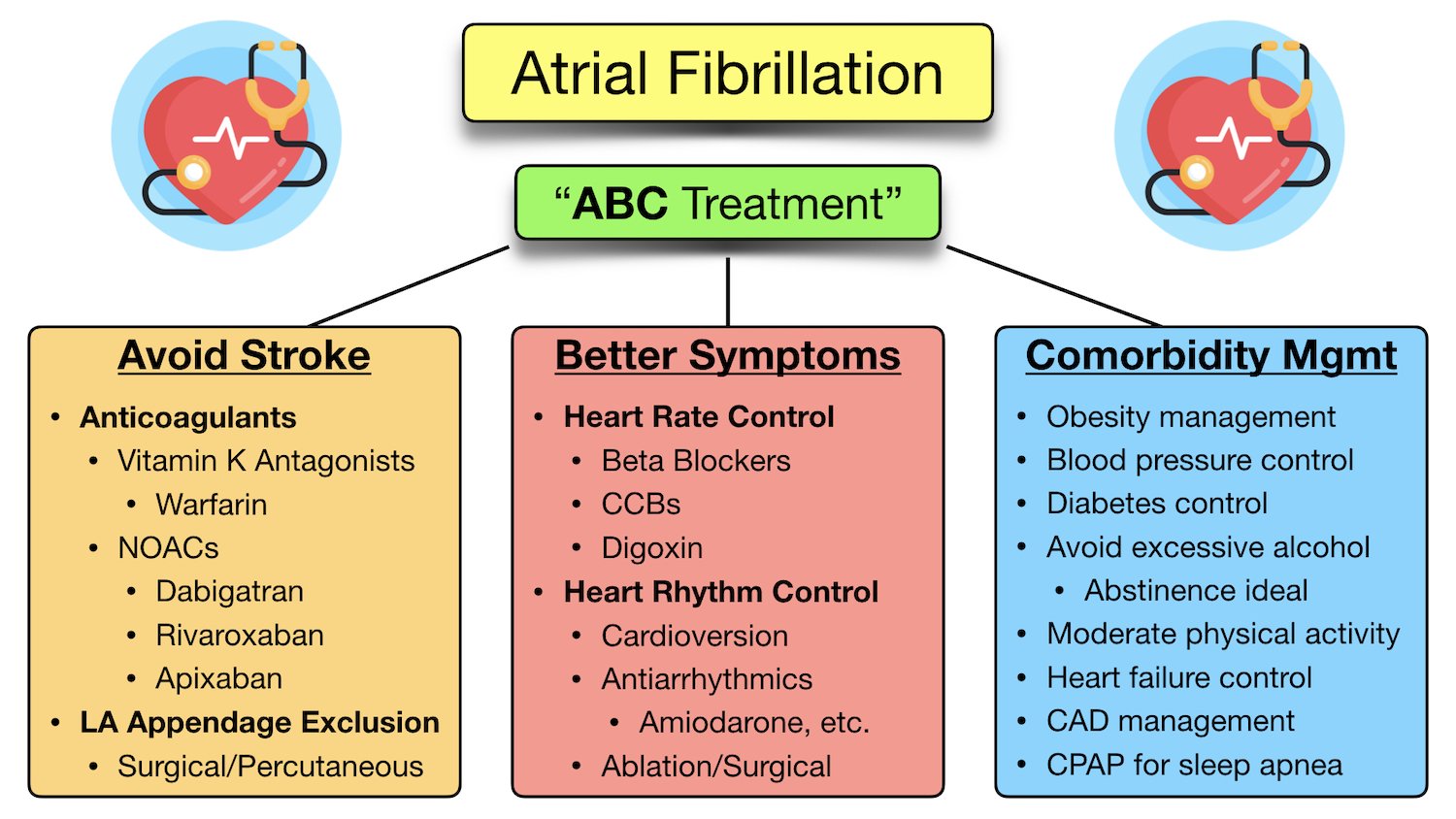
Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms Ecg Causes Treatment Definition It is characterised by disorganised atrial electrical activity and contraction. the incidence and prevalence of af is increasing. lifetime risk over the age of 40 years is ~25%. complications of af include haemodynamic instability, cardiomyopathy, cardiac failure, and embolic events such as stroke. ecg features of atrial fibrillation. Treatment with ablation is only meaningful in paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation. treatment with anticoagulants, rate control or rhythm control should be considered in all types of atrial fibrillation. other types of atrial fibrillation. the term lone atrial fibrillation is used to describe a patient younger than 60 years of age, who.
Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms Ecg Causes Treatment Definition

Comments are closed.