Autism And Stimming Aspergers Actuallyautistic Autism Adhd Neurodiversity
+(5).png)
Adhd Vs Autism How To Spot The Difference Graphic вђ Insights Of A Autistic people have become increasingly mobilised and vocal in defence of stimming. autism rights or neurodiversity activists believe that stims may serve as coping mechanisms, thus opposing attempts to eliminate non injurious forms of stimming (e.g. orsini & smith, 2010). Autistic adults highlighted the importance of stimming as an adaptive mechanism that helps them to soothe or communicate intense emotions or thoughts and thus objected to treatment that aims to eliminate the behaviour. keywords: adults; autism; neurodiversity; repetitive behaviour; repetitive movements; self stimulatory behaviour; stereotypies.
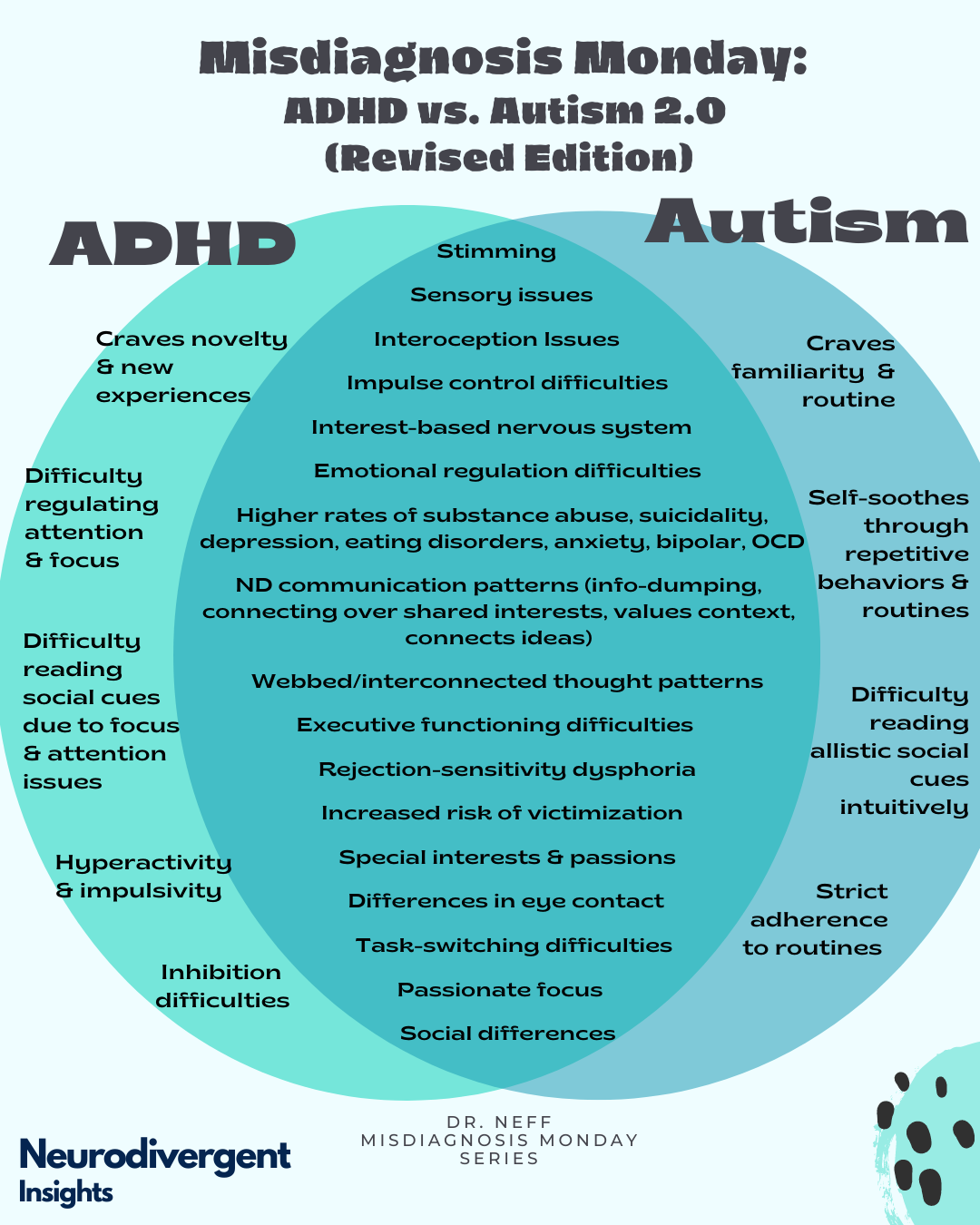
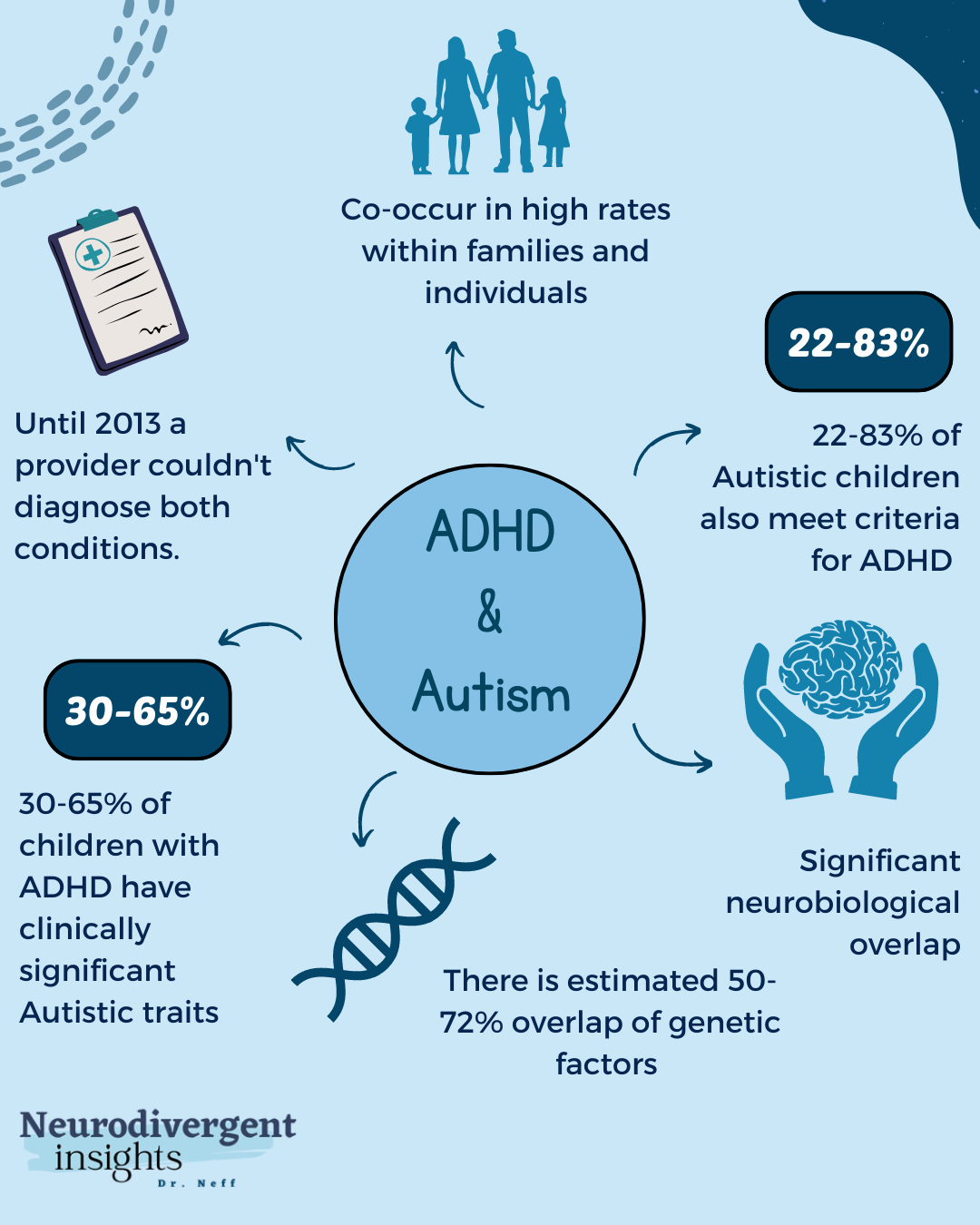
Adhd Autism Venn Diagram Raeedrabeaha Neurodiversity is most commonly discussed in reference to more readily recognised neurotypes, such as autism and adhd. this may simply be because these communities were early to adopt the concept. Although the neurodiversity movement has advocated for a shift away from the medical model’s foundation for autism intervention, many neurodiversity advocates are still in favor of intervention when it is (a) provided in a respectful manner, (b) focused on teaching useful skills, and (c) improves subjective quality of life (chapman & bovell. Neurodiversity is a broad term that covers many different types of people, such as those with attention deficit hyperactivity disorders (adhd), autism spectrum disorder (asd, including asperger’s syndrome), dyscalculia, dyslexia, dyspraxia, obsessive compulsive disorder (ocd), and tourette’s syndrome. Prior to 2013, an individual with “high functioning autism” was typically diagnosed with asperger’s disorder, also known as asperger’s syndrome. while the term asperger’s syndrome no longer formally exists in the diagnosis and insurance world, it is still a common term used to refer to an individual with high functioning autism.

Whatтащs The Difference Between юааadhdюаб And юааautismюаб R юааneurodiversityюаб Neurodiversity is a broad term that covers many different types of people, such as those with attention deficit hyperactivity disorders (adhd), autism spectrum disorder (asd, including asperger’s syndrome), dyscalculia, dyslexia, dyspraxia, obsessive compulsive disorder (ocd), and tourette’s syndrome. Prior to 2013, an individual with “high functioning autism” was typically diagnosed with asperger’s disorder, also known as asperger’s syndrome. while the term asperger’s syndrome no longer formally exists in the diagnosis and insurance world, it is still a common term used to refer to an individual with high functioning autism. Stimming behaviors often begin by age 3 and frequently occur when a child is engrossed in an activity or is excited, stressed or bored. an estimated 44% of people with autism report some type of stimming action. stimming can also refer to repetitive actions that are common among people without autism, such as jiggling a foot, biting fingernails. The #actuallyautistic guide to advocacy takes an in depth look at the key elements of effective, respectful, inclusive advocacy and allyship. every topic was chosen, shaped, and informed by #actuallyautistic perspectives. the step by step guide discusses various aspects of how autism is perceived, explores how best to speak up for individual.

Comments are closed.