Basic Information About Landfill Gas Us Epa
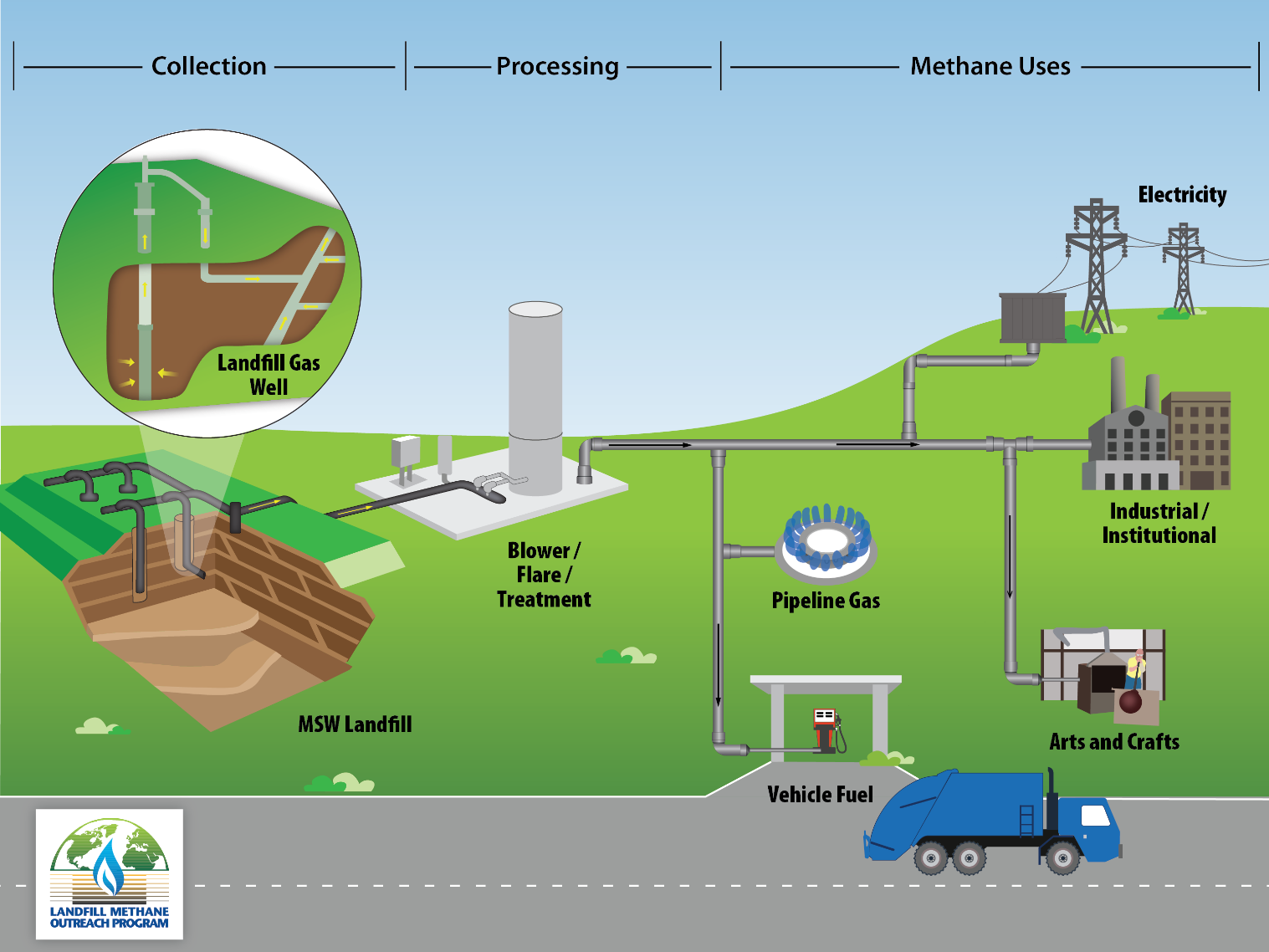
Basic Information About Landfill Gas Us Epa Learn more in chapter 1. landfill gas energy basics of lmop's lfg energy project development handbook. in october 2009, epa issued a rule (40 cfr part 98) that requires the reporting of (ghg) emissions from large sources and suppliers in the united states, and is intended to collect accurate and timely emissions data to inform future policy. Landfill gas (lfg) is a natural byproduct of the decomposition of organic material in landfills. lfg is composed of roughly 50 percent methane (the primary component of natural gas), 50 percent carbon dioxide (co 2) and a small amount of non methane organic compounds. methane is a potent greenhouse gas 28 to 36 times more effective than co 2 at.
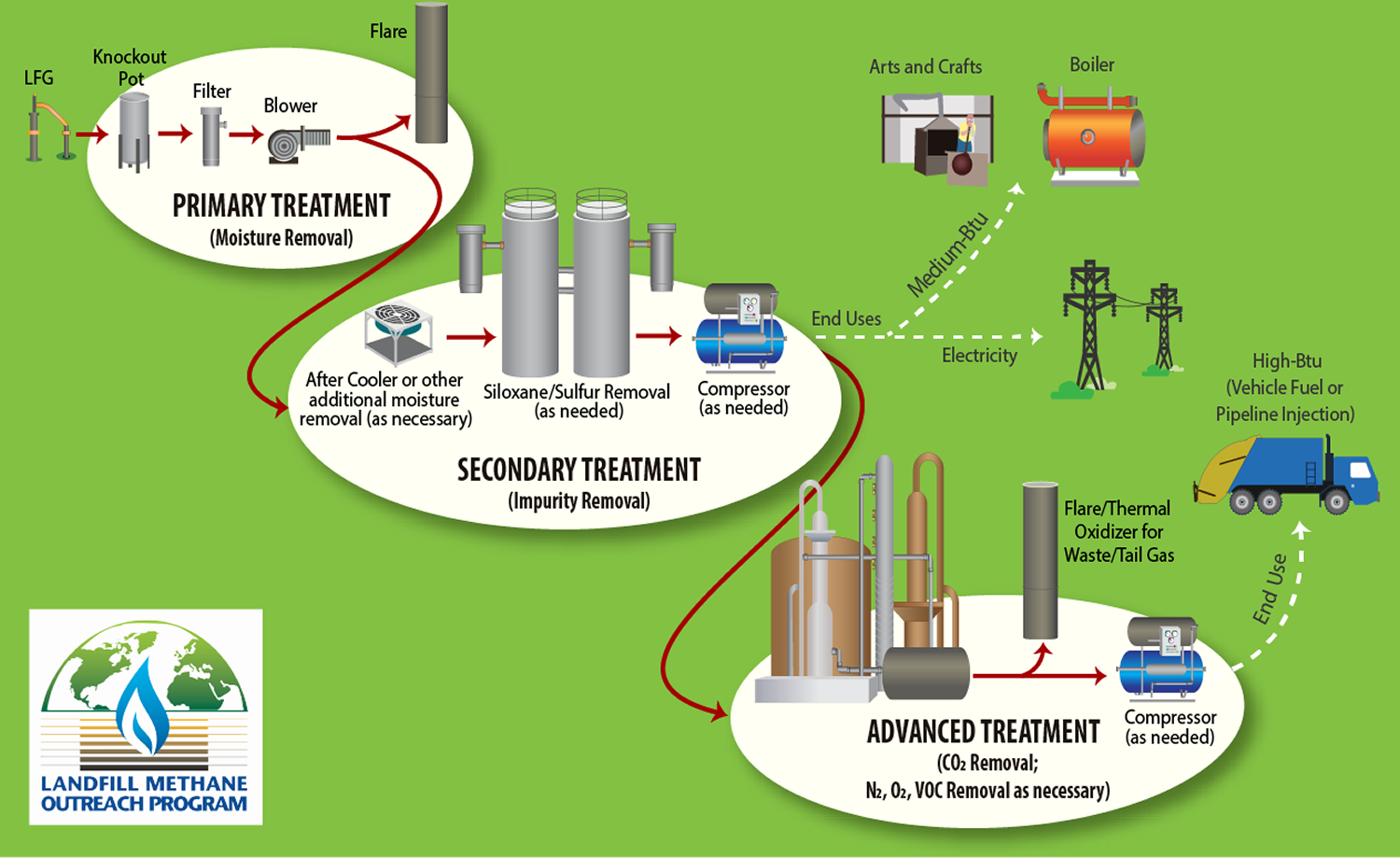
Basic Information About Landfill Gas Us Epa Lmop provides information about landfill gas (lfg), lfg energy projects and renewable natural gas (rng) to a wide range of organizations and individuals and provides answers to frequently asked questions as well as details about lmop's accomplishments. basics of lfg lfg is composed of about 50 percent methane, a greenhouse gas with a global. Landfills are located, designed, operated and monitored to ensure compliance with federal regulations. they are also designed to protect the environment from contaminants, which may be present in the waste stream. landfills cannot be built in environmentally sensitive areas, and they are placed using on site environmental monitoring systems. Frequent questions about landfill gas. lmop provides responses to some common questions that can help increase your understanding of the program, landfill gas (lfg), lfg energy projects and the lmop landfill and landfill gas energy project database. the questions and answers are organized into four categories below. The benefits of lfg energy projects are significant for the following reasons. on this page: reduce greenhouse gas emissions. reduce air pollution by offsetting the use of non renewable resources. create health and safety benefits. benefit the community and economy. reduce environmental compliance costs.

Basic Information About Landfill Gas Us Epa Frequent questions about landfill gas. lmop provides responses to some common questions that can help increase your understanding of the program, landfill gas (lfg), lfg energy projects and the lmop landfill and landfill gas energy project database. the questions and answers are organized into four categories below. The benefits of lfg energy projects are significant for the following reasons. on this page: reduce greenhouse gas emissions. reduce air pollution by offsetting the use of non renewable resources. create health and safety benefits. benefit the community and economy. reduce environmental compliance costs. Lmop is a voluntary program that works cooperatively with industry stakeholders and waste officials to reduce or avoid methane emissions from landfills. lmop encourages the recovery and beneficial use of biogas generated from organic municipal solid waste. learn more about lmop or join the lmop listserv. landfill gas (lfg) basics. This page provides an overview of the current landfill gas (lfg) energy industry including background information on lfg and why epa formed lmop, charts and data, helpful links to more information, and project case studies.

Comments are closed.