Basic Mechanics Gravity And Newton S Law Of Gravitation Owlcation
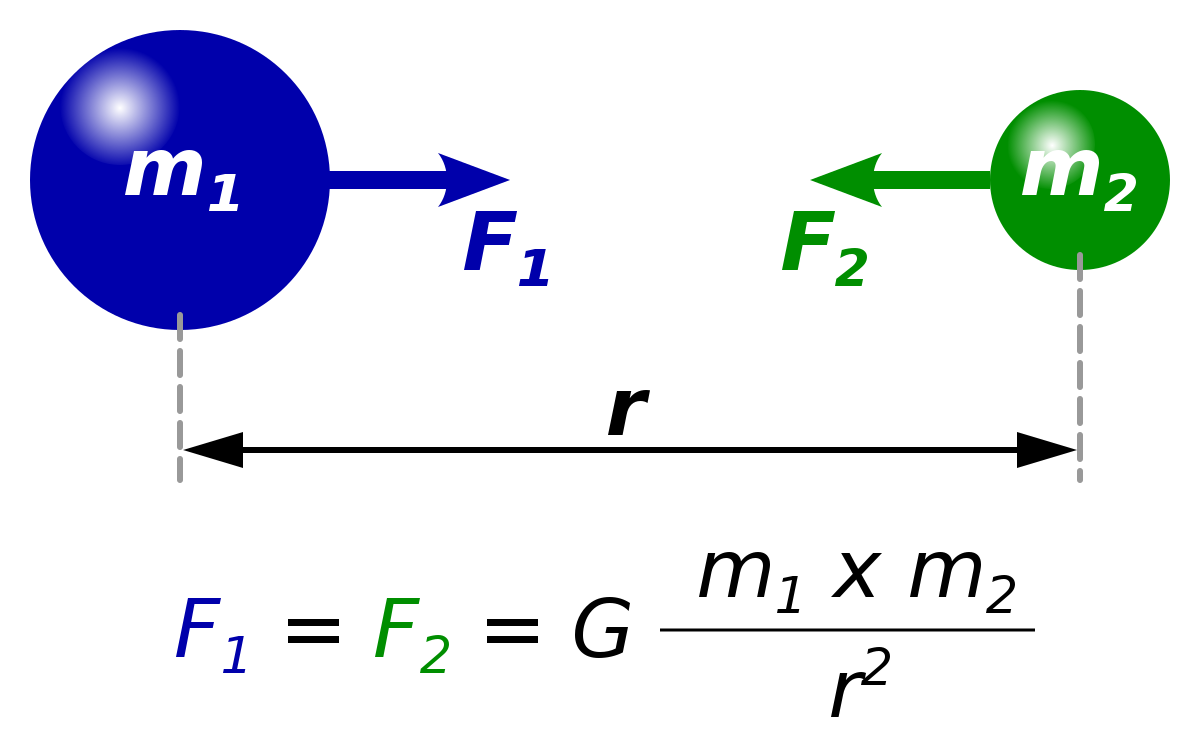
Basic Mechanics Gravity And Newton S Law Of Gravitation Owlcation Mathematical expression of newton's law of gravitation. the constant g in the above expression is known as the universal gravitational constant, and its value has been found to be equal to 6.674e 11 nm² kg². the direction of gravitational force is directed across the line joining the centers of mass of the two objects in question and. Basic mechanics: gravity and newton's law of gravitation gravity is a universal, weak, attractive force that all masses exert on each other. according to newton's law of gravitation, the magnitude of this force depends on the masses of the two bodies and the inverse square of the distance between them.
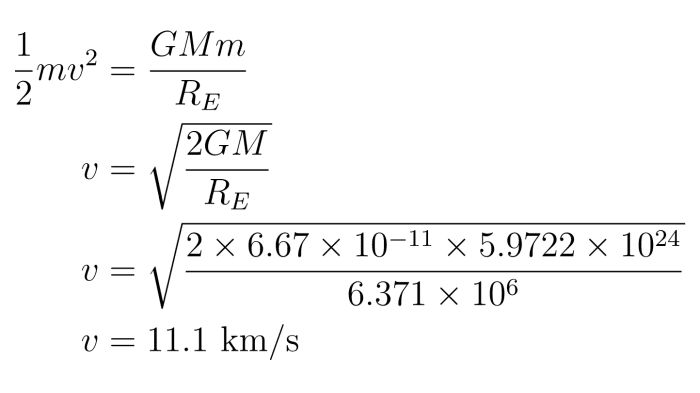
Basic Mechanics Gravity And Newton S Law Of Gravitation Owlcation Basic mechanics: gravity and newton's law of gravity is a universal, weak, attractive force that all masses exert on each other. according to newton's law of gravitation, the magnitude of this force depends on the masses of the two bodies and the inverse square of the distance between them. time gravity: a new theory on why time only goes. 4.2 newton’s first law of motion: inertia; 4.3 newton’s second law of motion: concept of a system; 4.4 newton’s third law of motion: symmetry in forces; 4.5 normal, tension, and other examples of forces; 4.6 problem solving strategies; 4.7 further applications of newton’s laws of motion; 4.8 extended topic: the four basic forces—an. Week 2: newton’s laws. week 2 introduction; lesson 4: newton’s laws of motion. 4.1 newton’s first and second laws; 4.2 newton’s third law; 4.3 reference frames; 4.4 non inertial reference frames; lesson 5: gravity. 5.1 universal law of gravitation; 5.2 worked example: gravity superposition; 5.3 gravity at the surface of the earth: the. The weight of an object mg is the gravitational force between it and earth. substituting mg for \ (f\) in newton’s universal law of gravitation gives. \ [mg = g\dfrac {mm} {r^2}, \] where \ (m\) is the mass of the object, \ (m\) is the mass of earth, and \ (r\) is the distance to the center of earth (the distance between the centers of mass.
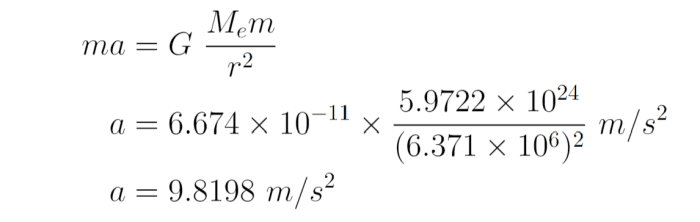
Basic Mechanics Gravity And Newton S Law Of Gravitation Owlcation Week 2: newton’s laws. week 2 introduction; lesson 4: newton’s laws of motion. 4.1 newton’s first and second laws; 4.2 newton’s third law; 4.3 reference frames; 4.4 non inertial reference frames; lesson 5: gravity. 5.1 universal law of gravitation; 5.2 worked example: gravity superposition; 5.3 gravity at the surface of the earth: the. The weight of an object mg is the gravitational force between it and earth. substituting mg for \ (f\) in newton’s universal law of gravitation gives. \ [mg = g\dfrac {mm} {r^2}, \] where \ (m\) is the mass of the object, \ (m\) is the mass of earth, and \ (r\) is the distance to the center of earth (the distance between the centers of mass. Newton’s law of gravitation. newton’s law of gravitation can be expressed as. f 12 = gm1m2 r2 rˆ12 f → 12 = g m 1 m 2 r 2 r ^ 12. 13.1. where f 12 f → 12 is the force on object 1 exerted by object 2 and rˆ12 r ^ 12 is a unit vector that points from object 1 toward object 2. as shown in figure 13.2, the f 12 f → 12 vector points from. Newton's law of universal gravitation.

Comments are closed.