Binomial Probabiilty Theorem
Ppt Binomial Probability Distribution Powerpoint Presentation Free Example. if you were to roll a die 20 times, the probability of you rolling a six is 1 6. this ends in a binomial distribution of (n = 20, p = 1 6). for rolling an even number, it’s (n = 20, p = ½). dice rolling is binomial. there are hundreds of ways you could measure success, but this is one of the simplest. something works, or it doesn’t. We can see these coefficients in an array known as pascal's triangle, shown in figure 13.6.2. figure 13.6.2. to generate pascal’s triangle, we start by writing a 1. in the row below, row 2, we write two 1 ′ s. in the 3 rd row, flank the ends of the rows with 1 ′ s, and add 1 1 to find the middle number, 2.

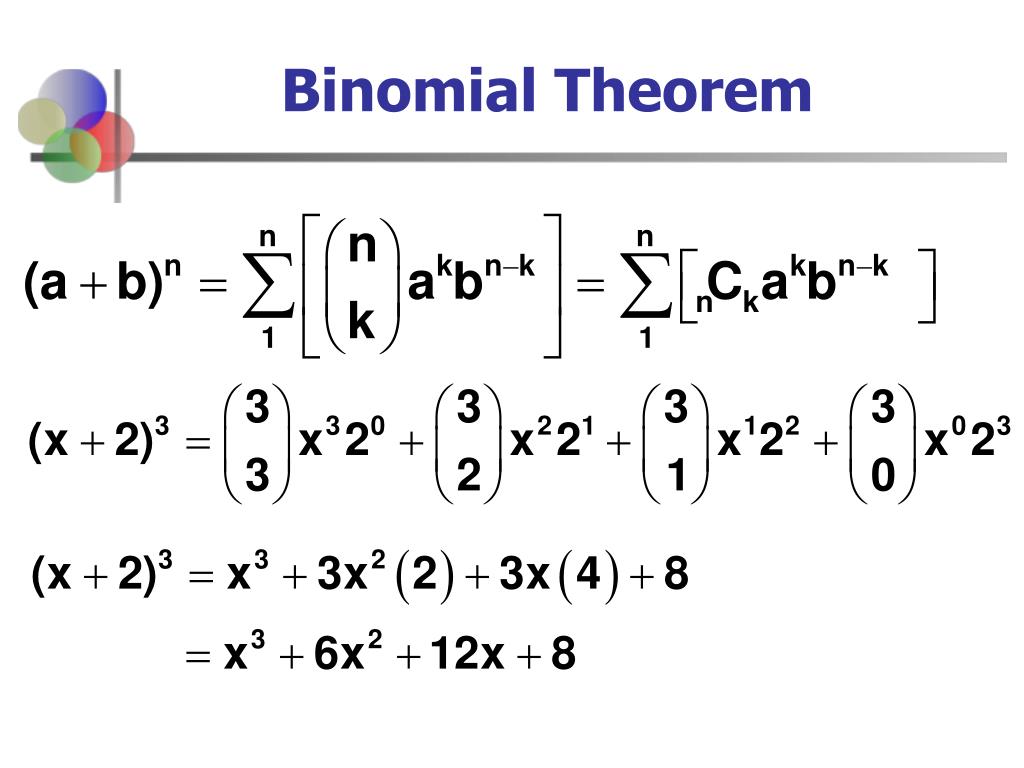
Ppt Binomial Probability Formula Powerpoint Presentation Id 2635610 The binomial theorem states that expending any binomial raised to a non negative integer power n gives a polynomial of n 1 terms (monomials) according to the formula: on the other hand, the binomial distribution describes a random variable whose value is the number (k) of “success” trials out of n independent bernoulli trials with. Binomial theorem. For the following exercises, use the binomial theorem to expand the binomial f (x) = (x 3) 4. f (x) = (x 3) 4. then find and graph each indicated sum on one set of axes. 40. Binomial probability theorem. the probability of obtaining k successes in n independent bernoulli trials is given by. p(n,k;p) = nck pkqn−k. where p denotes the probability of success and q = (1 − p) the probability of failure. we use the binomial probability formula to solve the following examples.

Binomial Distribution Fully Explained W 11 Examples For the following exercises, use the binomial theorem to expand the binomial f (x) = (x 3) 4. f (x) = (x 3) 4. then find and graph each indicated sum on one set of axes. 40. Binomial probability theorem. the probability of obtaining k successes in n independent bernoulli trials is given by. p(n,k;p) = nck pkqn−k. where p denotes the probability of success and q = (1 − p) the probability of failure. we use the binomial probability formula to solve the following examples. Binomial probability (basic) (article). The binomial distribution.

Comments are closed.