Boundary Layer Theory
Basic Boundary Layer Theory A boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid near a solid surface where viscous forces affect the flow. learn about the laminar and turbulent boundary layers, the prandtl boundary layer concept, and the effects of boundary layer on aerodynamics and heat transfer. This book covers the fundamentals and applications of boundary layer theory in fluid mechanics, with emphasis on the flow past bodies. it is a revised and updated version of schlichting's legendary textbook, featuring over 100 changes and updates, and supplementary material.

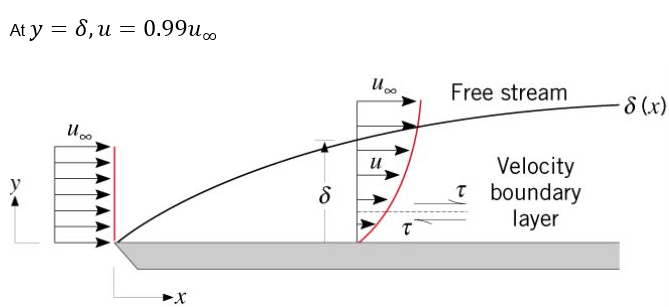
Theory Bites Boundary Layer Fluid Mechanics Empowering Pumps And Chapter 9: boundary layers and related topics 9.1: introduction; 9.2: boundary layer thickness definitions; 9.3: boundary layer on a flat plate: blasius solution; 9.4: falkner skan similarity solutions of the laminar boundary layer equations; 9.5: von karman momentum integral equation; 9.7: transition, pressure gradients, and boundary layer. Learn the basics of boundary layer theory, such as its applications, approximations, equations, and solutions. see examples of flat plate flow, momentum integral analysis, and skin friction formulas for laminar and turbulent boundary layers. Boundary layer, in fluid mechanics, thin layer of a flowing gas or liquid in contact with a surface such as that of an airplane wing or of the inside of a pipe. the fluid in the boundary layer is subjected to shearing forces. a range of velocities exists across the boundary layer from maximum to zero, provided the fluid is in contact with the. Boundary layer theory, developed by prandtl in 1904 [1], is a discovery that enabled breakthrough developments in flight and many other technical achievements. according to this theory, when a fluid flows past an object, frictional effects are significant only in a thin region close to the wall, where large transverse gradients of velocity exist.
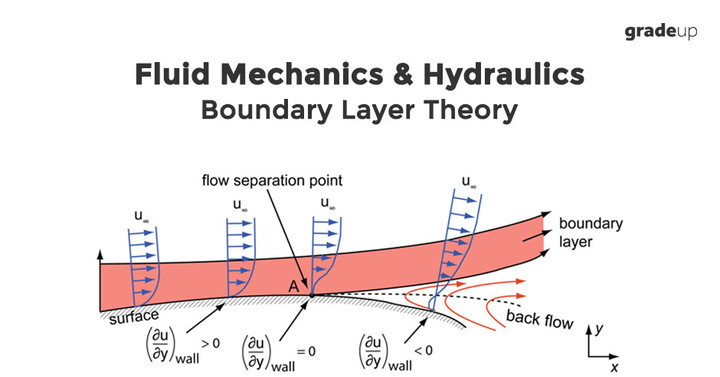
Boundary Layer Theory Study Notes For Civil Engineering Boundary layer, in fluid mechanics, thin layer of a flowing gas or liquid in contact with a surface such as that of an airplane wing or of the inside of a pipe. the fluid in the boundary layer is subjected to shearing forces. a range of velocities exists across the boundary layer from maximum to zero, provided the fluid is in contact with the. Boundary layer theory, developed by prandtl in 1904 [1], is a discovery that enabled breakthrough developments in flight and many other technical achievements. according to this theory, when a fluid flows past an object, frictional effects are significant only in a thin region close to the wall, where large transverse gradients of velocity exist. Prandtl's boundary layer theory. Learn about the boundary layer, a thin layer of fluid near the surface of an object or a fluid, and its effects on aerodynamic forces. find out how viscosity, reynolds number, and flow separation influence the boundary layer and the lift and drag coefficients.

Comments are closed.