Calculate Power Consumed By Resistor
How To Calculate The Power Delivered To A Resistor Using The Current Find the voltage (v) across resistor r 1 of power rating p 1 using the formula: v = √ (p 1 × r 1) calculate the power dissipated by the second resistor (r 2 ), p 2 = v 2 r 2. the overall voltage is 14.14 v, so the resulting power equals 20 w. Use omni's power dissipation calculator to determine the power dissipated in series and parallel resistor circuits. just enter the applied voltage and the resistances of the resistors. the calculator will calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit, the total current through the circuit, and the power dissipated by the resistors.

How To Calculate The Power Delivered To A Resistor Using Resistance Therefore, to calculate the power dissipated by the resistor, the formulas are as follows: p (power dissipated) = i2 (current) × r (resistance) or. p (power dissipated) = v2 (voltage) ÷ r (resistance) so, using the above circuit diagram as our reference, we can apply these formulas to determine the power dissipated by the resistor. voltage = 9v. Push the calculate button to determine the power dissipated by each resistor . series circuit schematic and power equations. figure 1 is the circuit schematic for resistors connected in series with an applied voltage v. figure 1. resistive series circuit schematic for power dissipation calculation. The above power triangle is great for calculating the power dissipated in a resistor if we know the values of the voltage across it and the current flowing through it. but we can also calculate the power dissipated by a resistance by using ohm’s law. ohms law allows us to calculate the power dissipation given the resistance value of the resistor. Dc circuit power calculator. voltage is energy per unit charge. current is the rate of electric charges moving through a conductor. electrical power is the product of voltage and current. calculate power from voltage & current (p = v * i) inputs. voltage. current.

In The Circuit Shown Calculate The Power Consumed By The 3 Ohms The above power triangle is great for calculating the power dissipated in a resistor if we know the values of the voltage across it and the current flowing through it. but we can also calculate the power dissipated by a resistance by using ohm’s law. ohms law allows us to calculate the power dissipation given the resistance value of the resistor. Dc circuit power calculator. voltage is energy per unit charge. current is the rate of electric charges moving through a conductor. electrical power is the product of voltage and current. calculate power from voltage & current (p = v * i) inputs. voltage. current. V. v v. there are two possible formulas for power dissipation. the first one requires you to know resistance and current: p = r\cdot i^2 p = r ⋅ i 2. alternatively, if you know the current and the voltage drop, you can use the other formula for power dissipation: p= v\cdot i p = v ⋅ i. the two equations are totally equivalent, and at a. Calculate the power consumed created by the resistor r1 in our simple circuit example. solution. the power consumed by the resistor r 1 can be expressed as. (vin −vout)iout = r2 (r1 r2)2v2in ( v i n − v o u t) i o u t = r 2 ( r 1 r 2) 2 v i n 2. we conclude that both resistors in our example circuit consume power, which points to the.
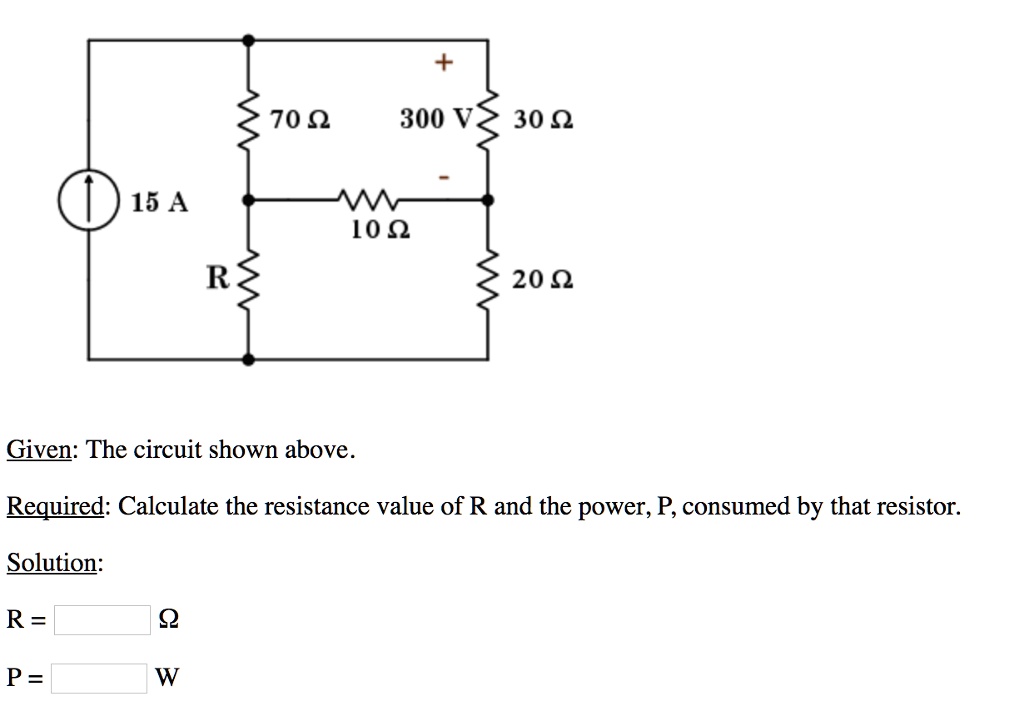
Solved 70 300 V 30 15 A 100 R 200 Given The Circuit Shown Above V. v v. there are two possible formulas for power dissipation. the first one requires you to know resistance and current: p = r\cdot i^2 p = r ⋅ i 2. alternatively, if you know the current and the voltage drop, you can use the other formula for power dissipation: p= v\cdot i p = v ⋅ i. the two equations are totally equivalent, and at a. Calculate the power consumed created by the resistor r1 in our simple circuit example. solution. the power consumed by the resistor r 1 can be expressed as. (vin −vout)iout = r2 (r1 r2)2v2in ( v i n − v o u t) i o u t = r 2 ( r 1 r 2) 2 v i n 2. we conclude that both resistors in our example circuit consume power, which points to the.

Comments are closed.