Calculus 2 Integral Test For Convergence And Divergence
Calculus 2 Integral Test For Convergence And Divergence Of Series Maths Figure 9.3.2: the sum of the areas of the rectangles is less than the sum of the area of the first rectangle and the area between the curve f(x) = 1 x2 and the x axis for x ≥ 1. since the area bounded by the curve is finite, the sum of the areas of the rectangles is also finite. now consider the series ∞ ∑ n = 1 1 n2. Section 10.6 : integral test. the last topic that we discussed in the previous section was the harmonic series. in that discussion we stated that the harmonic series was a divergent series. it is now time to prove that statement. this proof will also get us started on the way to our next test for convergence that we’ll be looking at.
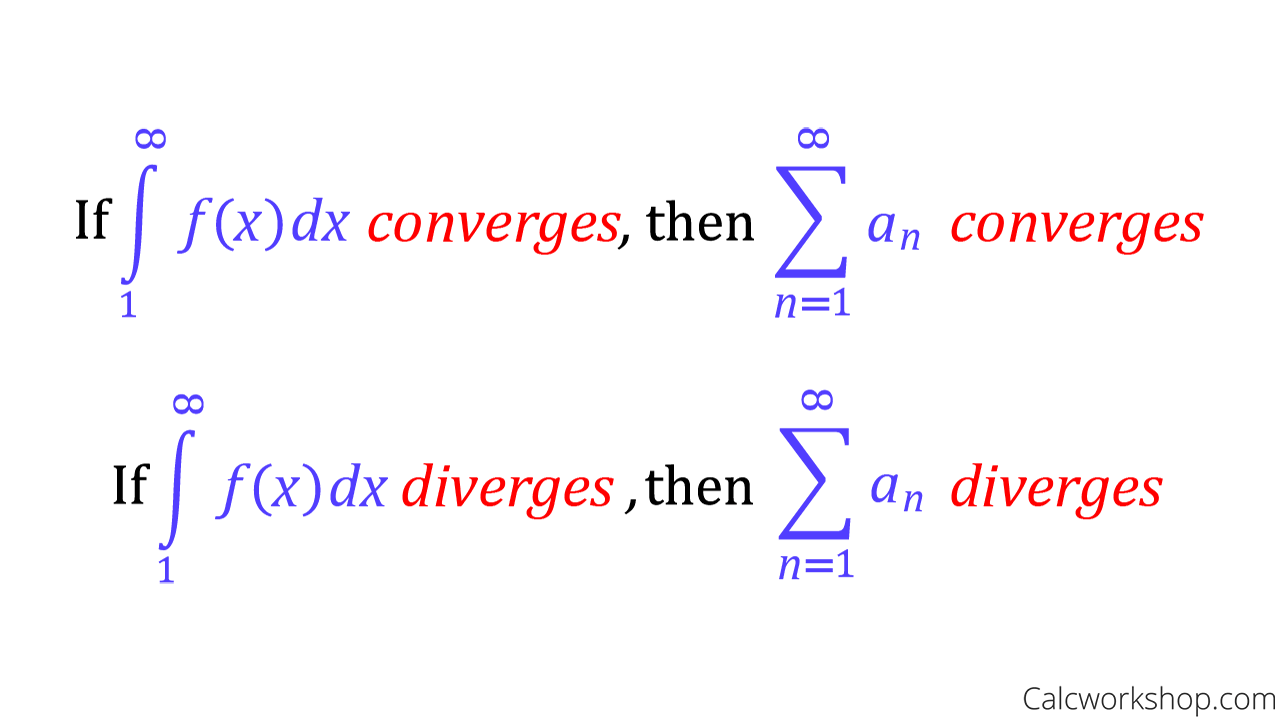
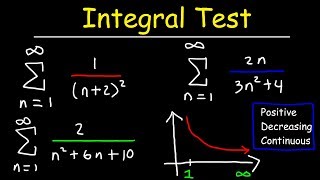
Integral Test Learning objectives. 5.3.1 use the divergence test to determine whether a series converges or diverges.; 5.3.2 use the integral test to determine the convergence of a series.; 5.3.3 estimate the value of a series by finding bounds on its remainder term. Theorem: divergence test. if limn → ∞an = c ≠ 0 or limn → ∞an does not exist, then the series ∞ ∑ n = 1an diverges. it is important to note that the converse of this theorem is not true. that is, if limn → ∞an = 0, we cannot make any conclusion about the convergence of ∞ ∑ n = 1an. for example, limn → 0(1 n) = 0, but the. This calculus 2 video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the integral test for convergence and divergence of a series with improper integrals. to p. The integral test for convergence is only valid for series that are 1) positive: all of the terms in the series are positive, 2) decreasing: every term is less than the one before it, a (n 1)> a n, and 3) continuous: the series is defined everywhere in its domain. the integral test tells us that, if the integral converges, then the series also.

Divergence Test Calculus 2 вђ Mhm Calculus вђ Empiretory This calculus 2 video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the integral test for convergence and divergence of a series with improper integrals. to p. The integral test for convergence is only valid for series that are 1) positive: all of the terms in the series are positive, 2) decreasing: every term is less than the one before it, a (n 1)> a n, and 3) continuous: the series is defined everywhere in its domain. the integral test tells us that, if the integral converges, then the series also. Introduction to the divergence and integral tests. in the previous section, we determined the convergence or divergence of several series by explicitly calculating the limit of the sequence of partial sums {sk} { s k }. in practice, explicitly calculating this limit can be difficult or impossible. luckily, several tests exist that allow us to. Calculus 2 lecture 9.3: using the integral test for convergence divergence of series, p series.

Comments are closed.