Catalysts Enzymes Overview Examples Expii

Catalysts Enzymes вђ Overview Examples Expii Enzyme are proteins (chains of amino acids) that speed up chemical reactions. because they make reactions go faster, enzymes are called catalysts. (the process of speeding up a reaction is called catalysis). think of a normal chemical reaction as a road with a low speed limit. Catalyst is a broad term used in chemistry to describe any substance that speeds up a chemical reaction and is not destroyed in the process. enzymes, a type of common, naturally occurring catalyst, function by lowering the activation energy required to cause a reaction, which increases the reaction rate. as a result, enzyme catalyzed reactions.

Catalysts Enzymes вђ Overview Examples Expii The activity of enzymes is dependent on temperature, ph, and regulatory molecules. if the enzyme is placed in conditions that it doesn't like, it can become denatured. denatured enzymes can be thought of as the burnt soup: just ruined. image source: by deena hauze. the image above shows a substrate and an enzyme after it was denatured. The central role of enzymes as biological catalysts. In chapter 1, this book will provide an overview of how do enzymes act as biological catalysts. the first chapter will explore what how do enzymes act as biological catalysts is, why how do enzymes act as biological catalysts is vital, and how to effectively learn about how do enzymes act as biological catalysts. 3. in chapter 2, this book will. An enzyme is an organic molecule and a type of protein. enzymes are a type of catalyst, meaning they speed up chemical reactions without being a part of the reaction themselves. at the end of a reaction, they can be reused. they are typically made of amino acids, and each type has a specific molecule or molecules that it can bind to.
Catalysts Enzymes Overview Examples Expii Vrogue Co In chapter 1, this book will provide an overview of how do enzymes act as biological catalysts. the first chapter will explore what how do enzymes act as biological catalysts is, why how do enzymes act as biological catalysts is vital, and how to effectively learn about how do enzymes act as biological catalysts. 3. in chapter 2, this book will. An enzyme is an organic molecule and a type of protein. enzymes are a type of catalyst, meaning they speed up chemical reactions without being a part of the reaction themselves. at the end of a reaction, they can be reused. they are typically made of amino acids, and each type has a specific molecule or molecules that it can bind to. Enzyme : classification, mechanism , mode of actiondeactivation of enzymes — overview & examples enzymes biology model induced fit weeblyenzyme competitive inhibition inhibitor regulation enzymes allosteric substrate inhibitors noncompetitive enzim active biology catalyst ap struktur binding kompetitif feedback binds. Enzymes enzyme proteins substrate work lock key active site mechanism role metabolism model they when high catalysis do complex madesolved to which class do the enzymes that catalyze the reaction enzymes reactions work biology enzyme energy diagram activation catalyzed chemical catalysed figure difference catalytic majorsenzyme catalysis.
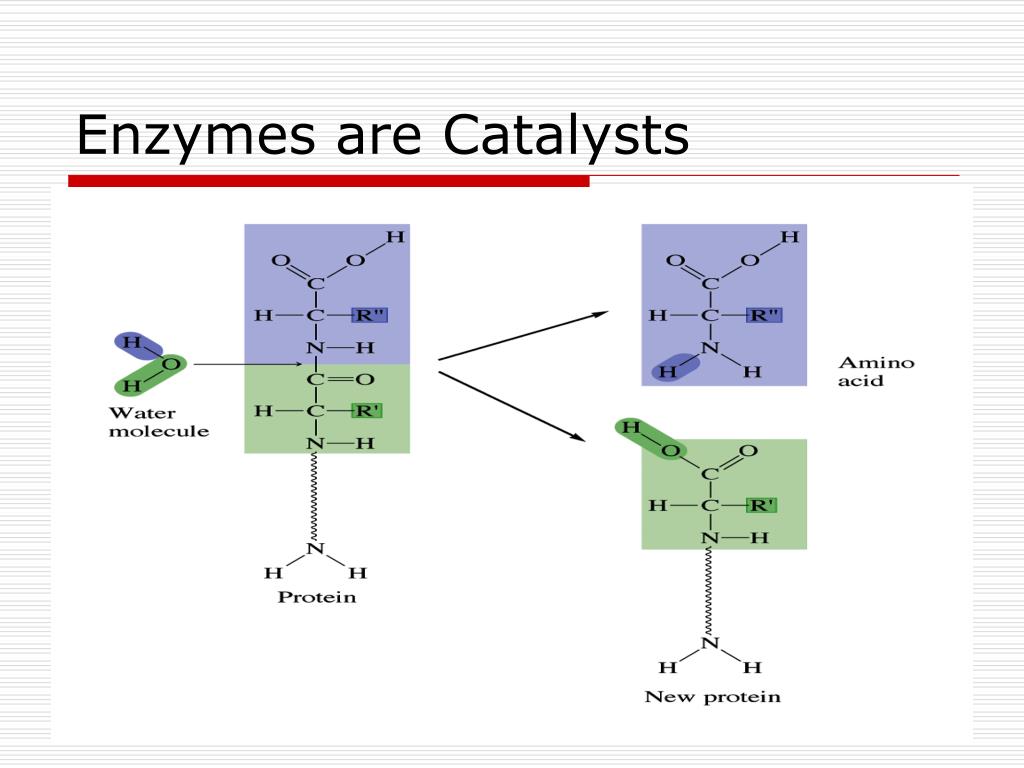
Catalysts Enzymes Overview Examples Expii Vrogue Co Enzyme : classification, mechanism , mode of actiondeactivation of enzymes — overview & examples enzymes biology model induced fit weeblyenzyme competitive inhibition inhibitor regulation enzymes allosteric substrate inhibitors noncompetitive enzim active biology catalyst ap struktur binding kompetitif feedback binds. Enzymes enzyme proteins substrate work lock key active site mechanism role metabolism model they when high catalysis do complex madesolved to which class do the enzymes that catalyze the reaction enzymes reactions work biology enzyme energy diagram activation catalyzed chemical catalysed figure difference catalytic majorsenzyme catalysis.

Comments are closed.