Changing States Of Matter Solid Liquid Gas Phase Change
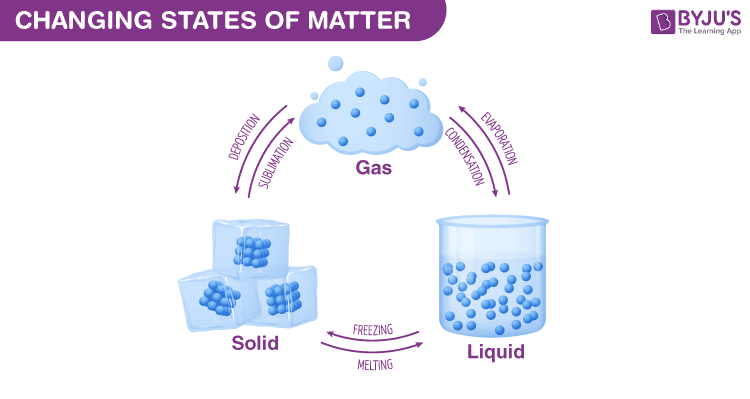
Chapter 10 Review States Of Matter Section 3 Answer Key 36 Pages A change of state is a physical change in a matter. they are reversible changes and do not involve any changes in the chemical makeup of the matter. common changes of the state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization. these changes are shown in the figure given below. Another way to list phase changes is by states of matter: solids: solids can melt into liquids or sublime into gases. solids form by deposition from gases or freezing of liquids. liquids: liquids can vaporize into gases or freeze into solids. liquids form by condensation of gases and melting of solids. gases: gases can ionize into plasma.
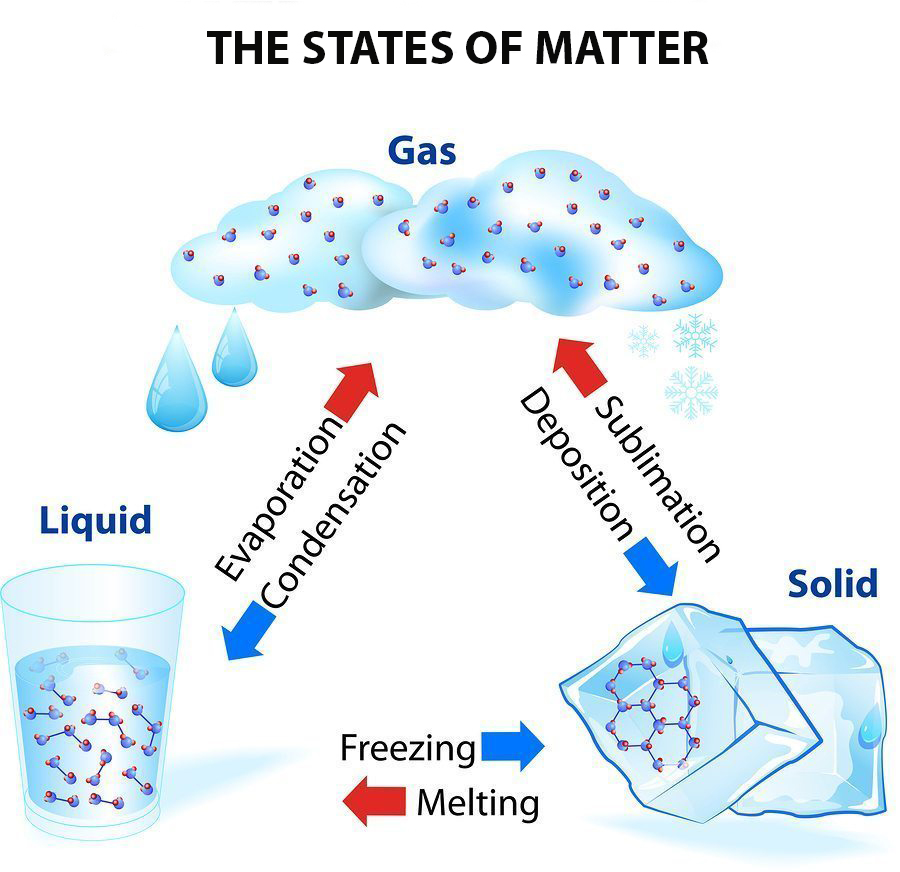
6th Grade Science Jeopardy Template A phase change or phase transition is a change between solid, liquid, gaseous, and sometimes plasma states of matter. the states of matter differ in the organization of particles and their energy. the main factors that cause phase changes are changes in temperature and pressure. at the phase transition, such as the boiling point between liquid. states of matter phet interactive simulations. Watch different types of molecules form a solid, liquid, or gas. add or remove heat and watch the phase change. change the temperature or volume of a container and see a pressure temperature diagram respond in real time. relate the interaction potential to the forces between molecules. Conversely, any transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state (liquid to solid, gas to liquid, or gas to solid) releases energy; it is exothermic. the energy change associated with each common phase change is shown in figure 11.5.1. in chapter 9, we defined the enthalpy changes associated with various chemical and physical processes.

Phase Change Evaporation Condensation Freezing Melting Sublimation My Watch different types of molecules form a solid, liquid, or gas. add or remove heat and watch the phase change. change the temperature or volume of a container and see a pressure temperature diagram respond in real time. relate the interaction potential to the forces between molecules. Conversely, any transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state (liquid to solid, gas to liquid, or gas to solid) releases energy; it is exothermic. the energy change associated with each common phase change is shown in figure 11.5.1. in chapter 9, we defined the enthalpy changes associated with various chemical and physical processes. In the change of state from liquid to solid energy is given off. the energy given off by this transition is the same amount as the energy required to freeze the matter. liquid gas. a very common phase change is between liquid and gases. this change of state is referred to as vaporization boiling (liquid to gas) or condensation (gas to liquid). The substance changes from a gas to a liquid. when a liquid is cooled to even lower temperatures, it becomes a solid. the volume never reaches zero because of the finite volume of the molecules. figure 13.5.1 13.5. 1: a sketch of volume versus temperature for a real gas at constant pressure.

Comments are closed.