Chapter 2 Position Time Graph Average And Instantaneous Velocity

Chapter 2 Position Time Graph Average And Instantaneous Velocity Consider figure 2.6, the graph of position versus time we looked at in the previous section. over the 50 second interval, find: (a) the average velocity, and (b) the average speed. solution (a) applying equation 2.2, we find that the average velocity is:. chapter 2 – motion in one dimension page 2 4 figure 2.6: a graph of your position. 2.3 position vs. time graphs physics.
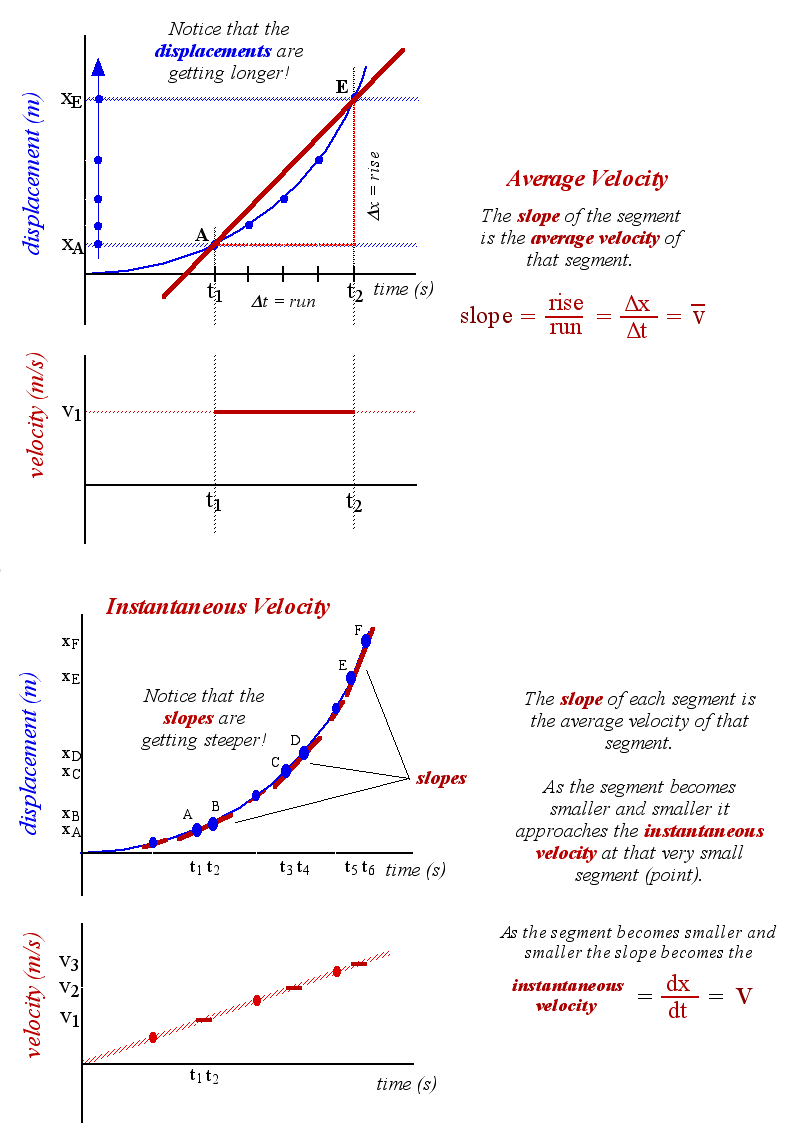
Chapter 2 Motion In A Line Explain the relationships between instantaneous velocity, average velocity, instantaneous speed, average speed, displacement, and time. calculate velocity and speed given initial position, initial time, final position, and final time. derive a graph of velocity vs. time given a graph of position vs. time. interpret a graph of velocity vs. time. The average speed is 12 km h. the displacement for the round trip is zero, since there was no net change in position. thus the average velocity is zero. another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. a plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful. The graph of position versus time in figure 2.46(a) is a curve rather than a straight line. the slope of the curve becomes steeper as time progresses, showing that the velocity is increasing over time. the slope at any point on a position versus time graph is the instantaneous velocity at that point. In symbols, average velocity is. ¯v = Δx Δt = xf −x0 tf −t0 v ¯ = Δ x Δ t = x f − x 0 t f − t 0. the si unit for velocity is m s. velocity is a vector and thus has a direction. instantaneous velocity →v v → is the velocity at a specific instant or the average velocity for an infinitesimal interval.
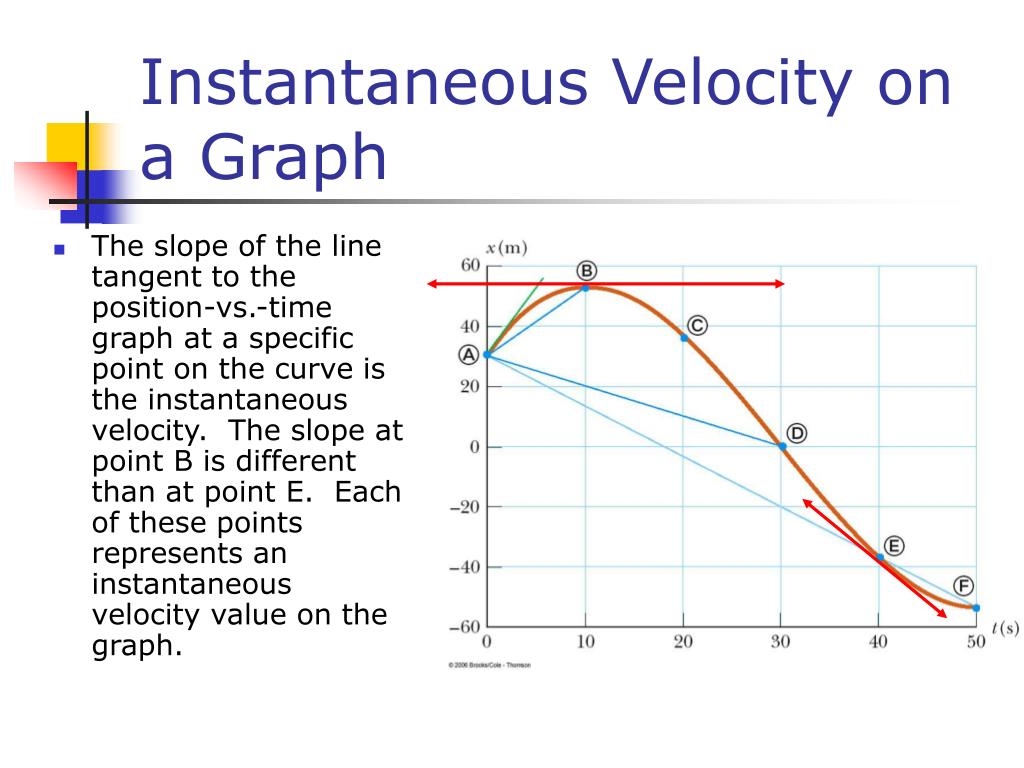
Ppt Chapter 2 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 602265 The graph of position versus time in figure 2.46(a) is a curve rather than a straight line. the slope of the curve becomes steeper as time progresses, showing that the velocity is increasing over time. the slope at any point on a position versus time graph is the instantaneous velocity at that point. In symbols, average velocity is. ¯v = Δx Δt = xf −x0 tf −t0 v ¯ = Δ x Δ t = x f − x 0 t f − t 0. the si unit for velocity is m s. velocity is a vector and thus has a direction. instantaneous velocity →v v → is the velocity at a specific instant or the average velocity for an infinitesimal interval. A position time graph—figure 2.3 • a position time graph (an x t graph) shows the particle’s position x as a function of time t. • the average x velocity is the slope of a line connecting the corresponding points on an x t graph. The average speed is 12 km h. the displacement for the round trip is zero, since there was no net change in position. thus the average velocity is zero. graphing. another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. a plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful.
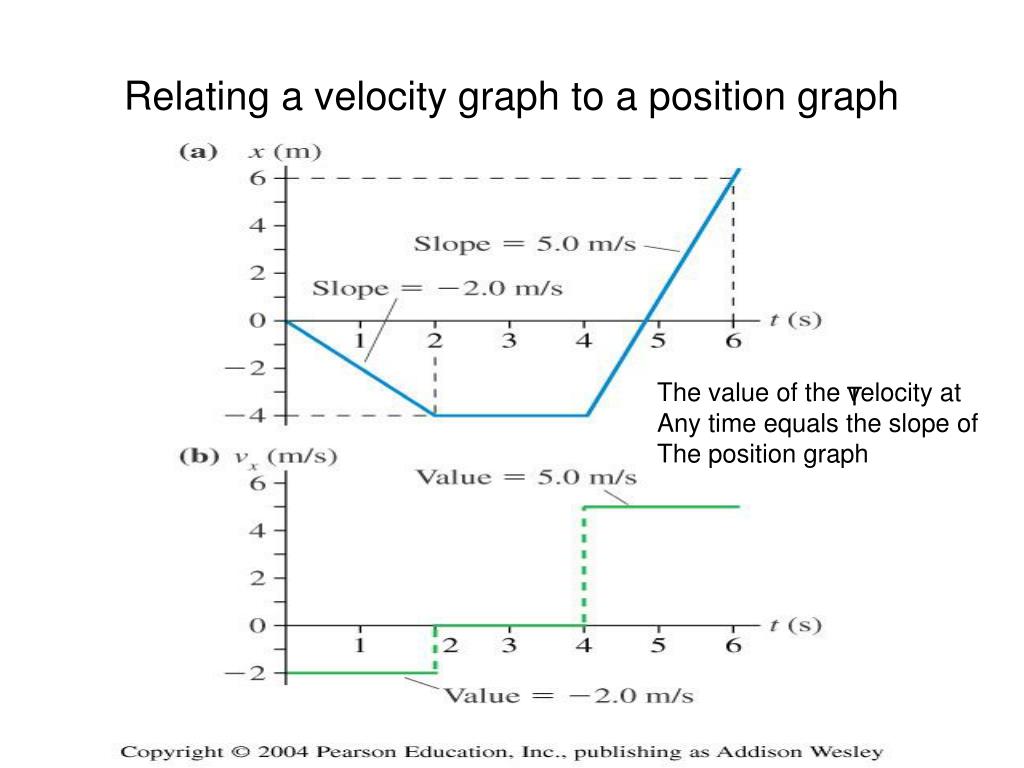
Ppt Chapter 2 Kinematics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id A position time graph—figure 2.3 • a position time graph (an x t graph) shows the particle’s position x as a function of time t. • the average x velocity is the slope of a line connecting the corresponding points on an x t graph. The average speed is 12 km h. the displacement for the round trip is zero, since there was no net change in position. thus the average velocity is zero. graphing. another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. a plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful.

Comments are closed.