Chromosomal Mutation Causes Mechanism Types Examples
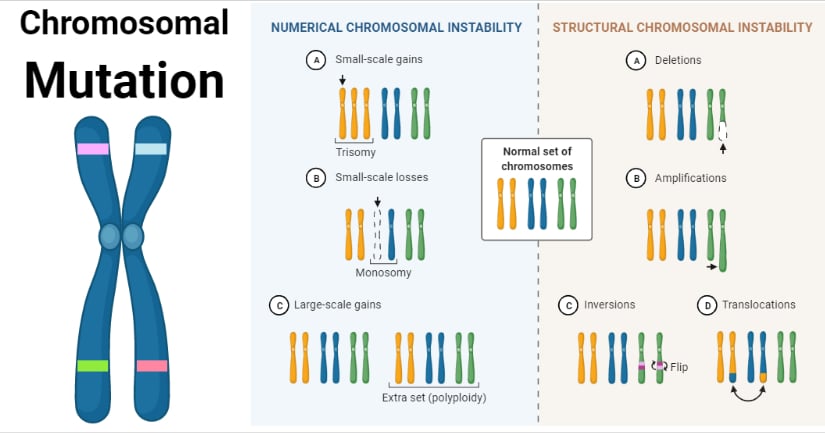
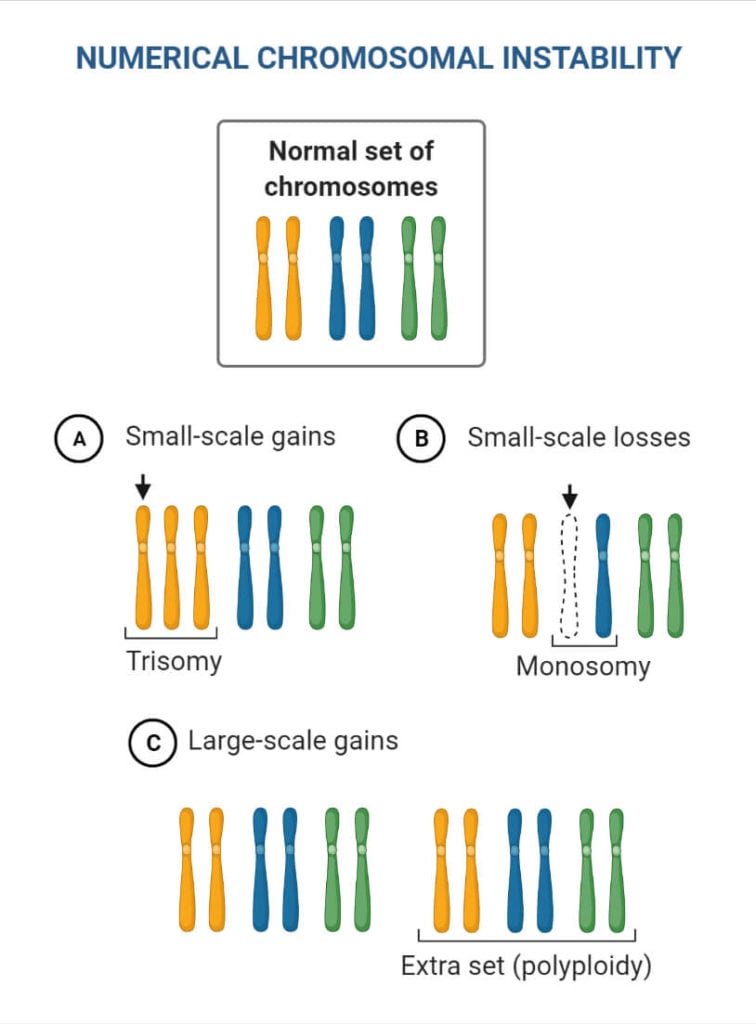
Chromosomal Mutation Causes Mechanism Types Examples The chromosomal mutation is the process of change in the chromosomes as a result of rearranged chromosome parts and changes in the number of individual chromosomes or chromosome set present in the genome. chromosome mutations can be detected either by microscopic examinations or genetic analysis, or both. Chromosomal mutations arise through various mechanisms that can be broadly categorized into changes in chromosome number and alterations in chromosome structure. firstly, chromosomal mutations related to chromosome number often stem from errors during cell division, particularly in the anaphase stage of mitosis or meiosis.
Chromosomal Mutation Causes Mechanism Types Examples The advantages of chromosomal mutations. believe it or not, random errors occurring during cell division can benefit organisms. listed below are some of them. 1. survival. mutations are essential for populations because they help some individuals adapt to their environment while they maintain their survival. Irregularities or accidents when cell division happens as well as during chromosomal crossing over or fertilization can all be causes of chromosomal mutation. all types of chromosomes can undergo chromosomal mutation. chromosomal mutation examples include chromosome deletion, duplication, inversion, and translation. these are known to cause. Mutation: causes, mechanisms, agents and significance. mutation is a process that produces a gene or chromosome that differs from the wild type (arbitrary standard for what “normal” is for an organism). it is most commonly defined as a spontaneous permanent change in a gene or chromosome which usually produces a detectable effect in the. For example, the very same mutation that causes sickle cell anemia in affected individuals (i.e., those people who have inherited two mutant copies of the beta globin gene) can confer a survival.

Comments are closed.