Coniferous Forest Tertiary Consumers
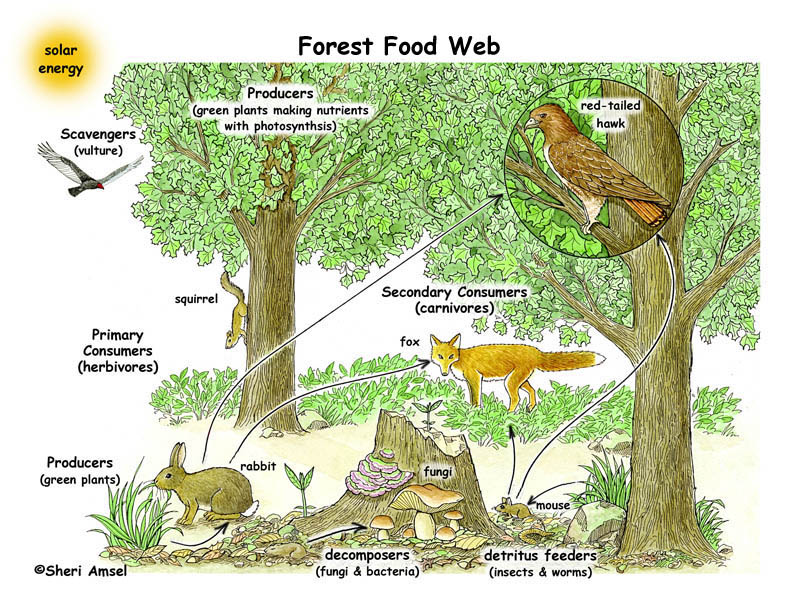
Food Chain In The Forest Tertiary consumers are top predators that eat both the primary and secondary consumers, keeping the food web in balance. bears are a top predator in the coniferous forest ecosystem in north america. Taiga food web: interconnected relationships between flora and fauna. scarlett dennis. july 7, 2023. the taiga, also known as the boreal forest, is the largest land biome on earth, stretching across north america, europe, and asia in the high northern latitudes. characterized by its dense coniferous forests, long, cold winters, and short, wet.
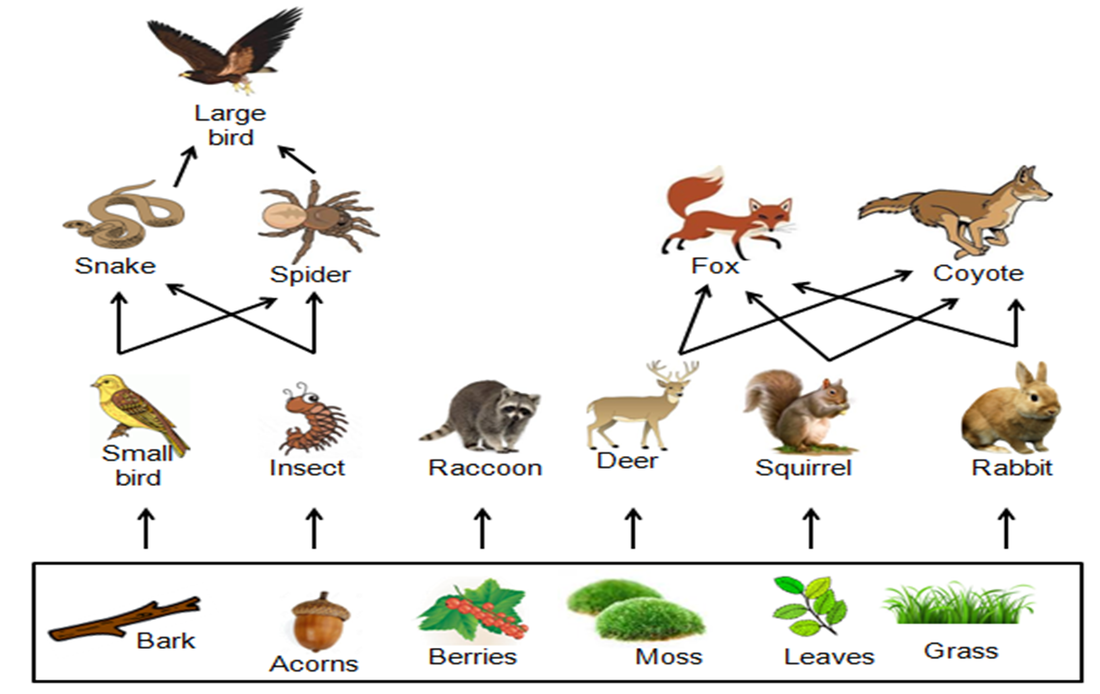
Food Webs And Trophic Levels Katie S Ecology Project Three types of woodlands are coniferous, deciduous and rainforest. any woodland food chain begins with producers like trees, shrubs, flowers and grasses. primary consumers include mice, insects, birds and deer. secondary consumers are smaller predators. tertiary consumers include bears and cougars. A host of insects perform primary consumer duties in the coniferous forest. indeed, many feed directly on the conifers themselves. for example, the southern pine beetle is an important source of mortality for many of the iconic pines of the american southeast, from loblolly to long leaf, as well as various species in the mountain woodlands of mexico and central america. The terrestrial forest (summer) and the english channel ecosystems exhibit inverted pyramids.note: trophic levels are not drawn to scale and the pyramid of numbers excludes microorganisms and soil animals. abbreviations: p=producers, c1=primary consumers, c2=secondary consumers, c3=tertiary consumers, s=saprotrophs (odum and barrett 2005). We can see examples of these levels in the diagram below. the green algae are primary producers that get eaten by mollusks—the primary consumers. the mollusks then become lunch for the slimy sculpin fish, a secondary consumer, which is itself eaten by a larger fish, the chinook salmon—a tertiary consumer.
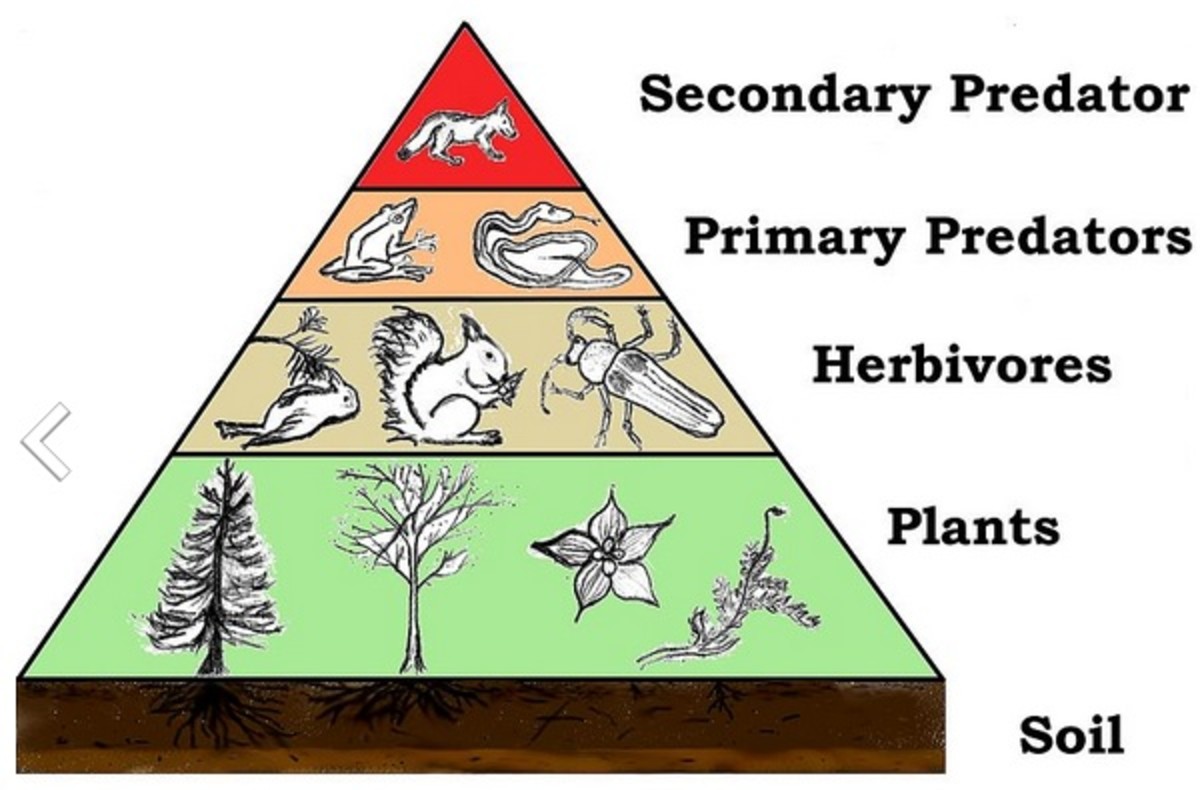
Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages The terrestrial forest (summer) and the english channel ecosystems exhibit inverted pyramids.note: trophic levels are not drawn to scale and the pyramid of numbers excludes microorganisms and soil animals. abbreviations: p=producers, c1=primary consumers, c2=secondary consumers, c3=tertiary consumers, s=saprotrophs (odum and barrett 2005). We can see examples of these levels in the diagram below. the green algae are primary producers that get eaten by mollusks—the primary consumers. the mollusks then become lunch for the slimy sculpin fish, a secondary consumer, which is itself eaten by a larger fish, the chinook salmon—a tertiary consumer. Coniferous forests: deer species such as the sitka deer or the sika deer are adapted to coniferous forests found in regions like north america and eurasia. chaparral and scrubland: in regions like california, mule deer can be found in areas with chaparral vegetation. mixed forests: these ecosystems have a combination of different tree species. Consumers are grouped into four categories: primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and quaternary consumers. primary consumers are the organisms that only consume producers. these are called herbivores. secondary consumers consume both producers and primary consumers, but are also consumed by other organisms.
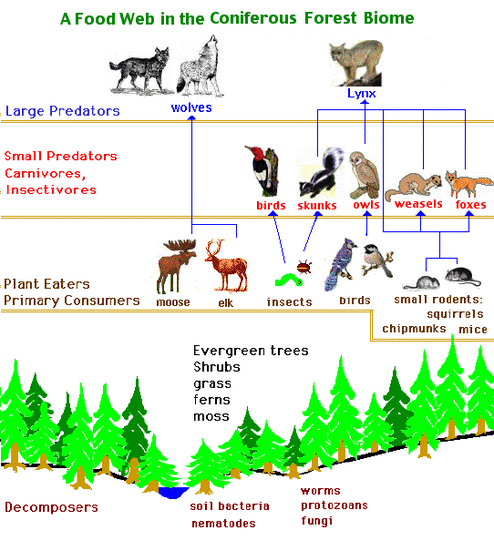
Food Chain Coniferous Forest Coniferous forests: deer species such as the sitka deer or the sika deer are adapted to coniferous forests found in regions like north america and eurasia. chaparral and scrubland: in regions like california, mule deer can be found in areas with chaparral vegetation. mixed forests: these ecosystems have a combination of different tree species. Consumers are grouped into four categories: primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and quaternary consumers. primary consumers are the organisms that only consume producers. these are called herbivores. secondary consumers consume both producers and primary consumers, but are also consumed by other organisms.

Comments are closed.