Consumer Budget Constraint

Consumer Theory 1 Budget Constraint Youtube Let's make p and q the price and quantity of items purchased and budget the amount of income one has to spend. budget = p 1 × q 1 p 2 × q 2. we can apply the budget constraint equation to alphonso's scenario: budget = p 1 × q 1 p 2 × q 2 $ 10 = $ 2 × q burgers $ 0.50 × q bus tickets. using a little algebra, let's turn this into the. Budget constraint. in economics, a budget constraint represents all the combinations of goods and services that a consumer may purchase given current prices within their given income. consumer theory uses the concepts of a budget constraint and a preference map as tools to examine the parameters of consumer choices .
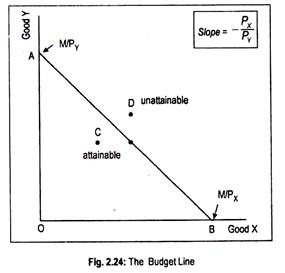
The Budget Constraint Of A Consumer With Diagram 3.1 description of the budget constraint. learning objective 3.1: define a budget constraint conceptually, mathematically, and graphically the budget constraint is the set of all the bundles a consumer can afford given that consumer’s income. This section provides a lesson on budget constraints. the point at which the indifference curve and the budget constraint cross is incorrect, because if the indifference curve is crossing the budget constraint the consumer could select another bundle on a higher indifference curve (where she or he obtains more utility) and still be within the budget set. Do you want to learn how consumers make choices under budget constraints? watch this video from khan academy and discover the concept of utility maximization with indifference curves. you will see how to draw and interpret a budget line, and how to find the optimal consumption bundle. khan academy is a free online platform that offers courses in various subjects, from math to economics. Figure 2.2 the budget constraint: alphonso’s consumption choice opportunity frontier each point on the budget constraint represents a combination of burgers and bus tickets whose total cost adds up to alphonso’s budget of $10. the relative price of burgers and bus tickets determines the slope of the budget constraint.
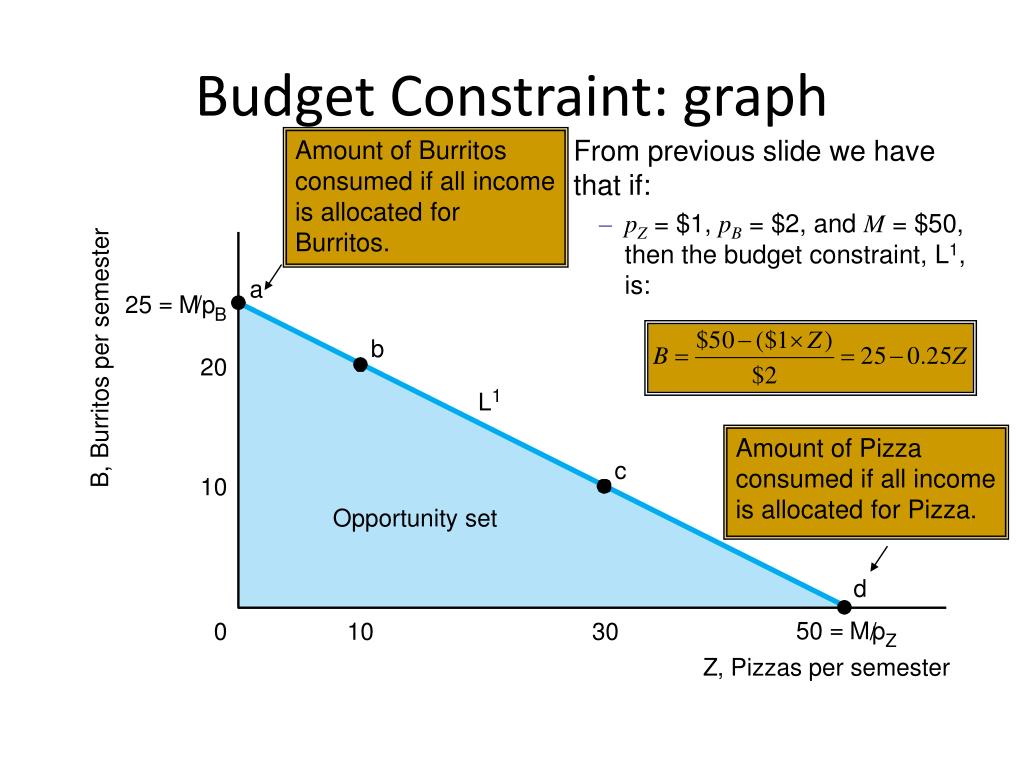
Ppt Budget Constraints Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 912224 Do you want to learn how consumers make choices under budget constraints? watch this video from khan academy and discover the concept of utility maximization with indifference curves. you will see how to draw and interpret a budget line, and how to find the optimal consumption bundle. khan academy is a free online platform that offers courses in various subjects, from math to economics. Figure 2.2 the budget constraint: alphonso’s consumption choice opportunity frontier each point on the budget constraint represents a combination of burgers and bus tickets whose total cost adds up to alphonso’s budget of $10. the relative price of burgers and bus tickets determines the slope of the budget constraint. Lecture 5: budget constraints. freely sharing knowledge with learners and educators around the world. learn more. mit opencourseware is a web based publication of virtually all mit course content. ocw is open and available to the world and is a permanent mit activity. Description. this lecture continues the discussion about consumer choice and what happens when budget constraints are introduced. see handout 3 for relevant graphs for this lecture.

Comments are closed.