Consumer Examples Economics

Consumer Spending Tutor2u Economics The definition of consumer economics with examples. consumer protection due to bounded rationality, consumers benefit from protections such as standards, regulations and laws that prohibit practices that are detrimental to fair commerce, health, product safety and sustainability. Consumer goods are products that are purchased for consumption by the average consumer. alternatively called final goods, consumer goods are the end result of production and manufacturing and are.
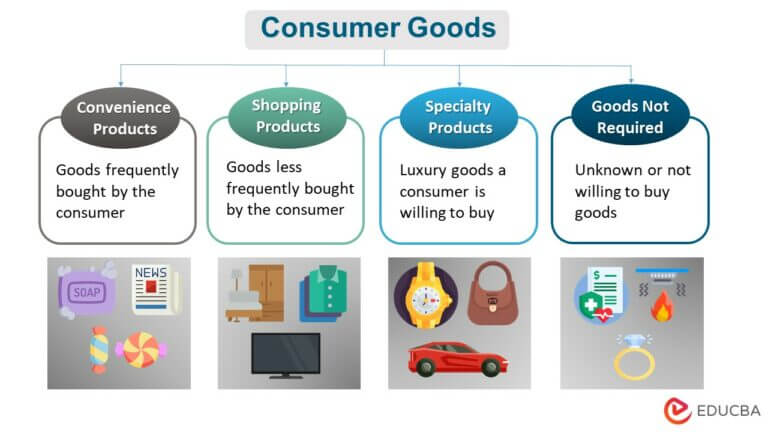
Consumer Goods Meaning Types Examples Benefits Consumers are the basic economic entities of an economy. all the consumers consume goods and services directly and indirectly to maximise satisfaction and utility. consumers have limited income and by which they want to satisfy their maximum utility (utility is the want satisfying capacity of a commodity). generally, consumer means an individual only; however, consumers will consist of a. Consumer theory is the study of how people decide to spend their money, given their preferences and budget constraints. a branch of microeconomics , consumer theory shows how individuals make. Marginal utility and total utility. visualizing marginal utility mu and total utility tu functions. utility maximization: equalizing marginal utility per dollar. deriving demand curve from tweaking marginal utility per dollar. lesson overview total utility and marginal utility. (see consumer good.) neoclassical (mainstream) economists generally consider consumption to be the final purpose of economic activity, and thus the level of consumption per person is viewed as a central measure of an economy’s productive success. the study of consumption behaviour plays a central role in both macroeconomics and microeconomics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ConsumerPriceIndexJPEG-5c8ffb0946e0fb0001f8d0ca.jpg)
Economics Marginal utility and total utility. visualizing marginal utility mu and total utility tu functions. utility maximization: equalizing marginal utility per dollar. deriving demand curve from tweaking marginal utility per dollar. lesson overview total utility and marginal utility. (see consumer good.) neoclassical (mainstream) economists generally consider consumption to be the final purpose of economic activity, and thus the level of consumption per person is viewed as a central measure of an economy’s productive success. the study of consumption behaviour plays a central role in both macroeconomics and microeconomics. Definition and examples. consumer goods are products that people buy and don’t use to make other things that are then sold. we can also call them final goods because when somebody buys them, they have reached their final destination. consumer goods are the end result of manufacturing and production. they are what we see on supermarket shelves. Consumer choice refers to the decisions made by individuals or households regarding the purchase of goods and services. it is based on the preferences, incomes, and the prices of goods and services available in the market. the theory of consumer choice is a fundamental component of microeconomics and helps to explain demand, market allocations.

Comments are closed.