Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient Table
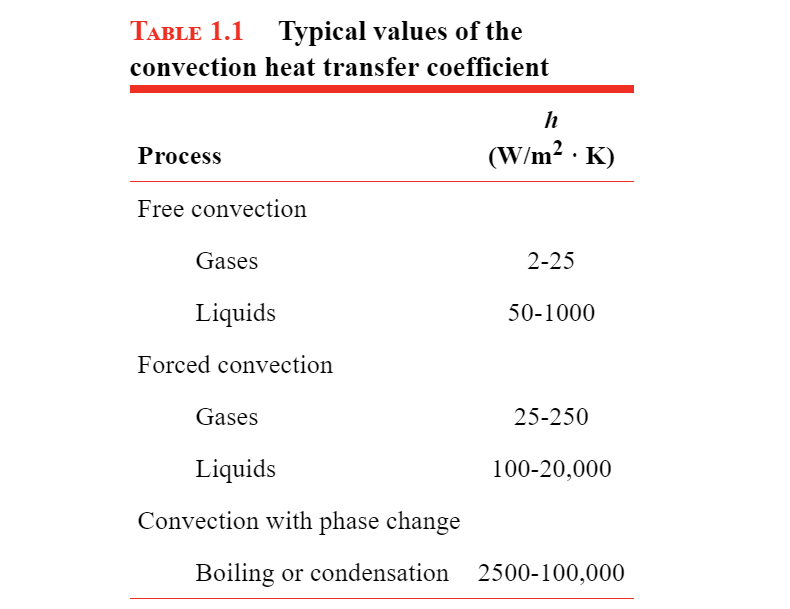
Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Convective heat transfer coefficients table chart. the following table charts of typical convective convection heat transfer coefficients for fluids and specific applications. typical values of heat transfer coefficient. flow type. (w m2 k) forced convection; low speed flow of air over a surface. 10. Convective heat transfer coefficient for air. the convective heat transfer coefficient for air flow can be approximated to. hc = 10.45 v 10 v1 2 (2) where. hc = heat transfer coefficient (kcal m2h°c) v = relative speed between object surface and air (m s) since. 1 kcal m2h°c = 1.16 w m2°c.

Convection Heat Transfer Coefficient Table The heat transfer coefficient is the proportionality coefficient between the heat flux and the thermodynamic driving force for the flow of heat (i.e., the temperature difference, Δt): h = q (ts k) where: q: amount of heat required (heat flux), w m2 i.e., thermal power per unit area, q = d\dot {q} da. h: heat transfer coefficient, w (m 2 k). In thermodynamics, the heat transfer coefficient or film coefficient, or film effectiveness, is the proportionality constant between the heat flux and the thermodynamic driving force for the flow of heat (i.e., the temperature difference, Δt ). it is used in calculating the heat transfer, typically by convection or phase transition between a. Typical values of α are shown in table 1, from which it can be seen that increases in velocity generally result in increases in heat transfer coefficient, so that α is smallest in natural convection and increases to 100 and more on flat surfaces with air velocities greater than around 50 m s. the heat transfer coefficient is considerably greater with liquid flows and greater again with two. The convection heat transfer process is strongly dependent upon the properties of the fluid being considered. correspondingly, the convective heat transfer coefficient (h), the overall coefficient (u o), and the other fluid properties may vary substantially for the fluid if it experiences a large temperature change during its path through the convective heat transfer device.

Comments are closed.