Cross Product Two Dimensions
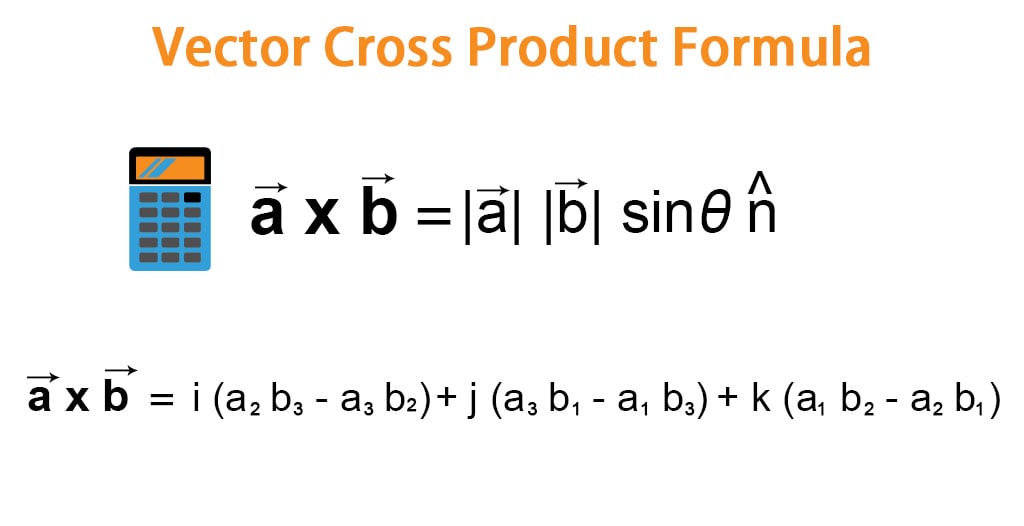
Cross Product Two Dimensions Parkertinsalinas 6. the cross product in 2 dimensions is a scalar give my a 2x2 determinant: (a, b) × (c, d) =∣∣∣a c b d∣∣∣ = ad − cb. the cross product in 3 dimensions is a vector given by the 3x3 determinant: (a, b, c) × (d, e, f) =∣∣∣∣∣ex a d ey b e ez c f ∣∣∣∣∣. e. a. abbott describes a 2d cross product nicely in his. You may already be familiar with the dot product, also called the scalar product. this product leads to a scalar quantity that is given by the product of the magnitudes of both vectors multiplied by the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. as for the cross product, it is a multiplication of vectors that leads to a vector.

Cross Product Of Two Vectors Explained Youtube In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three dimensional oriented euclidean vector space (named here ), and is denoted by the symbol . given two linearly independent vectors a and b, the cross product, a × b. The cross product (purple) is always perpendicular to both vectors, and has magnitude zero when the vectors are parallel and maximum magnitude ‖ ⇀ a‖‖ ⇀ b‖ when they are perpendicular. (public domain; lucasvb). example 12.4.1: finding a cross product. let ⇀ p = − 1, 2, 5 and ⇀ q = 4, 0, − 3 (figure 12.4.1). Learn how to calculate the cross product of two vectors in 3d and 2d, and what it means geometrically. the cross product measures the area spanned by two vectors, and is orthogonal to both of them. For starters, the cross product is an operation that takes two vectors and returns another vector perpendicular to both, while the dot product yields a number with no direction. the dot product is more easily generalized to higher or lower dimensions, while the cross product does not even exist in 2 d.

Kruisproduct Van Twee Vectoren Definitie Formule Voorbeelden Cril Learn how to calculate the cross product of two vectors in 3d and 2d, and what it means geometrically. the cross product measures the area spanned by two vectors, and is orthogonal to both of them. For starters, the cross product is an operation that takes two vectors and returns another vector perpendicular to both, while the dot product yields a number with no direction. the dot product is more easily generalized to higher or lower dimensions, while the cross product does not even exist in 2 d. Two vectors can be multiplied using the "cross product" (also see dot product) the cross product a × b of two vectors is another vector that is at right angles to both: and it all happens in 3 dimensions! the magnitude (length) of the cross product equals the area of a parallelogram with vectors a and b for sides: see how it changes for. The cross product is very useful for several types of calculations, including finding a vector orthogonal to two given vectors, computing areas of triangles and parallelograms, and even determining the volume of the three dimensional geometric shape made of parallelograms known as a parallelepiped. the following examples illustrate these.

Comments are closed.