Difference Between Primary And Secondary Consumers

What Is The Difference Between Primary Secondary And Tertiary Consumersођ 5 min read. the main difference between primary secondary and tertiary consumers is that primary consumers are the herbivores that feed on plants, and secondary consumers can be either carnivores, which prey on other animals, or omnivores, which feed on both animals and plants, whereas tertiary consumers are the apex predators that feed on both. This is also the amount of energy per year that's made available to the primary consumers, which eat the primary producers. the 10 % rule would predict that the primary consumers store only 2, 000 kcal m 2 year of energy in their own bodies, making energy available to their predators (secondary consumers) at a lower rate.

Secondary Consumer Animals The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. Secondary consumer definition. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. The first consumer in the chain, in this case the grasshopper, is also called the primary consumer. a consumer that only eats plants is called a herbivore. the frog is the secondary consumer.
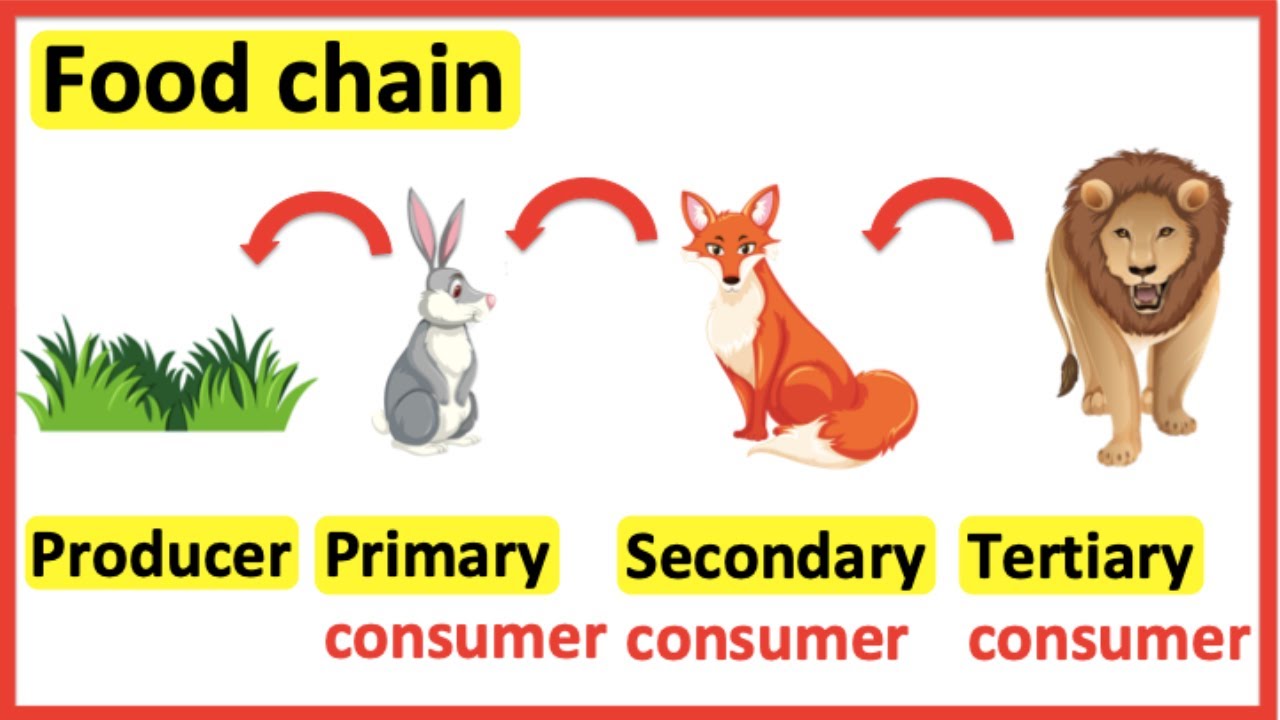
Can An Animal Simultaneously Produce And Consume In Nature Secondary consumer definition. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. The first consumer in the chain, in this case the grasshopper, is also called the primary consumer. a consumer that only eats plants is called a herbivore. the frog is the secondary consumer. These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. For example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. some other examples of primary consumers are white tailed deer that forage on prairie grasses, and zooplankton that eat microscopic algae in the water. next are the secondary consumers, which eat primary consumers. secondary consumers are mostly carnivores, from the.

Difference Between Primary And Secondary Consumers вђ Otosection These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. For example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. some other examples of primary consumers are white tailed deer that forage on prairie grasses, and zooplankton that eat microscopic algae in the water. next are the secondary consumers, which eat primary consumers. secondary consumers are mostly carnivores, from the.

Food Chains And Food Webs Playbuzz

Comments are closed.