Different Types Of Dna Mutations Gene Vs Chromosomal Their Causes
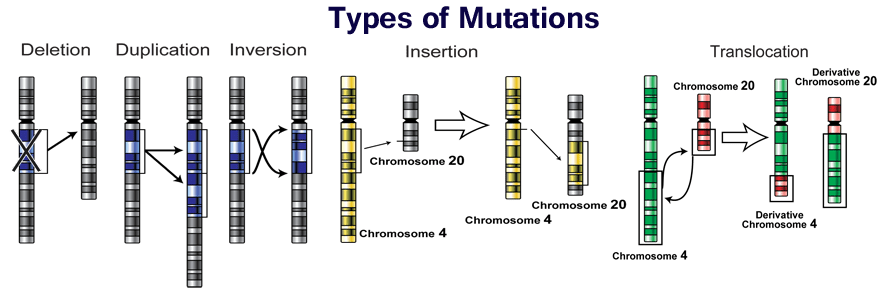
Different Types Of Dna Mutations Gene Vs Chromosomal Their Causes A genetic mutation is a change to a gene’s dna sequence to produce something different. it creates a permanent change to that gene’s dna sequence. genetic variations are important for humans to evolve, which is the process of change over generations. a sporadic genetic mutation occurs in one person. The types of mutations include: silent mutation: silent mutations cause a change in the sequence of bases in a dna molecule, but do not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein (figure 14.5.1 14.5. 1). missense mutation: this type of mutation is a change in one dna base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid.
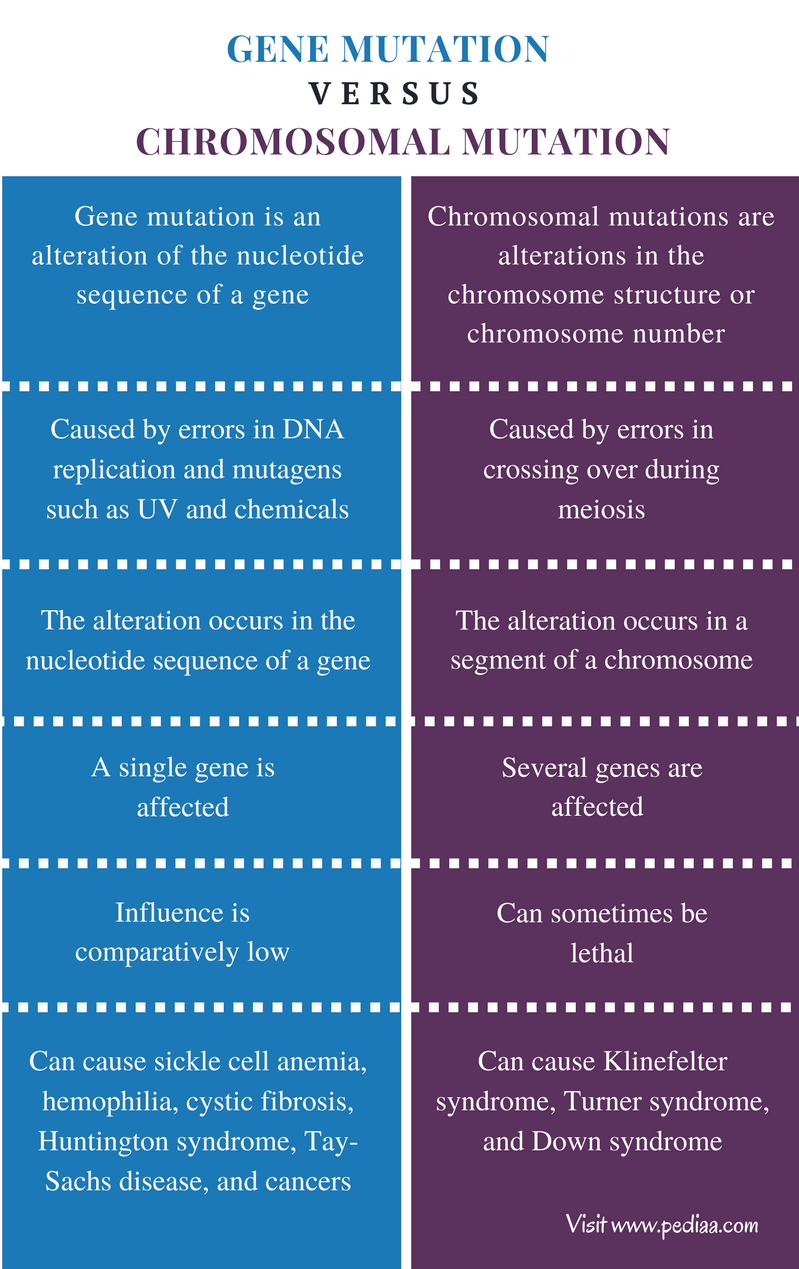
Difference Between Gene Mutation And Chromosomal Mutation Defini Genes contain the information, or "code", needed so your body can make the many proteins it needs to function. a genetic mutation is an alteration in the genetic code found in dna. a mutation. For example, sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution in the beta hemoglobin gene, which alters a single amino acid in the protein produced. change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change in the protein produced. these are called silent mutations. change an amino acid coding codon to a single “stop” codon. Gene and chromosomal mutations are two types of dna mutations affecting nucleic acid sequences and, as result, normal functions of cells and organisms. these changes are the result of an act of physical and chemical mutagens. the ames test may be used to estimate how strong those agents are. Anthony j.f. griffiths. mutation, an alteration in the genetic material (the genome) of a cell of a living organism or of a virus that is more or less permanent and that can be transmitted to the cell’s or the virus’s descendants. the genomes of organisms are all composed of dna, whereas viral genomes can be of dna or rna.
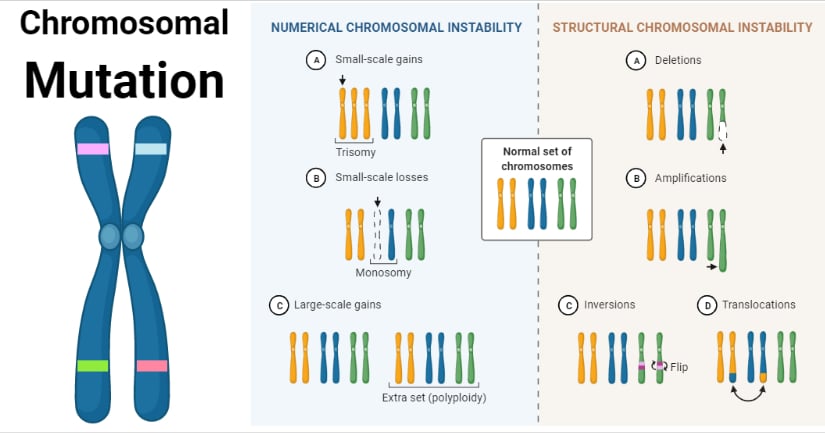
Chromosomal Mutation Causes Mechanism Types Examples Gene and chromosomal mutations are two types of dna mutations affecting nucleic acid sequences and, as result, normal functions of cells and organisms. these changes are the result of an act of physical and chemical mutagens. the ames test may be used to estimate how strong those agents are. Anthony j.f. griffiths. mutation, an alteration in the genetic material (the genome) of a cell of a living organism or of a virus that is more or less permanent and that can be transmitted to the cell’s or the virus’s descendants. the genomes of organisms are all composed of dna, whereas viral genomes can be of dna or rna. There are a variety of types of mutations. two major categories of mutations are germline mutations and somatic mutations. germline mutations occur in gametes. these mutations are especially significant because they can be transmitted to offspring and every cell in the offspring will have the mutation. somatic mutations occur in other cells of. Acquired mutations occur in one cell, and then are passed on to any new cells that come from that cell. this mutation cannot be passed on to a person's children, because it doesn’t affect their sperm or egg cells. this type of mutation is also called a sporadic mutation or a somatic mutation.

Comments are closed.