Differentiate Between Primary And Secondary Consumer Consumers Differentiates

Differentiate Between Primary And Secondary Consumers Giving Examples Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. 5 min read. the main difference between primary secondary and tertiary consumers is that primary consumers are the herbivores that feed on plants, and secondary consumers can be either carnivores, which prey on other animals, or omnivores, which feed on both animals and plants, whereas tertiary consumers are the apex predators that feed on both.
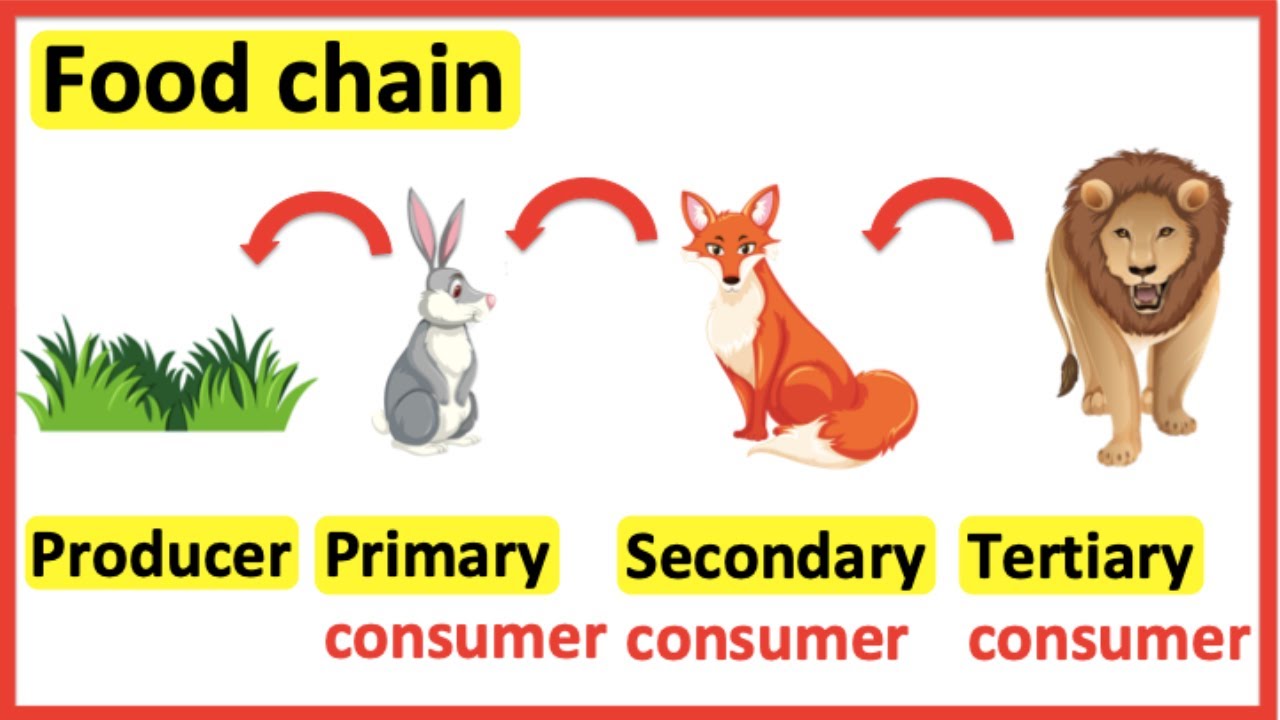
Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. A producer produces their own organic molecules while the consumers get organic molecules by consuming others. the food chain is a sequence of organisms that basically show who gets the organic nutrients by consuming other organisms. producers also known as autotrophs or self feeders they produce their own organic molecules like carbon, essentially feeding themselves. there are two types of. Animals that eat the primary consumers are secondary consumers. the primary consumer is prey and the secondary consumer is the predator. but predator can become prey. The opossum shrimp eats both primary producers and primary consumers; it is, therefore, both a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. the loss of energy in tropic levels it is rare to find food chains that have more than four or five links because the loss of energy limits the length of food chains.

Secondary Consumer Definition Examples Food Chain Lesson Study Animals that eat the primary consumers are secondary consumers. the primary consumer is prey and the secondary consumer is the predator. but predator can become prey. The opossum shrimp eats both primary producers and primary consumers; it is, therefore, both a primary consumer and a secondary consumer. the loss of energy in tropic levels it is rare to find food chains that have more than four or five links because the loss of energy limits the length of food chains. The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer the next one is the secondary consumer. Primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. regardless of what a secondary consumer is, it still must have primary consumers in its diet to survive.

Comments are closed.