Discrete Mathematics Why Does This Step Work In This Proof

Discrete Mathematics Why Does This Step Work In This Proof $\begingroup$ most proofs require a bit (or a lot, or an awful lot) of scratch paper. your random scribblings (or even foul language) doesn't need to appear to the world. it is so much better to present the polished result, and when somebody (like you here) asks, you look at them with supreme disdain (they don't have to know it took you weeks of hard work to come up with that "simple" idea ; ). Outline for mathematical induction. to show that a propositional function p(n) is true for all integers n ≥ a, follow these steps: base step: verify that p(a) is true. inductive step: show that if p(k) is true for some integer k ≥ a, then p(k 1) is also true. assume p(n) is true for an arbitrary integer, k with k ≥ a.

Discrete Mathematics Lecture 08 Methods Of Proof Direct Method Youtube This proof will contain several "steps" or "parts." before giving all of the steps to the proof of mathematical induction, it may be useful to reformulate the definition of the proof technique in terms of the notation that will be used throughout the sequence of steps in the explanation (for consistency and facilitated understanding):. Proofs discrete mathematics an open introduction. Proof by induction: strong form. example 1. example 2. one of the most powerful methods of proof — and one of the most difficult to wrap your head around — is called mathematical induction, or just “induction" for short. i like to call it “proof by recursion," because this is exactly what it is. In precalculus, discrete mathematics or real analysis, an arithmetic series is often used as a student's first example of a proof by mathematical induction. recall, from : mathematical induction is a method of mathematical proof typically used to establish a given statement for all natural numbers. it is done in two steps. the first.

Discrete Mathematics Proof By Induction Youtube Proof by induction: strong form. example 1. example 2. one of the most powerful methods of proof — and one of the most difficult to wrap your head around — is called mathematical induction, or just “induction" for short. i like to call it “proof by recursion," because this is exactly what it is. In precalculus, discrete mathematics or real analysis, an arithmetic series is often used as a student's first example of a proof by mathematical induction. recall, from : mathematical induction is a method of mathematical proof typically used to establish a given statement for all natural numbers. it is done in two steps. the first. The proof in the previous problem does not work. but if we modify the “fact,” we can get a working proof. prove that \(n 3 \lt n 7\) for all values of \(n \in \n\text{.}\) you can do this proof with algebra (without induction), but the goal of this exercise is to write out a valid induction proof. Proof by induction. proof by induction is a technique used in discrete mathematics to prove universal generalizations. a universal generalization is a claim which says that every element in some series has some property. for example, the following is a universal generalization: for any integer n ≥ 3, 2^n > 2n.

Examples Of Proof By Induction Discrete Math Youtube The proof in the previous problem does not work. but if we modify the “fact,” we can get a working proof. prove that \(n 3 \lt n 7\) for all values of \(n \in \n\text{.}\) you can do this proof with algebra (without induction), but the goal of this exercise is to write out a valid induction proof. Proof by induction. proof by induction is a technique used in discrete mathematics to prove universal generalizations. a universal generalization is a claim which says that every element in some series has some property. for example, the following is a universal generalization: for any integer n ≥ 3, 2^n > 2n.
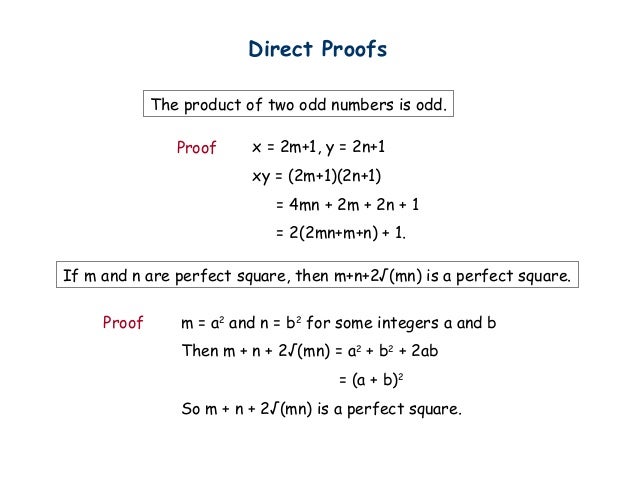
Proof Techniques In Discrete Mathematics Payment Proof 2020

Comments are closed.