Ecosystem Definition Structure Factors Types Functions

Ecosystem Definition Structure Factors Types Functions Ecosystem definition, structure, factors, types, functions. the ecosystem is the basic unit of our environment and comprises living organisms and non living and how they interact with each other. in simple words, a geographical area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, coexist to form a life bubble is. An ecosystem is a structural and functional unit of ecology where the living organisms interact with each other and the surrounding environment. in other words, an ecosystem is a chain of interactions between organisms and their environment. the term “ecosystem” was first coined by a.g.tansley, an english botanist, in 1935.
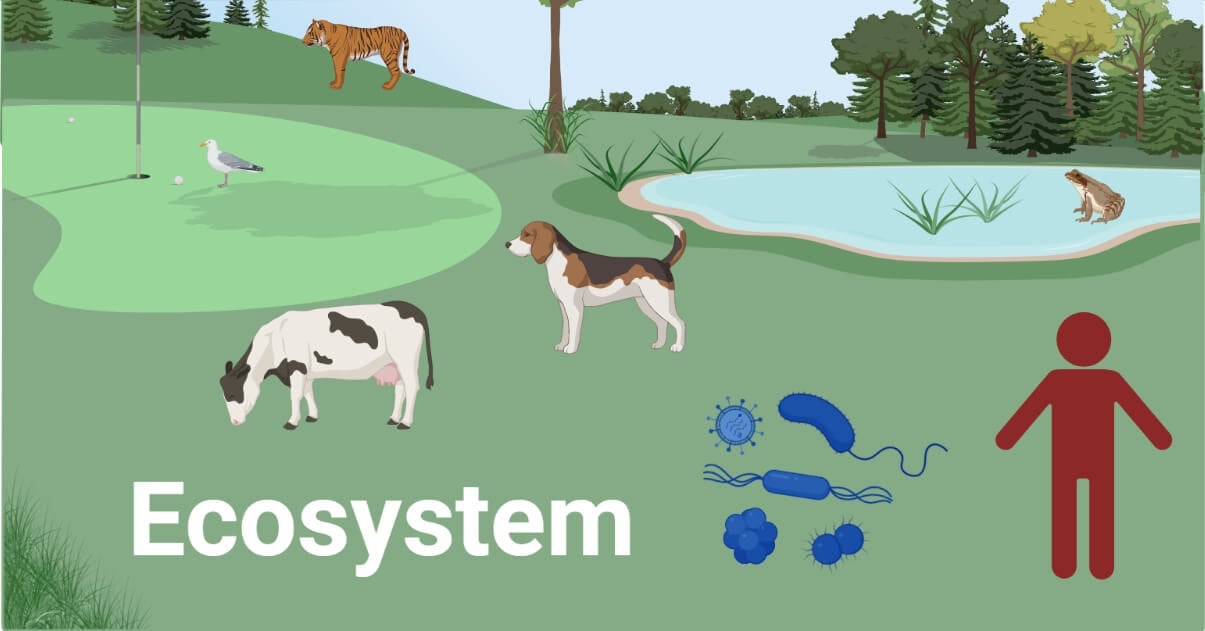
Ecosystem Definition Structure Factors Types Functions Ecosystem, the complex of living organisms, their physical environment, and all their interrelationships in a particular unit of space. a brief treatment of ecosystems follows. for full treatment, see biosphere. an ecosystem can be categorized into its abiotic constituents, including minerals, climate, soil, water, sunlight, and all other. An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life. ecosystems contain biotic or living, parts, as well as a biotic factors, or nonliving parts. biotic factors include plants, animals, and other organisms. Ecosystem function is the capacity of natural processes and components to provide goods and services that satisfy human needs, either directly or indirectly. ecosystem functions are subset of ecological processes and ecosystem structures. each function is the result of the natural processes of the total ecological sub system of which it is a part. Definition. an ecosystem or biome describes a single environment and every living (biotic) organism and non living (abiotic) factor that is contained within it or characterizes it. an ecosystem embodies every aspect of a single habitat, including all interactions between its different elements.
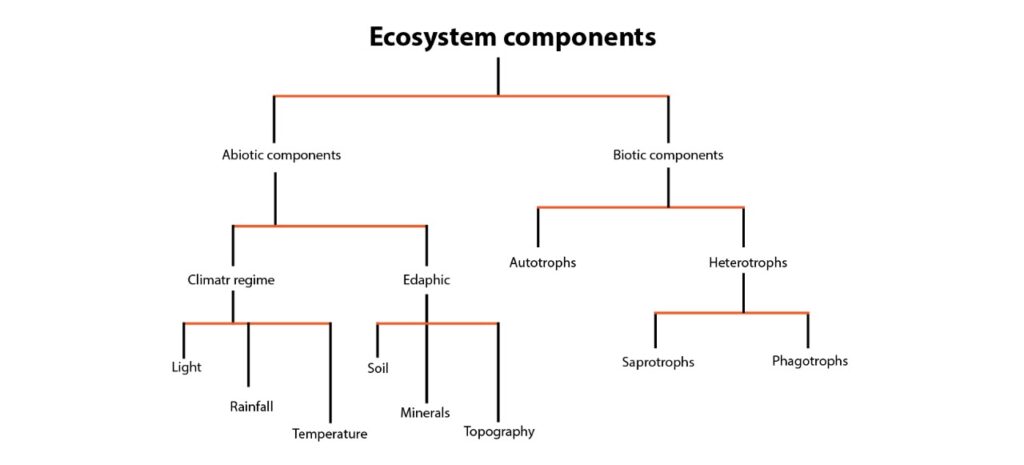
Ecosystem Definition Structure Functions Types Ecosystem function is the capacity of natural processes and components to provide goods and services that satisfy human needs, either directly or indirectly. ecosystem functions are subset of ecological processes and ecosystem structures. each function is the result of the natural processes of the total ecological sub system of which it is a part. Definition. an ecosystem or biome describes a single environment and every living (biotic) organism and non living (abiotic) factor that is contained within it or characterizes it. an ecosystem embodies every aspect of a single habitat, including all interactions between its different elements. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. internal factors are controlled, for example, by decomposition, root competition, shading, disturbance, succession, and the types of species present. while the. Biologists define an ecosystem as a community of living organisms and their physical environment, which includes both biotic and abiotic factors. biotic factors are living things in an interdependent ecological system like plants, animals, microbes and fungi. abiotic factors are non living things like water, sunlight, shelter, rocks, minerals.
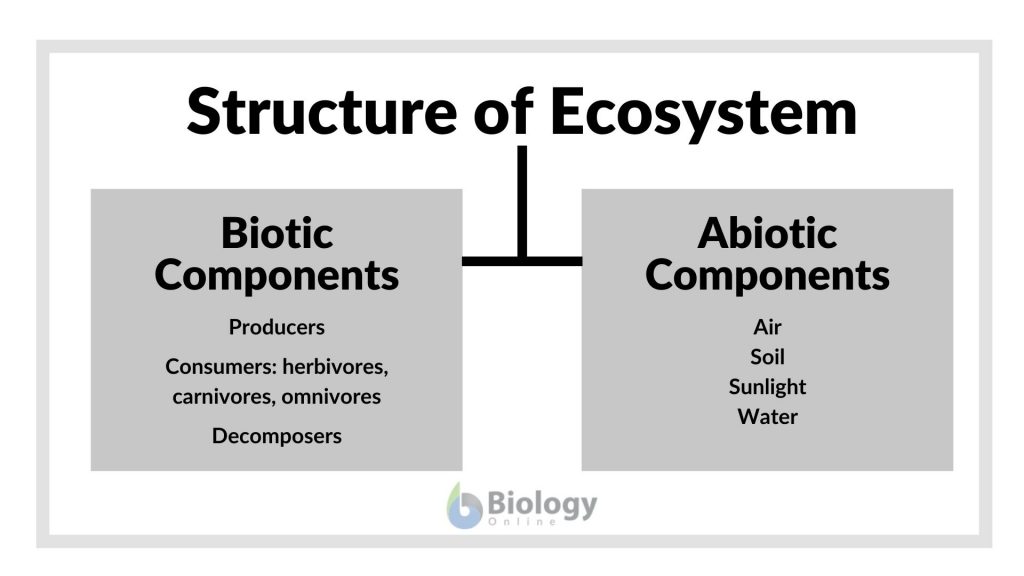
What Is Ecosystem Check Definition Structure Examples My Xxx Hot Girl External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. internal factors are controlled, for example, by decomposition, root competition, shading, disturbance, succession, and the types of species present. while the. Biologists define an ecosystem as a community of living organisms and their physical environment, which includes both biotic and abiotic factors. biotic factors are living things in an interdependent ecological system like plants, animals, microbes and fungi. abiotic factors are non living things like water, sunlight, shelter, rocks, minerals.
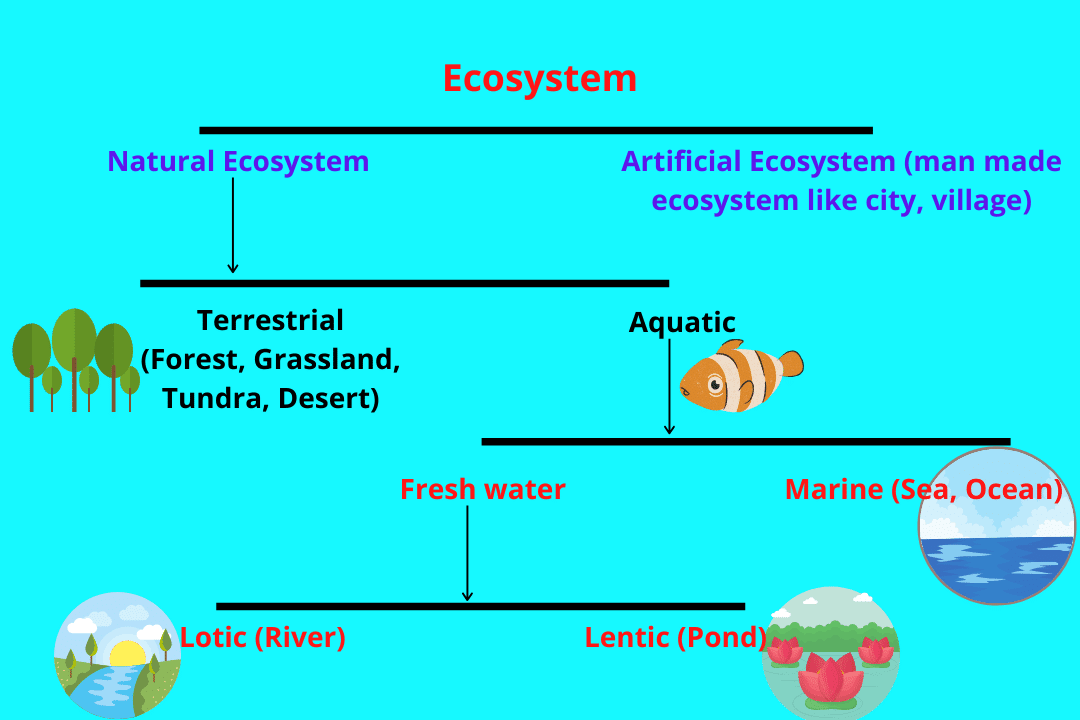
Ecosystem Definition Structure Factors Types Function Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.