Energy Flow In Ecosystem Diagram
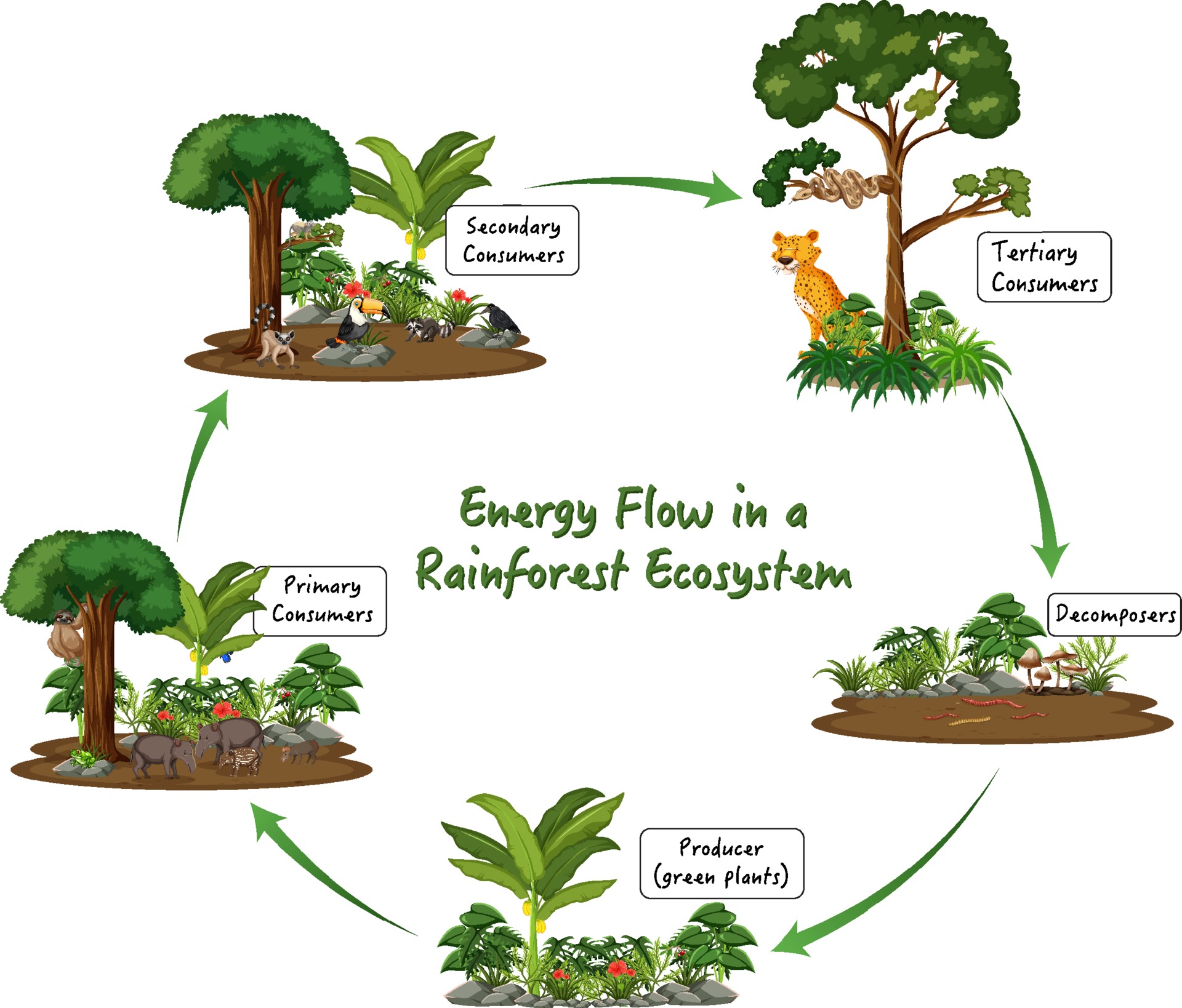
Energy Flow In A Rainforest Ecosystem Diagram 2288483 Vector Art At Learn how energy flows from the sun to organisms in an ecosystem through photosynthesis and food chains. see examples of energy flow diagrams and terms such as trophic levels, biomass and productivity. Learn how energy flows from producers to consumers in different food chains and food webs in the ecosystem. understand the laws of thermodynamics, trophic levels, and energy pyramids with examples and diagrams.
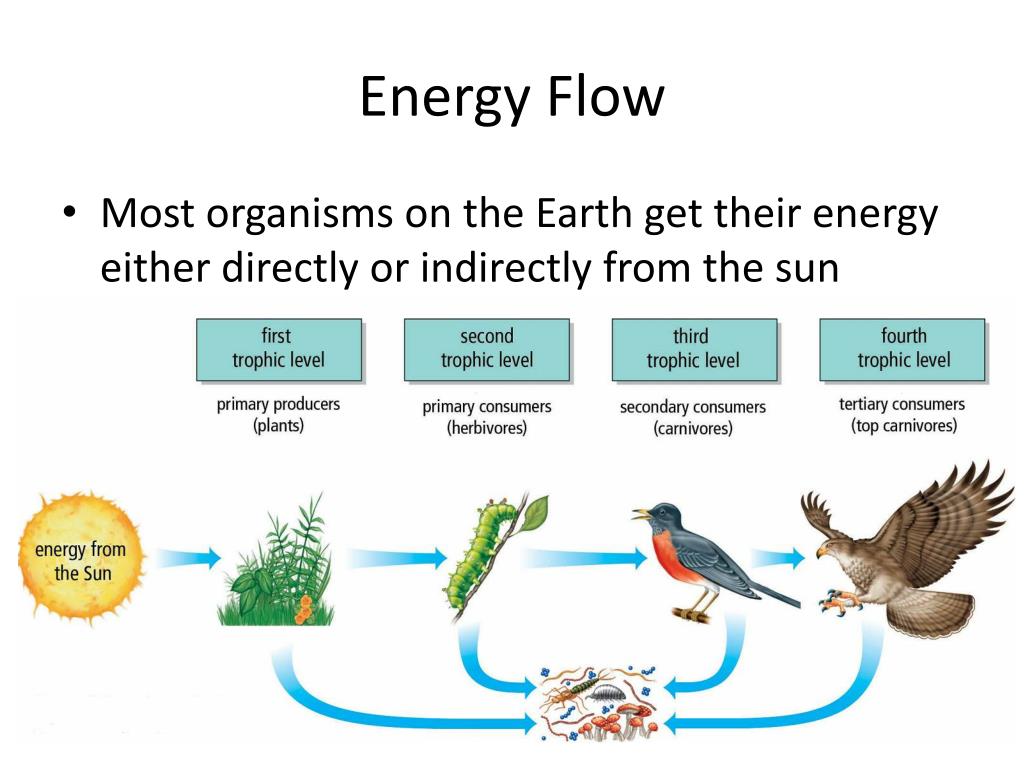
Ppt Energy Flow In An Ecosystem Powerpoint Presentation Free Energy flow in an ecosystem (with diagram) energy has been defined as the capacity to do work. energy exists in two forms potential and kinetic. potential energy is the energy at rest {i.e., stored energy) capable of performing work. kinetic energy is the energy of motion (free energy). An example of gross primary productivity is shown in the compartment diagram of energy flow within the silver springs aquatic ecosystem as shown (figure \(\pageindex{2}\)). in this ecosystem, the total energy accumulated by the primary producers (gross primary productivity) was shown to be 20,810 kcal m 2 yr. Energy flow (ecology) a food pyramid and a corresponding food web, demonstrating some of the simpler patterns in a food web. a graphic representation of energy transfer between trophic layers in an ecosystem. energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and. Figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: a (a) tidal pool ecosystem in matinicus island, maine, is a small ecosystem, while the (b) amazon rainforest in brazil is a large ecosystem. (credit a: modification of work by jim kuhn; credit b: modification of work by ivan mlinaric) there are three broad categories of ecosystems based on their general environment.
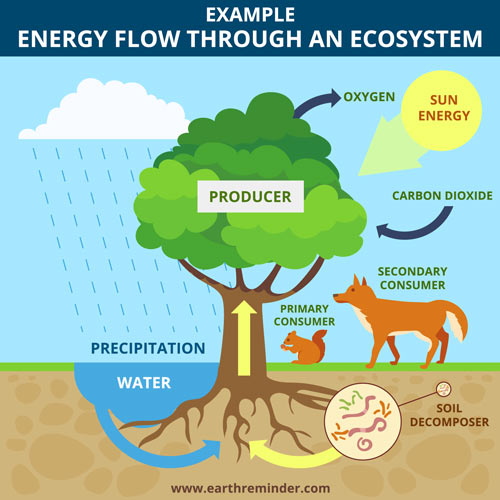
How Does Energy Flow Through An Ecosystem Earth Reminder Energy flow (ecology) a food pyramid and a corresponding food web, demonstrating some of the simpler patterns in a food web. a graphic representation of energy transfer between trophic layers in an ecosystem. energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and. Figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: a (a) tidal pool ecosystem in matinicus island, maine, is a small ecosystem, while the (b) amazon rainforest in brazil is a large ecosystem. (credit a: modification of work by jim kuhn; credit b: modification of work by ivan mlinaric) there are three broad categories of ecosystems based on their general environment. Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each. Energy flow in an ecosystem. organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs by how they ingest energy. autotrophs sustain themselves by using basic energy sources like sunlight. plants, which use photosynthesis to convert sunlight to grow and maintain themselves, are an example of autotrophs. all other organisms feed on other organisms.

Energy Flow Biology Britannica Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each. Energy flow in an ecosystem. organisms are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs by how they ingest energy. autotrophs sustain themselves by using basic energy sources like sunlight. plants, which use photosynthesis to convert sunlight to grow and maintain themselves, are an example of autotrophs. all other organisms feed on other organisms.

Energy Flow Biology Britannica

Comments are closed.