Eosinophilic Esophagitis Eoe Spectrum Of Response Non Response

Eosinophilic Esophagitis Eoe Spectrum Of Response Non Response Eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic condition, which can affect both children and adults and encompasses a spectrum of disorders; it is a common cause of esophageal dysphagia, esophageal narrowing and food impaction.1 – 6 given its increased recognition in the past 3 decades,2 we discuss recent evidence related to eosinophilic esophagitis as well as recommendations about its management. Introduction. eosinophilic esophagitis (eoe) is a chronic, immune‑mediated inflammatory disease that is characterized by esophageal dysfunction and transmural infiltration of the esophagus by eosinophils. 1,2 eoe is diagnosed in children and adults into their 50s after demonstrating an eosinophil rich inflammation in esophageal biopsies, taken during an upper gastrointestinal endoscopic.

Eosinophilic Oesophagitis And Food Allergy Medicine Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis (eoe) clinical decision support tool. 1recommendation in favor of empiric elimination diets is based on the published experience with the six food elimination diet (sfed). patients who put a higher value on avoiding the challenges of adherence to diet involving elimination of multiple common food staples. Abstract. eosinophilic esophagitis is an immune allergic pathology of multifactorial etiology (genetic and environmental) that affects both pediatric and adult patients. its symptoms, which include heartburn, regurgitation, and esophageal stenosis (with dysphagia being more frequent in eosinophilic esophagitis in young adults and children), are. A panel of experts defined eosinophilic esophagitis as "a chronic, immune antigen mediated, esophageal disease characterized clinically by symptoms related to esophageal dysfunction and histologically by eosinophil predominant inflammation" [ 1 ]. in the past, eosinophilic esophagitis was abbreviated as "ee," but because of confusion with. Eosinophilic esophagitis (eoe) is a th2, antigen driven disease in which chronic, eosinophil rich inflammation causes symptoms of esophageal dysfunction. 2 esophageal symptoms due to eoe can manifest in multiple ways including heartburn regurgitation, vomiting, dysphagia, food impactions, and even abdominal pain. the differential diagnosis for eoe is broad and can include gastroesophageal.
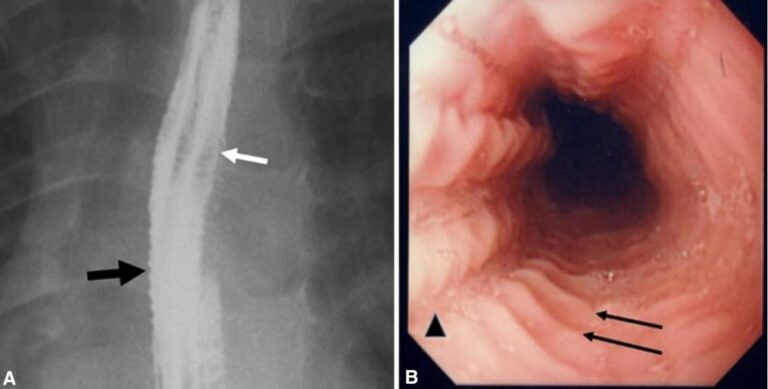
Esofagitis Concise Medical Knowledge A panel of experts defined eosinophilic esophagitis as "a chronic, immune antigen mediated, esophageal disease characterized clinically by symptoms related to esophageal dysfunction and histologically by eosinophil predominant inflammation" [ 1 ]. in the past, eosinophilic esophagitis was abbreviated as "ee," but because of confusion with. Eosinophilic esophagitis (eoe) is a th2, antigen driven disease in which chronic, eosinophil rich inflammation causes symptoms of esophageal dysfunction. 2 esophageal symptoms due to eoe can manifest in multiple ways including heartburn regurgitation, vomiting, dysphagia, food impactions, and even abdominal pain. the differential diagnosis for eoe is broad and can include gastroesophageal. Endoscopy plays a critical role in caring for and evaluating the patient with eosinophilic esophagitis (eoe). endoscopy is essential for diagnosis, assessment of response to therapy, treatment of esophageal strictures, and ongoing monitoring of patients in histologic remission. to date, less invasive testing for identifying or grading eoe severity has not been established, whereas diagnostic. Eosinophilic esophagitis (eoe) is an eosinophil rich, th2 antigen–mediated disease of increasing pediatric and adult worldwide prevalence. diagnosis requires greater than or equal to 15 eosinophils per high power field on light microscopy. symptoms reflect esophageal dysfunction, and typical endoscopic features include linear furrows, white plaques, and concentric rings. progressive disease.

Comments are closed.