Evaluate The Integral Sin 2x 1 Cos 2 X Dx Natural Logarithms

Evaluate The Integral Sin 2 X Dx Using Integration By Parts Youtube In the field of graphical representation to build three dimensional models. symbolab is the best integral calculator solving indefinite integrals, definite integrals, improper integrals, double integrals, triple integrals, multiple integrals, antiderivatives, and more. integration is a way to sum up parts to find the whole. The integral calculator solves an indefinite integral of a function. you can also get a better visual and understanding of the function and area under the curve using our graphing tool. integration by parts formula: ? u d v = u v ? v d u. step 2: click the blue arrow to submit. choose "evaluate the integral" from the topic selector and click to.

Integral Of Cos 2x Sin X Youtube The integral calculator lets you calculate integrals and antiderivatives of functions online — for free! our calculator allows you to check your solutions to calculus exercises. it helps you practice by showing you the full working (step by step integration). all common integration techniques and even special functions are supported. To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary. here are some examples illustrating how to ask for an integral using plain english. integrate x (x 1) integrate x sin(x^2) integrate x sqrt(1 sqrt(x)) integrate x (x 1)^3 from 0 to infinity; integrate 1 (cos(x) 2) from 0 to 2pi; integrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi. The input recognizes various synonyms for functions such as asin, arsin, arcsin, sin^ 1. multiplication signs and parentheses are automatically added, so an entry like 2sinx is equivalent to 2*sin(x) list of mathematical functions and constants: • ln(x) — natural logarithm • sin(x) — sine • cos(x) — cosine • tan(x) — tangent. Du dx = −2sinxcosx → du = −2sinxcosxdx. before we apply this substitution, look at the modified integral (which has sin2x replaced with its equivalent 2sinxcosx ): ∫ 2sinxcosx 1 cos2x dx. hm that numerator looks familiar. it's almost the expression for du! du = −2sinxcosxdx. ∫ 2sinxcosx 1 cos2x dx. all we have to do is apply a.

Solved Evaluate Integral Sin 2 X Cos 2 X Dx Chegg The input recognizes various synonyms for functions such as asin, arsin, arcsin, sin^ 1. multiplication signs and parentheses are automatically added, so an entry like 2sinx is equivalent to 2*sin(x) list of mathematical functions and constants: • ln(x) — natural logarithm • sin(x) — sine • cos(x) — cosine • tan(x) — tangent. Du dx = −2sinxcosx → du = −2sinxcosxdx. before we apply this substitution, look at the modified integral (which has sin2x replaced with its equivalent 2sinxcosx ): ∫ 2sinxcosx 1 cos2x dx. hm that numerator looks familiar. it's almost the expression for du! du = −2sinxcosxdx. ∫ 2sinxcosx 1 cos2x dx. all we have to do is apply a. Integrating products and powers of sin x and cos x. a key idea behind the strategy used to integrate combinations of products and powers of \(\sin x\) and \(\cos x\) involves rewriting these expressions as sums and differences of integrals of the form \(∫\sin^jx\cos x\,dx\) or \(∫\cos^jx\sin x\,dx\). 16.3 the fundamental theorem of line integrals. recall the fundamental theorem of calculus for a single variable function f: zb a. f0(x)dx = f(b) f(a) it says that we may evaluate the integral of a derivative simply by knowing the values of the function at the endpoints of the interval of integration [a,b]. the fundamental theorem of line.
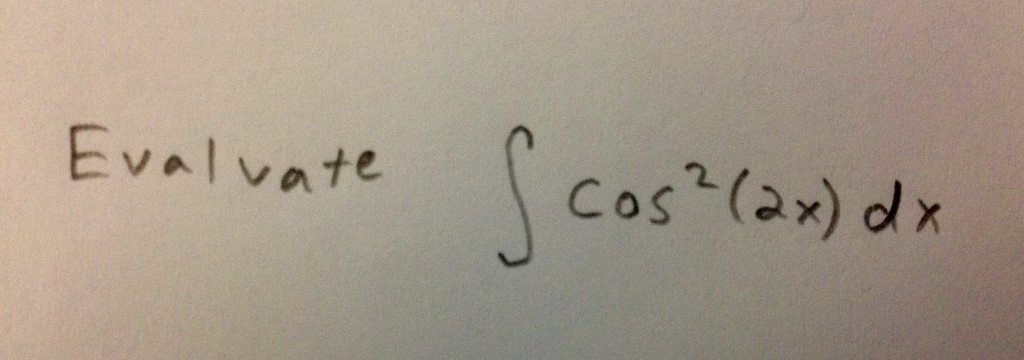
Solved Evaluate Integral Cos 2 2x Dx Chegg Integrating products and powers of sin x and cos x. a key idea behind the strategy used to integrate combinations of products and powers of \(\sin x\) and \(\cos x\) involves rewriting these expressions as sums and differences of integrals of the form \(∫\sin^jx\cos x\,dx\) or \(∫\cos^jx\sin x\,dx\). 16.3 the fundamental theorem of line integrals. recall the fundamental theorem of calculus for a single variable function f: zb a. f0(x)dx = f(b) f(a) it says that we may evaluate the integral of a derivative simply by knowing the values of the function at the endpoints of the interval of integration [a,b]. the fundamental theorem of line.

Comments are closed.