Explain The Structure And Functioning Of An Ecosystem
Ecosystem Definition Structure Functions Types So the functional units of an ecosystem or functional components that work together in an ecosystem are: productivity – it refers to the rate of biomass production. energy flow – it is the sequential process through which energy flows from one trophic level to another. the energy captured from the sun flows from producers to consumers and. The functions of ecosystem are related to the flow of energy and cycling of materials through structural components of the ecosystem. according to woodbury (1954), ecosystem is a complex in which habitat, plants and animals are considered as one interesting unit, the materials and energy of one passing in and out of the others. advertisements.

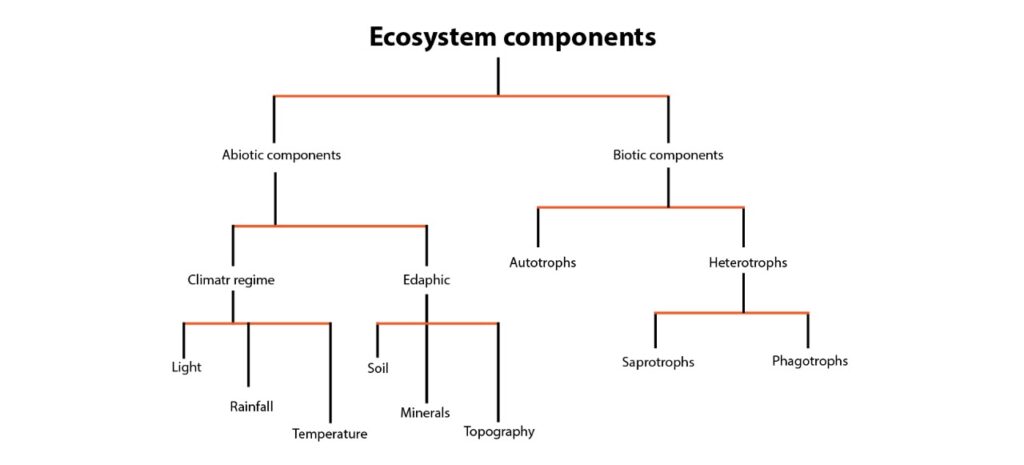
Ecosystem Definition Structure Factors Types Functions Ecosystem, the complex of living organisms, their physical environment, and all their interrelationships in a particular unit of space. a brief treatment of ecosystems follows. for full treatment, see biosphere. an ecosystem can be categorized into its abiotic constituents, including minerals, climate, soil, water, sunlight, and all other. An ecosystem consists of a community of organisms together with their physical environment. ecosystems can be of different sizes and can be marine, aquatic, or terrestrial. broad categories of terrestrial ecosystems are called biomes. in ecosystems, both matter and energy are conserved. energy flows through the system—usually from light to. An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life. ecosystems contain biotic or living, parts, as well as a biotic factors, or nonliving parts. biotic factors include plants, animals, and other organisms. The ecosystem is a balance or equilibrium between living and non living factors of the ecosystem where they tend to interact with each other. all living things, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, depend on non living substances to survive and maintain the equilibrium of the natural environment. this relationship between the living.

Explain The Structure And Functioning Of An Ecosystem An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life. ecosystems contain biotic or living, parts, as well as a biotic factors, or nonliving parts. biotic factors include plants, animals, and other organisms. The ecosystem is a balance or equilibrium between living and non living factors of the ecosystem where they tend to interact with each other. all living things, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, depend on non living substances to survive and maintain the equilibrium of the natural environment. this relationship between the living. In ecology, ecosystems are classified into different types based on the region or on the basis of the environment like land or water. it can also be grouped based on the amount of energy the ecosystem consumes. classification in basic ecosystem are : 1. terrestrial ecosystem. 2. aquatic ecosystem. E. an ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system that environments and their organisms form through their interaction. [ 2]: 458 the biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. external factors such as climate, parent material which.

Comments are closed.