Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Definition Properties And Examples

Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Definition Properties And Examples What are exponential and logarithmic functions? exponential function definition: an exponential function is a mathematical function in the form y = f(x) = b x, where “x” is a variable and “b” is a constant which is called the base of the function such that b > 1. the most commonly used exponential function base is the transcendental. When evaluating a logarithmic function with a calculator, you may have noticed that the only options are log 10 log 10 or log, called the common logarithm, or ln, which is the natural logarithm. however, exponential functions and logarithm functions can be expressed in terms of any desired base b. b.

Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Thinglink College Algebra The product property of the logarithm allows us to write a product as a sum: logb(xy) = logbx logby. the quotient property of the logarithm allows us to write a quotient as a difference: logb(x y) = logbx − logby. the power property of the logarithm allows us to write exponents as coefficients: logbxn = nlogbx. 1.5.1: the relationship between logarithmic and exponential functions. we saw earlier that an exponential function is any function of the form f(x) = bx, where b> 0 and b ≠ 1. a logarithmic function is any function of the form g(x) = logb(x), where b> 0 and b ≠ 1. it is no coincidence that both forms have the same restrictions on b because. The general form of the exponential function is f(x) = abx, where a is any nonzero number, b is a positive real number not equal to 1. if b> 1,the function grows at a rate proportional to its size. if 0 <b <1, the function decays at a rate proportional to its size. let’s look at the function f(x) = 2x from our example. Logarithmic functions. a logarithm is simply an exponent that is written in a special way. for example, we know that the following exponential equation is true: \displaystyle {3}^ {2}= {9} 32 = 9. in this case, the base is \displaystyle {3} 3 and the exponent is \displaystyle {2} 2. we can write this equation in logarithm form (with identical.

Exponential And Logarithmic Expressions Youtube The general form of the exponential function is f(x) = abx, where a is any nonzero number, b is a positive real number not equal to 1. if b> 1,the function grows at a rate proportional to its size. if 0 <b <1, the function decays at a rate proportional to its size. let’s look at the function f(x) = 2x from our example. Logarithmic functions. a logarithm is simply an exponent that is written in a special way. for example, we know that the following exponential equation is true: \displaystyle {3}^ {2}= {9} 32 = 9. in this case, the base is \displaystyle {3} 3 and the exponent is \displaystyle {2} 2. we can write this equation in logarithm form (with identical. This video defines a logarithms and provides examples of how to convert between exponential equations and logarithmic equations. in order to solve equations that contain exponentials, we need logarithmic functions. logarithmic functions are the inverses of exponential functions. the properties of logarithms are used frequently to help us. Before solving some equations involving exponential and logarithmic functions, let’s review the basic properties of logarithms. if [latex]a,b,c>0,b\ne 1, [ latex] and [latex]r [ latex] is any real number, then. solve each of the following equations for [latex]x. [ latex] now we can solve the quadratic equation.
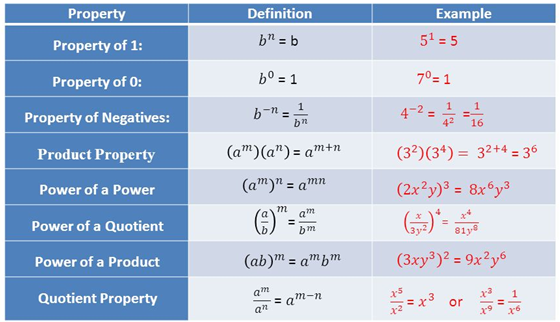
Exponential And Logarithmic Functions W3schools This video defines a logarithms and provides examples of how to convert between exponential equations and logarithmic equations. in order to solve equations that contain exponentials, we need logarithmic functions. logarithmic functions are the inverses of exponential functions. the properties of logarithms are used frequently to help us. Before solving some equations involving exponential and logarithmic functions, let’s review the basic properties of logarithms. if [latex]a,b,c>0,b\ne 1, [ latex] and [latex]r [ latex] is any real number, then. solve each of the following equations for [latex]x. [ latex] now we can solve the quadratic equation.

Comments are closed.