Forearm Amputee

One Recruited Forearm Amputee With The Evoked Tactile Sensation Of The Forearm amputations form a part of the larger umbrella of upper extremity amputations, but are the most common type, and can occur at different levels from elbow to wrist.[1] the most common cause is trauma, infection, vascular disease, and malignancy.[2] the mechanism of trauma in civilians is primarily industrial crush injuries and in the military both direct combat injury and indirect. Distal forearm amputation. whereas maintaining length remains an important consideration in the upper extremity, the underlying soft tissues in the distal forearm consist of relatively avascular structures, such as fascia and tendon, and may not always offer adequate padding for the bony stump.

Tall One Leg Amputee Lady With Forearm Crutches Amputada Youtube Transplantation of a hand or arm is an operation tailored to each person's needs, type of injury and anatomy. the operation transplants an upper extremity, usually at the level of the forearm or wrist, but sometimes above the elbow, to help restore function after the loss of an arm or hand. our expert rehabilitation team helps you learn to use. A forearm amputation is the loss of the entire hand, which may also include an associated portion of the forearm at any point from the carpus to just distal of the elbow. 1,6 forearm amputations can be partial or complete. 2 with a partial amputation, there may be a structure still connecting part of the hand or forearm to the stump. Amputations: types, causes, recovery tips, and more. The true frequency of acquired amputation of the wrist and forearm is unknown. published estimates of amputated limbs, including those of the upper extremities, vary significantly. prevalences of 350,000 1,000,000 persons with amputations and annual incidences of 20,000 30,000 new amputations have been cited.
Patient With Bilateral Proximal Forearm Level Amputation Download Amputations: types, causes, recovery tips, and more. The true frequency of acquired amputation of the wrist and forearm is unknown. published estimates of amputated limbs, including those of the upper extremities, vary significantly. prevalences of 350,000 1,000,000 persons with amputations and annual incidences of 20,000 30,000 new amputations have been cited. Amputation johns hopkins medicine amputation. Forearm amputation. most common ue amputation proximal to wrist. maintain minimum of 5cm of ulna for prosthesis fitting preserve elbow flexion. biceps tendon transfer to ulna. preservation of length for maximal prono supination. 6 8cm of distal radius ulna resection to provide muscle coverage.
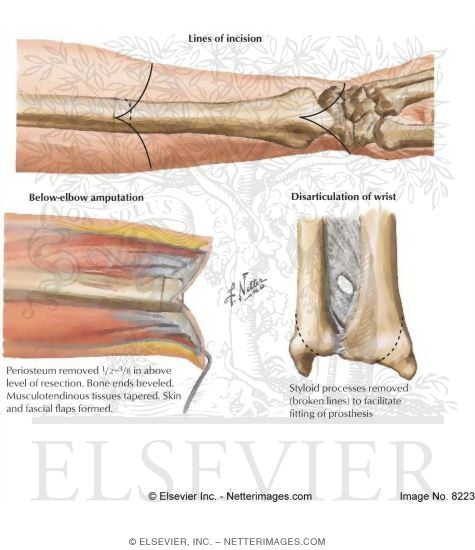
Forearm Amputation Amputation johns hopkins medicine amputation. Forearm amputation. most common ue amputation proximal to wrist. maintain minimum of 5cm of ulna for prosthesis fitting preserve elbow flexion. biceps tendon transfer to ulna. preservation of length for maximal prono supination. 6 8cm of distal radius ulna resection to provide muscle coverage.
Sak Amputee Women With Metal Forearm Crutches Flickr

Comments are closed.