Form 2 Ii Maths Ii Chapter 6 Coordinate Geometry Ii Lesson 1
Chapter 6 Coordinate Geometry Ii 1.9k views, 44 likes, 0 loves, 2 comments, 9 shares, facebook watch videos from salaama girls' secondary school: form 2 ii maths ii chapter 6 coordinate geometry ii lesson 1. A coordinate plane is a 2d plane which is formed by the intersection of two perpendicular lines known as the x axis and y axis. distance formula. it is used to find the distance between two points situated in a (x 1,y 1) and b (x 2,y 2) section formula. it is used to divide any line into two parts, in m:n ratio.

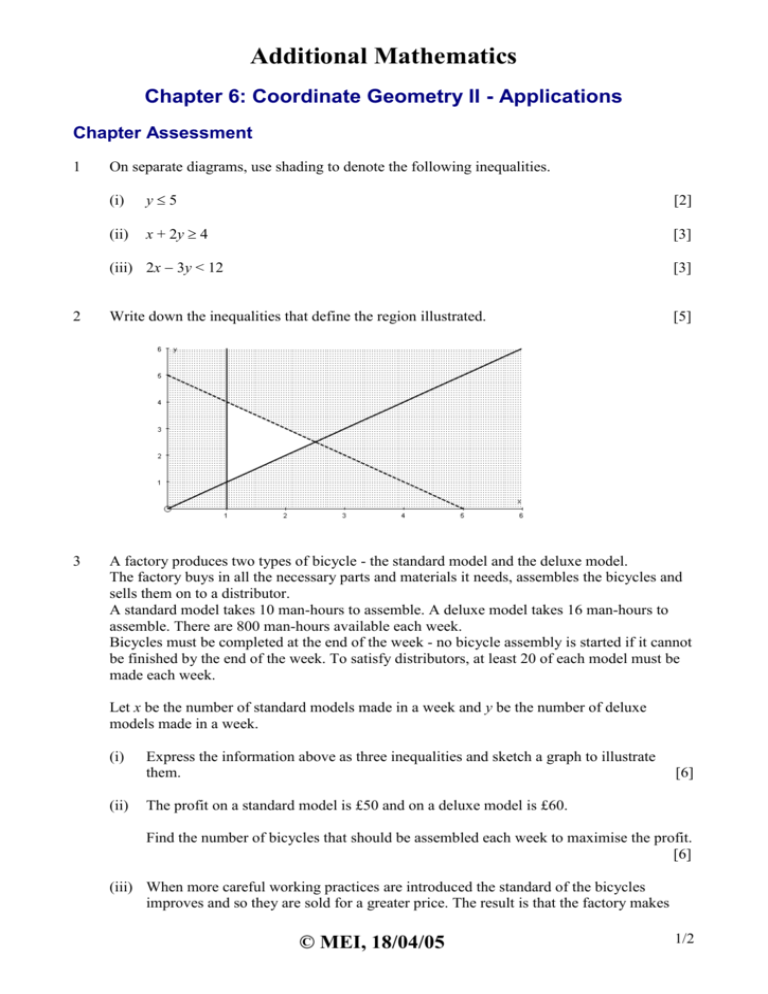
Chapter 6 Coordinate Geometry Chaptersix Coordinate Geometry 2c linear coordinate geometry in this section we revise the concepts of linear coordinate geometry. a straight line passes through the points a(−2,6) and b(4,7). find: a the distance ab b the midpoint of line segment ab c the gradient of line ab d the equation of line ab e the equation of the line parallel to ab which passes through the point. Form 2 ii maths ii chapter 6 coordinate geometry perpendicular lines ii lesson 5. 3.5k views, 80 likes, 0 loves, 10 comments, 18 shares, facebook watch videos from salaama girls' secondary school: form 2 ii maths ii chapter 6 coordinate geometry parallel lines ii lesson 4. To introduce the idea, consider the grid above. the columns of the grid are lettered a,b,c etc. the rows are numbered 1,2,3 etc from the top. we can see that the x is in box d3; that is, column d, row 3. d and 3 are called the coordinates of the box. it has two parts: the row and the column. there are many boxes in each row and many boxes in.

123328034 6 Coordinate Geometry Doc 6 Coordinate Geometry 3.5k views, 80 likes, 0 loves, 10 comments, 18 shares, facebook watch videos from salaama girls' secondary school: form 2 ii maths ii chapter 6 coordinate geometry parallel lines ii lesson 4. To introduce the idea, consider the grid above. the columns of the grid are lettered a,b,c etc. the rows are numbered 1,2,3 etc from the top. we can see that the x is in box d3; that is, column d, row 3. d and 3 are called the coordinates of the box. it has two parts: the row and the column. there are many boxes in each row and many boxes in. 2. without plotting the points, indicate the quadrant in which they will lie, if. (i) ordinate is 3 and abscissa is –5. (ii) abscissa is –3 and ordinate is – 5. (iii) ordinate is 3 and abscissa is 5. solution: (i) ordinate is 3 and abscissa is –5. here, the x coordinate is 5, and the y coordinate is 3. Example #1. q. find the midpoint of the line in fig 2. solution: use the above formula and substitute the values of x and y to work out the midpoint of the line joining a and b. put points a (2, 2) and b (5, 8) in above equation: ans: distance between two points. we want to find the length of pq where point p and q are given by the coordinates.

Comments are closed.