Fourier Transform Of Product Of Two Functions
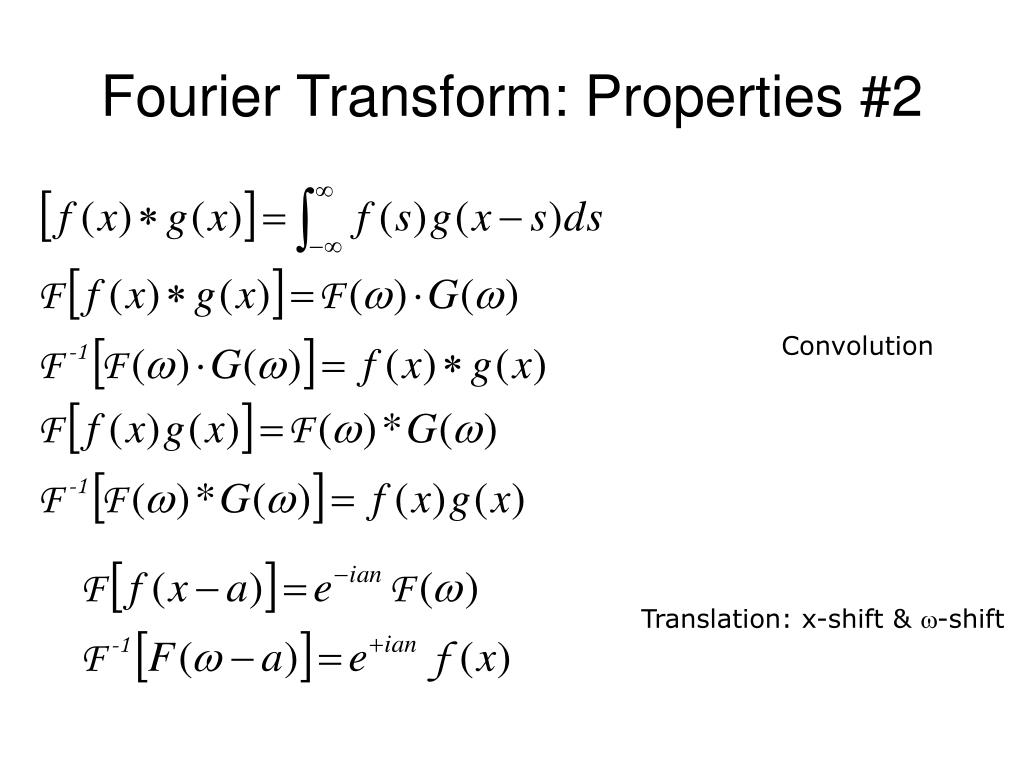
Ppt Fourier Analysis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 192350 10.4k 35 47. maybe i am reading your answer or the article incorrectly. you seem to be stating that the fourier transform of x is the convolution of fourier (f) and fourier (g). but your second link appears to state that fourier (x) = fourier (f) x fourier (g), where the transforms of f and g are multiplied, not convolved. For help clarifying this question so that it can be reopened, visit the help center. closed 14 years ago. the fourier transform of the product of two functions f (x) and g (x) is given as: f[f(x)g(x)] = ∫ ∞ −∞ f(ω′)g(ω −ω′)dω′ = convolution of f(ω′)g(ω′) f [f (x) g (x)] = ∫ − ∞ ∞ f (ω ′) g (ω − ω.
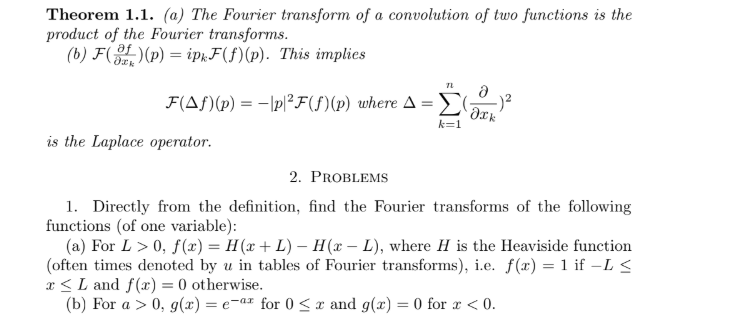
Solved Theorem 1 1 A The Fourier Transform Of A Chegg Convolution theorem. Figure 9.5.1: plots of the gaussian function f(x) = e − ax2 2 for a = 1, 2, 3. we begin by applying the definition of the fourier transform, ˆf(k) = ∫∞ − ∞f(x)eikxdx = ∫∞ − ∞e − ax2 2 ikxdx. the first step in computing this integral is to complete the square in the argument of the exponential. This result e ectively gives us two transform pairs for every transform we nd. exercise what signal x(t) has a fourier transform e jf? cu (lecture 7) ele 301: signals and systems fall 2011 12 13 37 shift theorem the shift theorem: x(t ˝) ,ej2ˇf˝x(f) proof: cu (lecture 7) ele 301: signals and systems fall 2011 12 14 37. For the fourier transform one again can de ne the convolution f g of two functions, and show that under fourier transform the convolution product becomes the usual product (fgf)(p) = fe(p)eg(p) the fourier transform takes di erentiation to multiplication by 2ˇipand one can.

Comments are closed.