Gcse Physics P2 Distance Time Graphs D T Graphs Teaching Resources
Gcse Physics P2 Distance Time Graphs D T Graphs Teaching Resources Gcse physics p2 distance time graphs (d t graphs) completely resourced lesson on distance time graphs with key content from aqa and edexcel physics. lesson begins with a review of the use of graphs to present data and relationships, highlighting key graph vocabulary and trends. speed, distance and time is briefly recapped with the equation. The lesson includes an background context on distance time graphs, how to draw and infer from these graphs and how to calculate speed from dt graphs, worksheets and scaffolds to support, and several other activities for students to complete throughout the lesson. the lesson follows aqa gcse physics specification (p2) with gcse exam style.
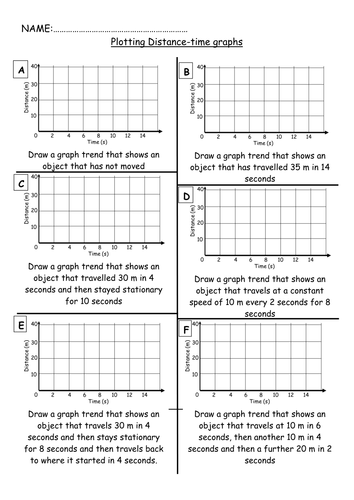
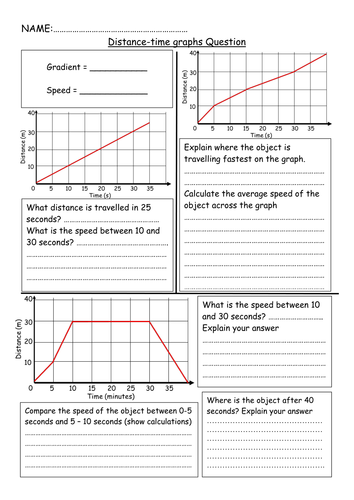
Gcse Physics P2 Distance Time Graphs D T Graphs Teaching Resources Calculate the speed of the train. step 1: draw a large gradient triangle on the graph. the image below shows a large gradient triangle drawn with dashed lines. and are labelled, using the units as stated on each axis. step 2: convert units for distance and time into standard units. the distance travelled = 8 km = 8000 m. Differentiated objectives: developing learners will be able to interpret information from distance time graphs. secure learners will be able to identify the scale used on distance time graphs. excelling learners will be able to plot information onto a distance time graph. main: walkthrough examples followed by practice questions on worksheets. Gcse; aqa; describing motion aqa distance time graphs. the movement of objects can be described using motion graphs and numerical values. these are both used to help in the design of faster and. Visual maths resources ltd is a company registered in england and wales with a company no. 10607102 with a registered office at 71 75 shelton street, wc2h 9jq. cazoom maths is the trading name of visual maths resources ltd. this resource has an image of a distance time graph and has the different types of line and gradients.

Distance Time Graph Gcse Teaching Resources Gcse; aqa; describing motion aqa distance time graphs. the movement of objects can be described using motion graphs and numerical values. these are both used to help in the design of faster and. Visual maths resources ltd is a company registered in england and wales with a company no. 10607102 with a registered office at 71 75 shelton street, wc2h 9jq. cazoom maths is the trading name of visual maths resources ltd. this resource has an image of a distance time graph and has the different types of line and gradients. Aqa gcse physics forces and motion distance time graphs. distance time graphs help us visualise how far an object travels in a given period of time. below is an example of a distance time graph. the time in seconds (s) is always on the x axis and the distance in metres (m) is always on the y axis. If the line on a distance time graph curves the other way (when the gradient becomes flatter), then the object will be decelerating, as each second the distance travelled is less than the previous second. as before, a flat line (gradient equals zero) means that the object is stationary (at rest). gcse physics keywords: constant speed.

Gcse Maths Physics Distance Time Graphs Learnly Aqa gcse physics forces and motion distance time graphs. distance time graphs help us visualise how far an object travels in a given period of time. below is an example of a distance time graph. the time in seconds (s) is always on the x axis and the distance in metres (m) is always on the y axis. If the line on a distance time graph curves the other way (when the gradient becomes flatter), then the object will be decelerating, as each second the distance travelled is less than the previous second. as before, a flat line (gradient equals zero) means that the object is stationary (at rest). gcse physics keywords: constant speed.
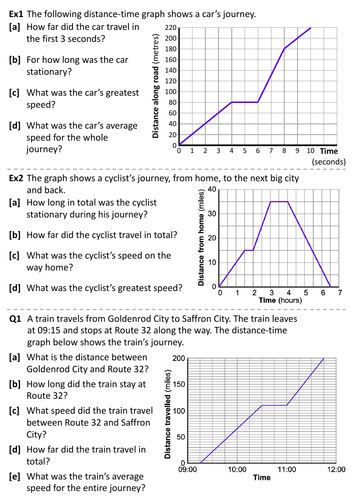
Distance Time Graphs Teaching Resources

Comments are closed.