Grade 10 The Remainder Theorem Find The Remainder If A Polynomial Is

Polynomial Remainder Theorem Proof And Solved Examples Remainder theorem of polynomial | examples. F (c) = r. so we get this: the remainder theorem: when we divide a polynomial f (x) by x−c the remainder is f (c) so to find the remainder after dividing by x c we don't need to do any division: just calculate f (c) let us see that in practice: example: the remainder after 2x 2 −5x−1 is divided by x−3.
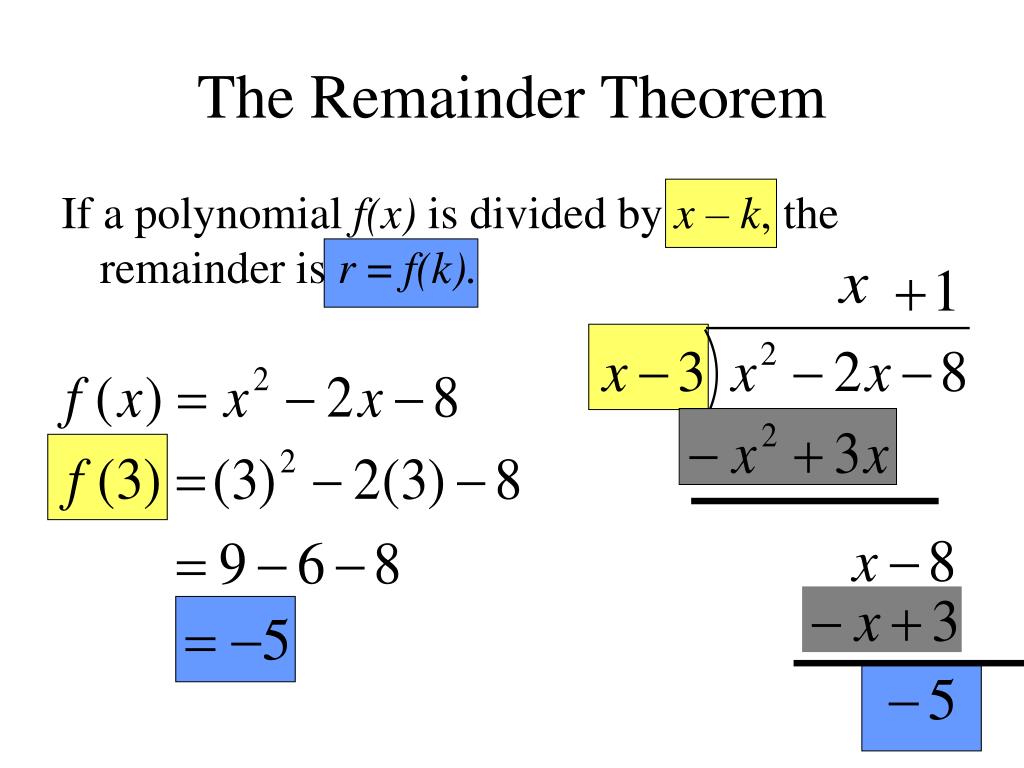
How To Find Remainder Of Polynomials The remainder theorem in class 9 is used to find the remainder when a polynomial p(x) is divided by (ax b). the remainder theorem is further extended to prove the factor theorem where we can determine whether (ax b) is a factor of p(x) or not. if the remainder is 0, then (ax b) is a factor of a polynomial p(x), otherwise, it is not. Remainder theorem and factor theorem. a special case of the remainder theorem called the factor theorem is used when we need to find the factors of a given polynomial based on its zeros. let us consider the polynomial f(x) = x 2 – 6x 8 and find the remainder when x = 2 and x = 1. using the remainder theorem, we get. The remainder theorem states that the remainder when p(x) is divided by a linear polynomial of the form $(x − a)$ is given by p(a). the factor theorem states that $(x − a)$ is a factor of p(x) if and only if f(a) $= 0$. remainder theorem is used to find the remainder of the polynomial division only when the divisor polynomial is linear. If p(x) is divided by the linear polynomial x – a, then the remainder is p (a). this is the remainder theorem. it helps us to find the remainder without actual division. let’s take a look at the application of the remainder theorem with the help of an example. example 1: find the remainder when t 3 – 2t 2 t 1 is divided by t – 1.

Quick And Easy Way To Find The Remainder Of A Polynomial Use The The remainder theorem states that the remainder when p(x) is divided by a linear polynomial of the form $(x − a)$ is given by p(a). the factor theorem states that $(x − a)$ is a factor of p(x) if and only if f(a) $= 0$. remainder theorem is used to find the remainder of the polynomial division only when the divisor polynomial is linear. If p(x) is divided by the linear polynomial x – a, then the remainder is p (a). this is the remainder theorem. it helps us to find the remainder without actual division. let’s take a look at the application of the remainder theorem with the help of an example. example 1: find the remainder when t 3 – 2t 2 t 1 is divided by t – 1. Option 3: use remainder theorem. the best method to find the remainder of this problem is the remainder theorem. the number that will be substituted in the polynomial is [latex]{ – 1}[ latex]. the value of [latex]{ – 1}[ latex], when raised to some power, will simply alternate either to positive [latex]1[ latex] or negative [latex]1[ latex]. The point of the remainder theorem is that there is a simpler, quicker way to evaluate a polynomial p(x) at a given value of x, and this simpler way is to not evaluate p(x) at all, but to instead do the synthetic division at that same value of x. the last number in the synthetic division result is the value you're wanting, being the evaluated value of the polyomial.

Finding The Remainder Of A Polynomial Option 3: use remainder theorem. the best method to find the remainder of this problem is the remainder theorem. the number that will be substituted in the polynomial is [latex]{ – 1}[ latex]. the value of [latex]{ – 1}[ latex], when raised to some power, will simply alternate either to positive [latex]1[ latex] or negative [latex]1[ latex]. The point of the remainder theorem is that there is a simpler, quicker way to evaluate a polynomial p(x) at a given value of x, and this simpler way is to not evaluate p(x) at all, but to instead do the synthetic division at that same value of x. the last number in the synthetic division result is the value you're wanting, being the evaluated value of the polyomial.

The Remainder Theorem Grade 10 Module Answers And Explanations Youtube

Comments are closed.