Handout On The Unit Circle And Basic Trigonometric Identities
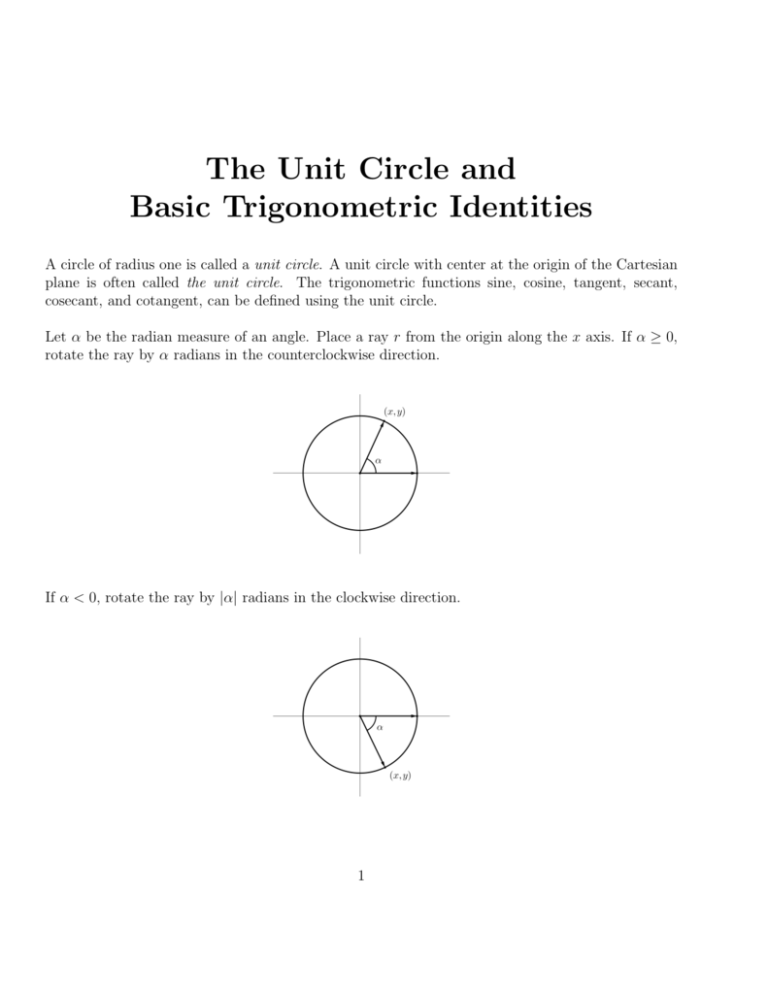
Handout On The Unit Circle And Basic Trigonometric Identities Unit circle quick lesson printable pdf chart. We then obtain the following trigonometric identity: cos 2 ( θ ) sin 2 ( θ ) = 1. the identity cos 2 ( θ ) sin 2 ( θ ) = 1 applies to an angle drawn in any circle of radius r, not just the unit circle. a short justification is shown below. we begin with the general equation of a circle of radius r: 2. y.
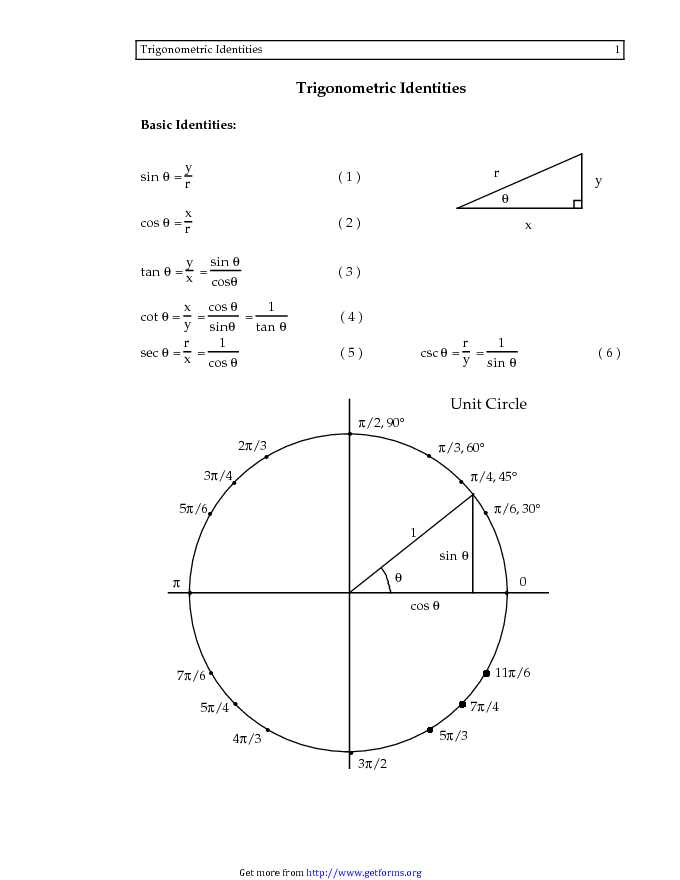
Trigonometric Identities Unit Circle Download Mathematics Chart For To define our trigonometric functions, we begin by drawing a unit circle, a circle centered at the origin with radius 1, as shown in figure 2. the angle (in radians) that t t intercepts forms an arc of length s. s. using the formula s = r t, s = r t, and knowing that r = 1, r = 1, we see that for a unit circle, s = t. s = t. 33provided by the academic center for excellence 3 the unit circle updated october 2019 . the unit circle by triangles . another method for solving trigonometric functions is the triangle method. to do this, the unit circle is broken up into more common triangles: the 45°−45°−90° and 30°−60°−90° triangles. some examples of. Determine exact values of trig ratios for common radian measures. the unit circle is a circle of radius one, centered at the origin, that summarizes all the 30 60 90 and 45 45 90 triangle relationships that exist. when memorized, it is extremely useful for evaluating expressions like cos(135∘) cos ( 135 ∘) or sin(−5π 3) sin ( − 5 π 3). 3.5: trigonometric functionsreference evans 6.1 consider a right angled triangle with angle θ and side lengths x, y and h as shown: θ. x y h. the trigonometric functions sine, cosine and tangent of θ are defined as: sinθ = opposite hypotenuse = y h , cosθ = adjacent hypotenuse = x h tanθ = opposite adjacent = y x = sinθ cosθ. 71.

Comments are closed.