History Of Mathematics Project Pythagorean Theorem
History Of Mathematics Project Pythagorean Theorem The pythagorean theorem is a fundamental result in euclidean geometry that relates the side lengths of a right triangle through the simple relationship a ² b ² = c ². the relationship was known to the ancient scholars and builders of babylon, egypt, china and india. while pythagoras lived and wrote from 569–475 bce, the result that now. Pythagorean triple. pythagorean theorem, the well known geometric theorem that the sum of the squares on the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square on the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle)—or, in familiar algebraic notation, a2 b2 = c2. although the theorem has long been associated with greek mathematician philosopher.

History Of Mathematics Project Pythagorean Theorem History of mathematics project virtual exhibition. pythagorean theorem. the pythagorean theorem relates the side lengths of a right triangle and was known to the ancient scholars and builders of babylonia, egypt, greece, china and india. The pythagorean school's emphasis on the interplay between mathematics, music, and philosophy left a lasting impact on western intellectual history. development of the pythagorean theorem in ancient greece. the pythagorean theorem, attributed to the ancient greek mathematician pythagoras, is a fundamental concept in geometry and mathematics. Pythagorean theorem. the sum of the areas of the two squares on the legs ( a and b) equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse ( c ). in mathematics, the pythagorean theorem or pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. The pythagorean theorem states that a² b² = c². this is used when we are given a triangle in which we only know the length of two of the three sides. c is the longest side of the angle known as the hypotenuse. if a is the adjacent angle then b is the opposite side. if b is the adjacent angle then a is the opposite side.
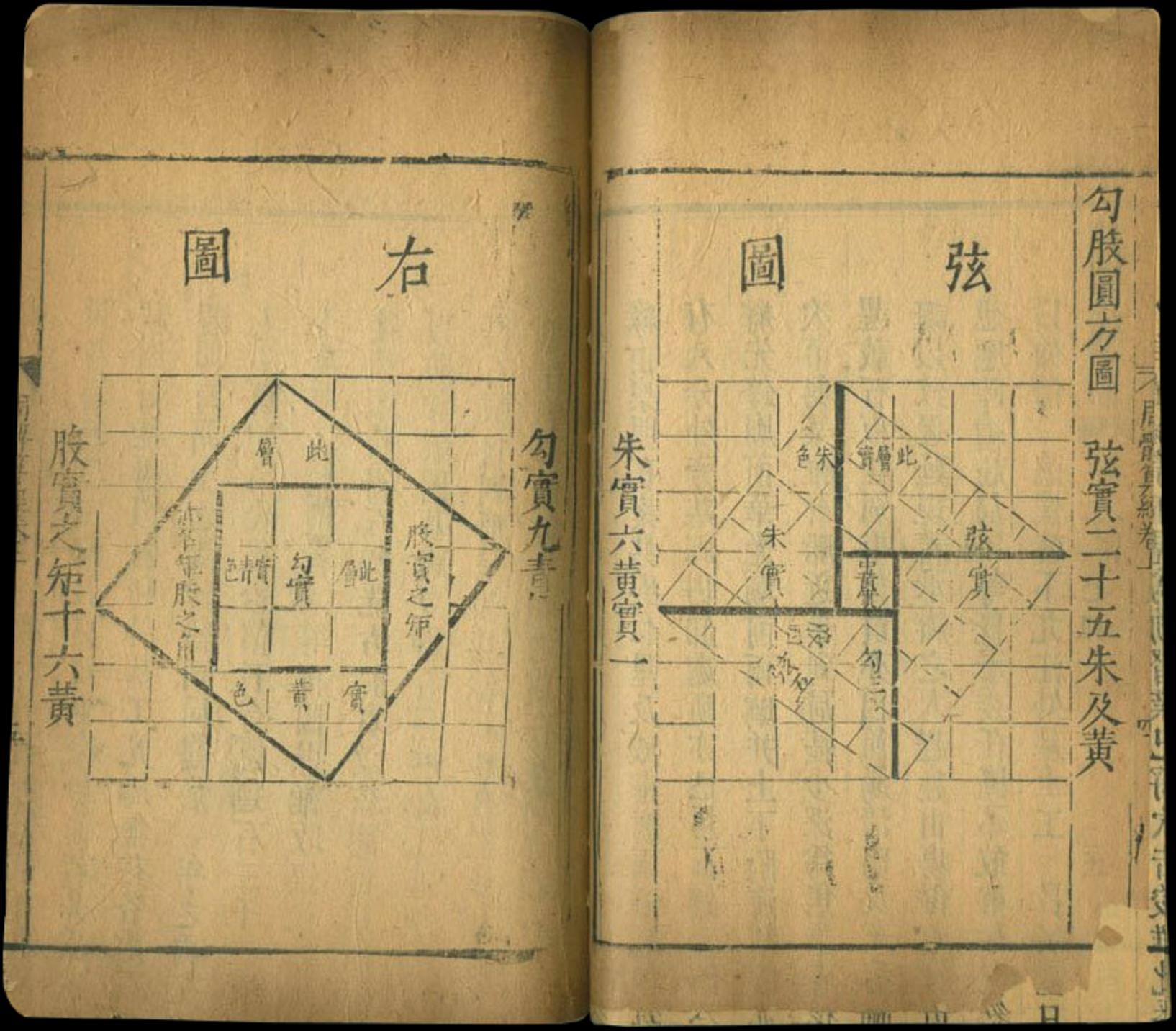
History Of Mathematics Project Pythagorean Theorem Pythagorean theorem. the sum of the areas of the two squares on the legs ( a and b) equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse ( c ). in mathematics, the pythagorean theorem or pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. The pythagorean theorem states that a² b² = c². this is used when we are given a triangle in which we only know the length of two of the three sides. c is the longest side of the angle known as the hypotenuse. if a is the adjacent angle then b is the opposite side. if b is the adjacent angle then a is the opposite side. The pythagorean theorem, also known as pythagoras' theorem, or the hypotenuse theorem, is largely credited to the greek mathematician, pythagoras of samos (570 495 b.c.). though many knew of this relationship of right triangles and hypotenuses long before pythagoras, it is named after him because he wrote the first known proof which spread. The second leg is 7 meters longer than the first. remember to isolate the length of the hypotenuse on one side of the equation representing the pythagorean theorem. that is, \ (x^2 (x 7)^2 = 13^2\). note that the legs go on one side of the equation, the hypotenuse on the other. square and simplify.

Comments are closed.