How Do You Calculate Consumer Surplus

How To Calculate Consumer Surplus 12 Steps With Pictures Consumer surplus is an economic measurement to calculate the benefit (i.e., surplus) of what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus its market price. the consumer surplus formula is based on an economic theory of marginal utility. the theory explains that spending behavior varies with the preferences of individuals. That is, the consumer surplus formula is the following: consumer surplus = maximum price willing to pay actual market price. if you would like to estimate the consumer surplus for a whole economy, you need to use a slightly extended version of the formula, which you can reach in the related information of this consumer surplus calculator.

How To Calculate Consumer Surplus 12 Steps With Pictures Learn the definition and formula of consumer surplus, the excess cost that consumers are willing to pay for a product or service in comparison to the actual market price. see examples of how to calculate consumer surplus with a demand supply graph and price discrimination. Consumer surplus, also known as buyer’s surplus, is the economic measure of a customer’s excess benefit. it is calculated by analyzing the difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay for a product and the actual price they pay, also known as the equilibrium price. a surplus occurs when the consumer’s willingness to pay for a. Learn how to calculate consumer surplus using a graph or a formula. consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum price willing to pay and the actual price for a product. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above.
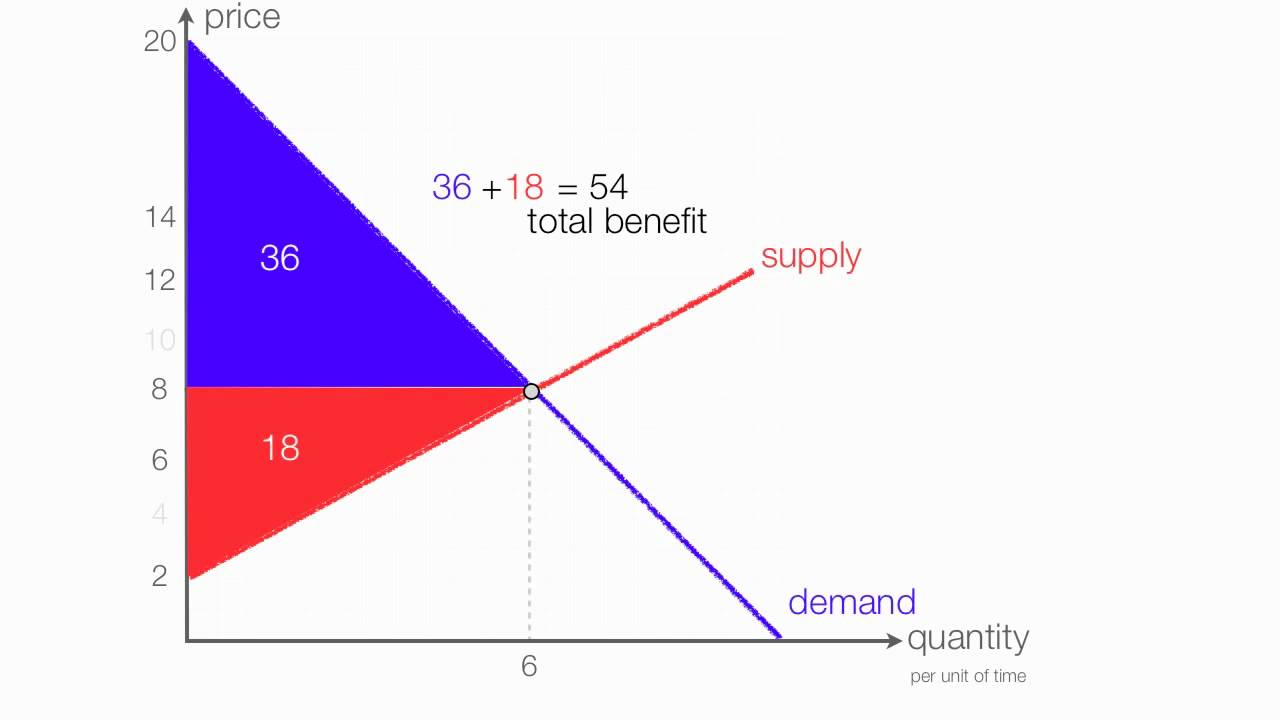
How To Calculate Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus With A Price Learn how to calculate consumer surplus using a graph or a formula. consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum price willing to pay and the actual price for a product. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Consumer surplus is the benefit or good feeling of getting a good deal. for example, let’s say that you bought an airline ticket for a flight to disney world during school vacation week for $100. Numerical example 1. suppose the demand for a commodity is given by. p = d (q) = 0.8q 150. and the supply for the same commodity is given by. p = s (q) = 5.2q. , where q is the quantity of the commodity and p is the price in usd. consumer surplus is calculated as: step 1: calculate equilibrium quantity.

How To Calculate Consumer Surplus 12 Steps With Pictures Consumer surplus is the benefit or good feeling of getting a good deal. for example, let’s say that you bought an airline ticket for a flight to disney world during school vacation week for $100. Numerical example 1. suppose the demand for a commodity is given by. p = d (q) = 0.8q 150. and the supply for the same commodity is given by. p = s (q) = 5.2q. , where q is the quantity of the commodity and p is the price in usd. consumer surplus is calculated as: step 1: calculate equilibrium quantity.

Comments are closed.