How Does The Equation Wl 2 8 Get In A Simply Supported
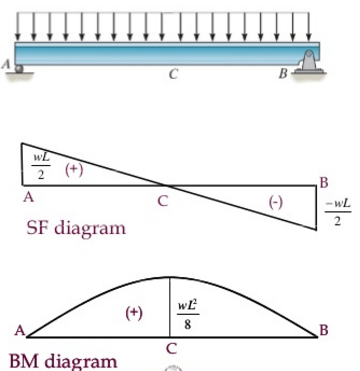
Bending Moment And Fixed Moment Calculations Civil 40 Off Equivalent point load = wl. end reaction r 1 =r 2 =wl 2 . shear load v max =wl 2 . bending moment m max =[latex]\frac{(wl)^2}{8}[ latex] figure 9 1: the end reactions, maximum values of the shear load, and the bending moment in a simple beam supported by a pinned joint and a roller. sign conventions. Calculation example: the maximum bending moment on a simply supported beam loaded with a uniformly distributed load is given by the formula m = wl^2 8, where m is the maximum bending moment, w is the uniformly distributed load, and l is the length of the beam.
What Is The Role Of The Equation Wl 2 8 In A Simply Supported Be Simply supported beam: moment and shear hand calculation. Simply supported beam – moment & shear force. Unit of measurement: newton metres (n m) or pound foot or foot pound (ft.lb) bending moment is directly proportional to tensile and compressive stresses. increase in tensile and compressive stresses results in the increase in the bending moment. these stresses also depend on the second moment of area of the cross section of the element. Beam deflection tables.
Solved Loading Deflection Maximum Bending Moment Reaction 49 Off Unit of measurement: newton metres (n m) or pound foot or foot pound (ft.lb) bending moment is directly proportional to tensile and compressive stresses. increase in tensile and compressive stresses results in the increase in the bending moment. these stresses also depend on the second moment of area of the cross section of the element. Beam deflection tables. It also calculates support reactions and maximum bending moment (max b.m.) value as well as its distance from support a. in this case the maximum value of bending moment will occur at the midspan and will be equal to wl 2 8. the typical diagrams for shear force and bending moment are also shown here. Example 2. find the ultimate deflection of the simply supported beam, under uniform distributed load, that is depicted in the schematic. its cross section can be either a or b, shown in the figure below. both cross sections feature the same dimensions, but they differ in orientation of the axis of bending (neutral axis shown with dashed red line).

Solved In A Simply Supported Beam Subjected To Uniformly Distributed It also calculates support reactions and maximum bending moment (max b.m.) value as well as its distance from support a. in this case the maximum value of bending moment will occur at the midspan and will be equal to wl 2 8. the typical diagrams for shear force and bending moment are also shown here. Example 2. find the ultimate deflection of the simply supported beam, under uniform distributed load, that is depicted in the schematic. its cross section can be either a or b, shown in the figure below. both cross sections feature the same dimensions, but they differ in orientation of the axis of bending (neutral axis shown with dashed red line).

Solved In A Simply Supported Beam Subjected To Uniformly Distributed

Comments are closed.