How To Prevent Surgical Site Infection
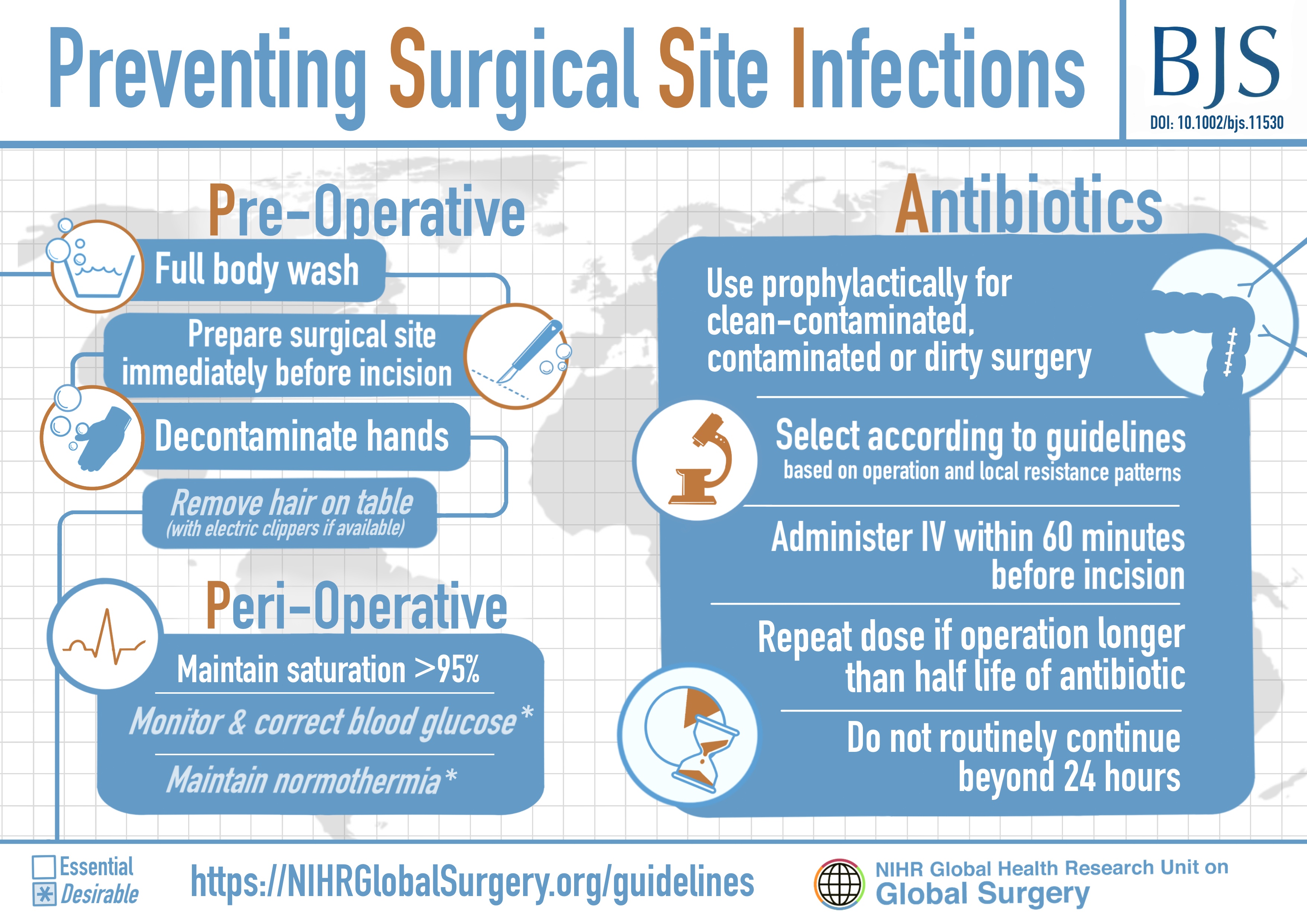
Global Guidelines For Prevention Of Surgical Site Infection Published Infection caused by microorganisms from an outside source following surgery is less common. most surgical site infections are preventable. measures can be taken in the pre , intra and postoperative phases of care to reduce the risk of infection. surgical site infections can have a significant effect on quality of life for the patient. Guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection (1999) organ transplantation. sources print share. national center for emerging and zoonotic infectious diseases (ncezid) occupationally acquired infections and healthcare workers. updated recommendations on chlorhexidine impregnated (c i) dressings.

5 Strategies To Reduce Surgical Site Infection Infographic Medline Learn about the types, causes, risk factors, and prevention of surgical site infections (ssis), which occur on the part of the body where the surgery took place. find out how to recognize the signs and symptoms of ssis and how they are treated. Key points. a surgical site infection (ssi) is an infection in the part of the body where a surgery took place. ssis can generally be treated with antibiotics but may require additional medical care. there are ways to reduce your risk of contracting an ssi. Surgical site infections (ssis) are responsible for about 20% of all healthcare associated infections (hais) and at least 5% of patients undergoing a surgical procedure develop a surgical site infection [,, ]. the incidence of ssis is 2–5% in patients undergoing inpatient surgery; however, the number of ssis is likely to be underestimated. Cdc and healthcare infection control practices advisory committee guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection, provides evidence based strategies for ssi prevention 9. most recently, the strategies to prevent surgical site infections in acute care hospitals: 2022 update was published providing acute care hospitals with.

How To Prevent Surgical Site Infection Youtube Surgical site infections (ssis) are responsible for about 20% of all healthcare associated infections (hais) and at least 5% of patients undergoing a surgical procedure develop a surgical site infection [,, ]. the incidence of ssis is 2–5% in patients undergoing inpatient surgery; however, the number of ssis is likely to be underestimated. Cdc and healthcare infection control practices advisory committee guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection, provides evidence based strategies for ssi prevention 9. most recently, the strategies to prevent surgical site infections in acute care hospitals: 2022 update was published providing acute care hospitals with. Ipc training resources. surgical site infections are caused by bacteria that get in through incisions made during surgery. they threaten the lives of millions of patients each year and contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance. in low and middle income countries, 11% of patients who undergo surgery are infected in the process. Surgical site infections (ssis) are infections of the incision or organ or space that occur after surgery. 1 surgical patients initially seen with more complex comorbidities 2 and the emergence of antimicrobial resistant pathogens increase the cost and challenge of treating ssis. 3 5 the prevention of ssi is increasingly important as the number.

Infection Prevention And Control Ipc training resources. surgical site infections are caused by bacteria that get in through incisions made during surgery. they threaten the lives of millions of patients each year and contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance. in low and middle income countries, 11% of patients who undergo surgery are infected in the process. Surgical site infections (ssis) are infections of the incision or organ or space that occur after surgery. 1 surgical patients initially seen with more complex comorbidities 2 and the emergence of antimicrobial resistant pathogens increase the cost and challenge of treating ssis. 3 5 the prevention of ssi is increasingly important as the number.

Surgical Site Infections

Comments are closed.