How To Test The Axillary Nerve From Brachial Plexus C5 C6

How To Test The Axillary Nerve From Brachial Plexus C5 C6 Youtube Johngibbonsbodymaster.co.ukjohn gibbons is a registered osteopath, lecturer and multi published author and is demonstrating how to test the axilla. Posterior branch of axillary nerve; sensory . superior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve. lateral shoulder sensation; origin: brachial plexus . middle trunk posterior divison posterior cord ; c5 and c6 fibers; course: arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. anterior to the subscapularis muscle and posterior to the axillary artery.

Axillary Nerve Brachial Plexus Anatomical course. the axillary nerve is formed within the axilla area of the upper limb. it is a direct continuation of the posterior cord from the brachial plexus – and therefore contains fibres from the c5 and c6 nerve roots. in the axilla, the axillary nerve is located posterior to the axillary artery and anterior to the subscapularis muscle. Axillary nerve: anatomy, course, function. Brachial plexus: anatomy, branches and mnemonics. For those who. comprehensive anatomy of brachial plexus from the 5 contributing roots to the 5 terminal branches along with regional and sensory distributions to explain brachial plexus injuries and their clinical presentation. the origin, course, and function of the axillary, radial, musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar nerves through the upper.
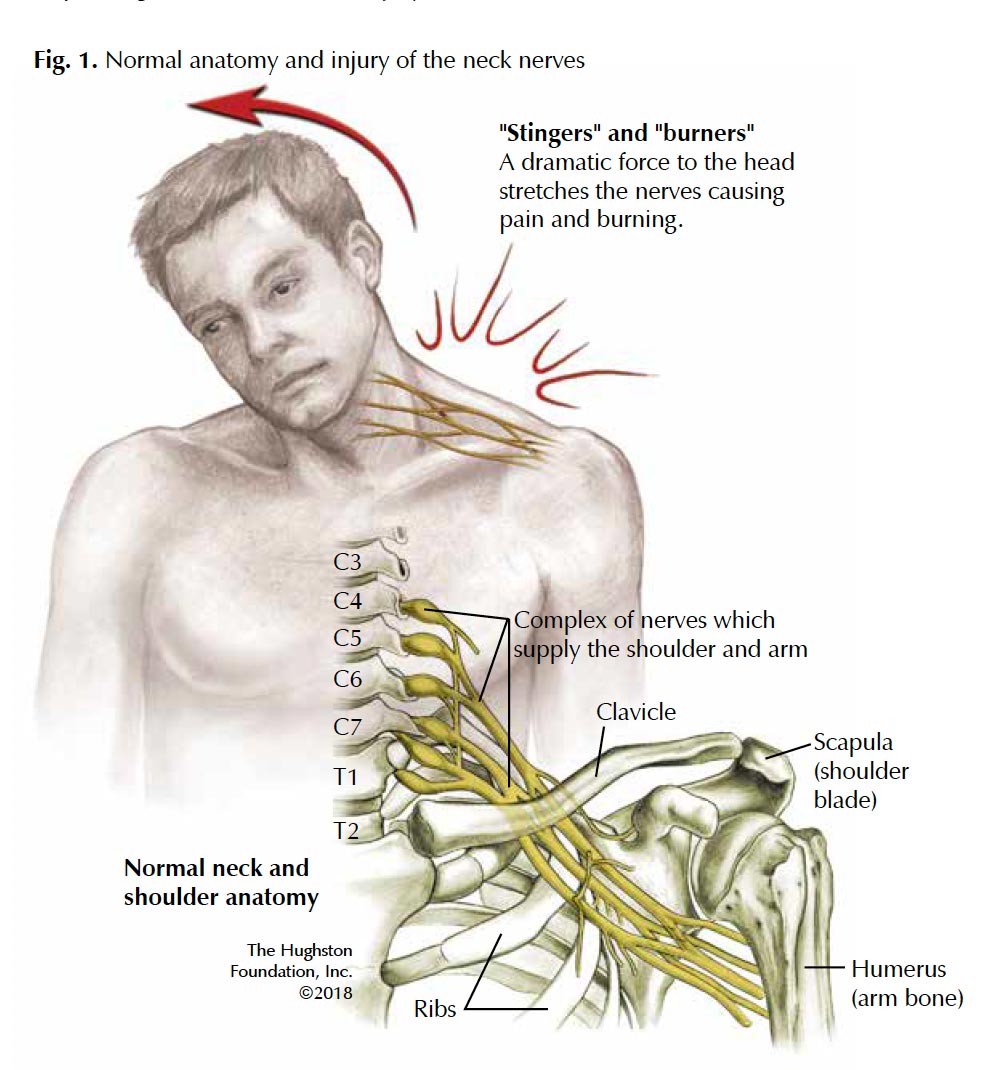
Brachial Plexus Traumatic Nerve Injuries Hughston Clinic Brachial plexus: anatomy, branches and mnemonics. For those who. comprehensive anatomy of brachial plexus from the 5 contributing roots to the 5 terminal branches along with regional and sensory distributions to explain brachial plexus injuries and their clinical presentation. the origin, course, and function of the axillary, radial, musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar nerves through the upper. Axillary nerve has been shown to run 3 5 cm from the acromion in 20% of patients. damage to nerve with a muscle split here will denervate the anterior deltoid. terminates in small cutaneous branches for the anterior anterolateral skin. posterior branch. supplies the teres minor and posterior deltoid muscles. Ulnar nerve (c8,t1) radial nerve (c5,6,7,8,t1) axillary nerve (c5,6) *note that all branches from the medial cord carry c8,t1 fibers, and that the higher spinal segments in the brachial plexus (c5 c6) tend to innervate muscles more proximal on the upper extremity whereas the lower segments (c8,t1) tend to innervate more distal muscles such as.
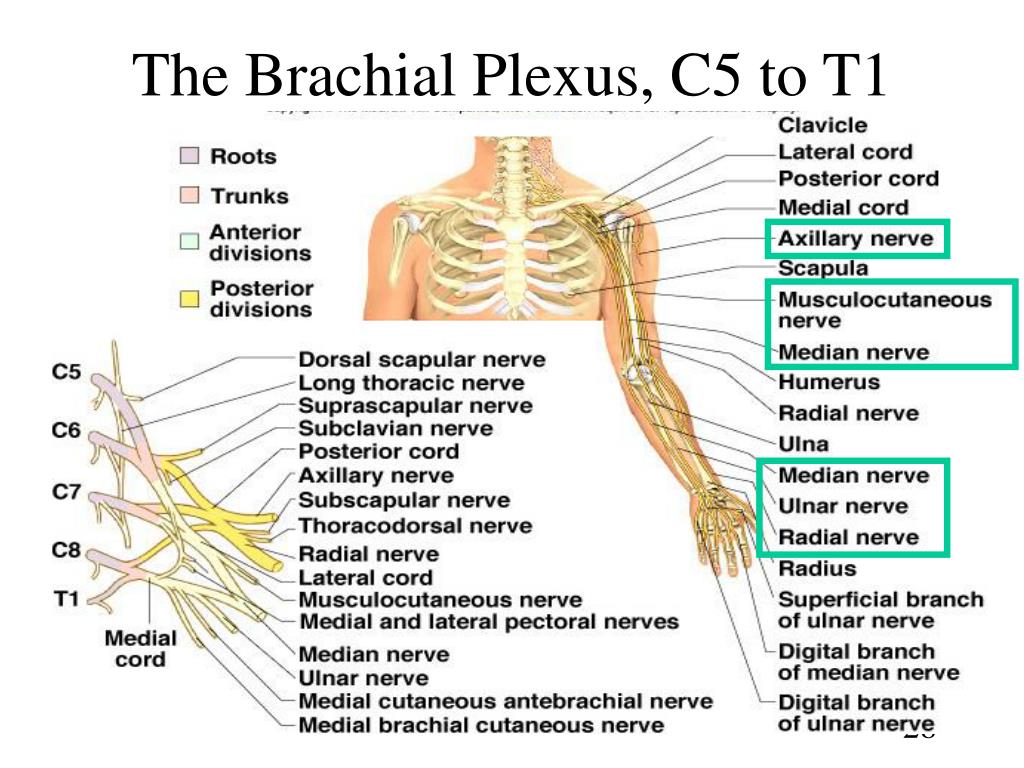
Brachial Plexus C5 C6 Axillary nerve has been shown to run 3 5 cm from the acromion in 20% of patients. damage to nerve with a muscle split here will denervate the anterior deltoid. terminates in small cutaneous branches for the anterior anterolateral skin. posterior branch. supplies the teres minor and posterior deltoid muscles. Ulnar nerve (c8,t1) radial nerve (c5,6,7,8,t1) axillary nerve (c5,6) *note that all branches from the medial cord carry c8,t1 fibers, and that the higher spinal segments in the brachial plexus (c5 c6) tend to innervate muscles more proximal on the upper extremity whereas the lower segments (c8,t1) tend to innervate more distal muscles such as.

Comments are closed.