Illustration Of Back Muscles By Science Source In 2021 Anatomy
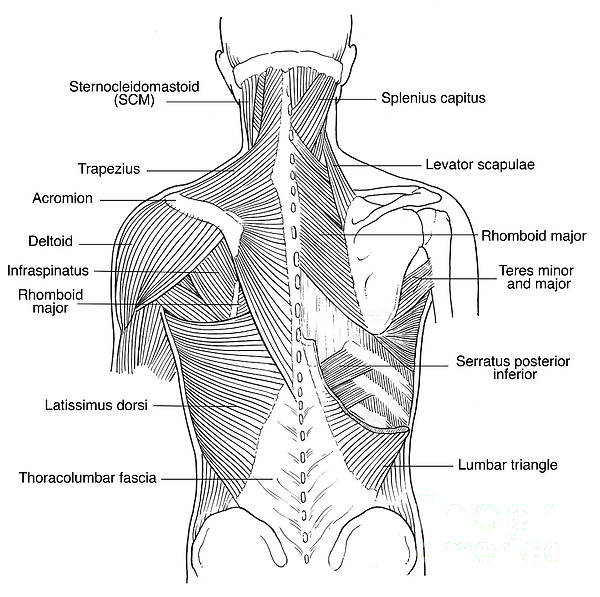
Illustration Of Back Muscles By Science Source The back is a key topographical region of the body, with crucial importance for posture, locomotion, and upper and lower limb movements. [1] the spine, located in the midline, divides the body into unequal anterior and posterior segments. in the posterior segment, the body area between the neck and gluteal regions is defined as the back region. The back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; extrinsic and intrinsic. the back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbs.

Illustration Of Back Muscles Photograph By Science Source The muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. they provide movements of the spine, stability to the trunk, as well as the coordination between the movements of the limbs and trunk. the extrinsic (superficial) back muscles, which lie most superficially on the back. This human anatomy module is composed of diagrams, illustrations and 3d views of the back, cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal areas as well as the various vertebrae. it contains the osteology, arthrology and myology of the spine and back. it is particularly interesting for physiotherapists, osteopaths, rheumatologists, neurosurgeons. The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.

Back Muscles Artwork High Res Vector Graphic Getty Images The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine. The deep muscles of the back are well developed, and collectively extend from the sacrum to the base of the skull. they are associated with the movements of the vertebral column, and the control of posture. the muscles themselves are covered by deep fascia, which plays a key role in their organisation. The deep muscles of the back are well developed, and collectively extend from the sacrum to the base of the skull. they are associated with the movements of the vertebral column, and the control of posture. the muscles themselves are covered by deep fascia, which plays a key role in their organisation. anatomically, the deep back muscles can be.

Comments are closed.