Improper Integral 1 X 2 X From Infinity To 2 Improper Integral S

Improper Integral Of 1 X 2 From 2 To Infinity Youtube Free improper integral calculator solve improper integrals with all the steps. type in any integral to get the solution, free steps and graph. In this section we will look at integrals with infinite intervals of integration and integrals with discontinuous integrands in this section. collectively, they are called improper integrals and as we will see they may or may not have a finite (i.e. not infinite) value. determining if they have finite values will, in fact, be one of the major.

Evaluate Improper Integral 1 X 2 X Dx Over 1 Infinityођ An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called an improper integral. two examples are. ∫∞ 0 dx 1 x2 and ∫1 0dx x. the first has an infinite domain of integration and the integrand of the second tends to ∞ as x approaches the left end of the domain of integration. Improper integrals are definite integrals that cover an unbounded area. one type of improper integrals are integrals where at least one of the endpoints is extended to infinity. for example, ∫ 1 ∞ 1 x 2 d x is an improper integral. it can be viewed as the limit lim b → ∞ ∫ 1 b 1 x 2 d x . another type of improper integrals are. Step 1: write the improper integral along with the upper and lower limits. ∫∞ 1 1 x2 dx ∫ 1 ∞ 1 x 2 d x. step 2: take the general equation to solve the above expression. step 3: now write the given expression according to the above equation. step 4: now integrate the above expression. Figure 7.7.1: to integrate a function over an infinite interval, we consider the limit of the integral as the upper limit increases without bound. definition: improper integral. let f(x) be continuous over an interval of the form [a, ∞). then ∫ ∞ a f(x)dx = lim t → ∞ ∫t af(x)dx, provided this limit exists.

Improper Integral Of 1 1 X 2 From Infinity To Infinityо Step 1: write the improper integral along with the upper and lower limits. ∫∞ 1 1 x2 dx ∫ 1 ∞ 1 x 2 d x. step 2: take the general equation to solve the above expression. step 3: now write the given expression according to the above equation. step 4: now integrate the above expression. Figure 7.7.1: to integrate a function over an infinite interval, we consider the limit of the integral as the upper limit increases without bound. definition: improper integral. let f(x) be continuous over an interval of the form [a, ∞). then ∫ ∞ a f(x)dx = lim t → ∞ ∫t af(x)dx, provided this limit exists. This solution was automatically generated by our smart calculator: solve the integral by applying the formula $\displaystyle\int\frac {x'} {x^2 a^2}dx=\frac {1} {a}\arctan\left (\frac {x} {a}\right)$. add the initial limits of integration. replace the integral's limit by a finite value. evaluate the definite integral. Take the integral from 1 to 1 of (1 x^2)*dx as an example, as the function is discontinuous at x=0. or 2. one of the integration limits contains positive or negative infinity. an example with both conditions would be the integral from 0 to infinity of 1 (x^2) *dx.
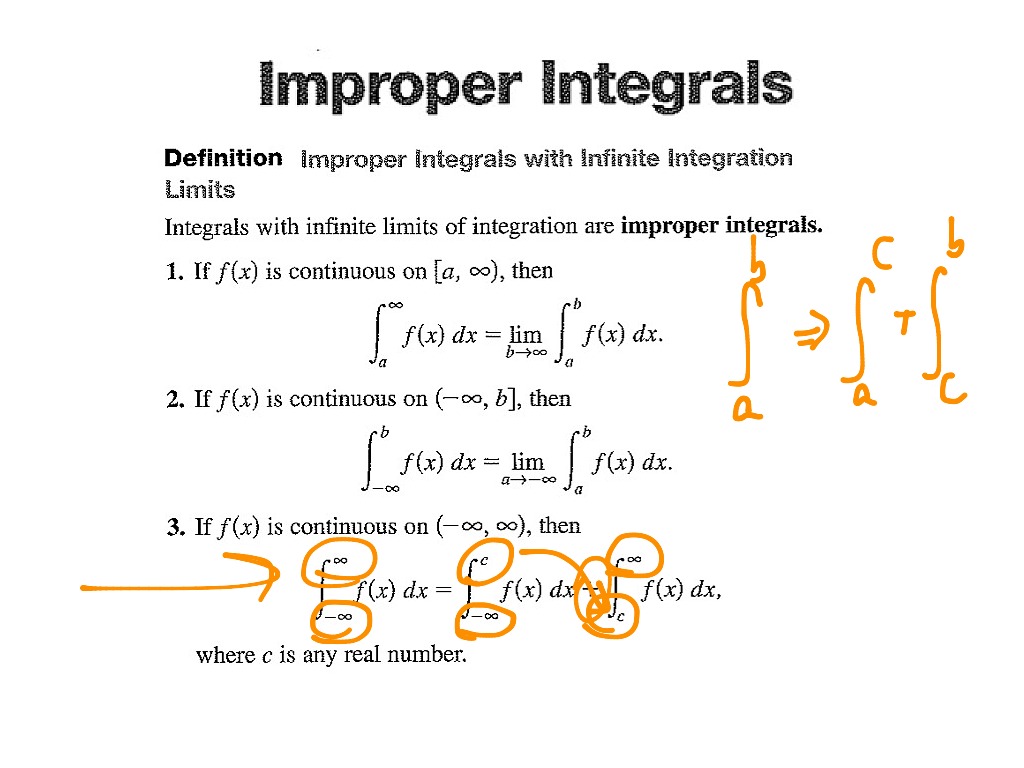
Improper Integrals Infinity Introduction Math Calculus Integrals This solution was automatically generated by our smart calculator: solve the integral by applying the formula $\displaystyle\int\frac {x'} {x^2 a^2}dx=\frac {1} {a}\arctan\left (\frac {x} {a}\right)$. add the initial limits of integration. replace the integral's limit by a finite value. evaluate the definite integral. Take the integral from 1 to 1 of (1 x^2)*dx as an example, as the function is discontinuous at x=0. or 2. one of the integration limits contains positive or negative infinity. an example with both conditions would be the integral from 0 to infinity of 1 (x^2) *dx.
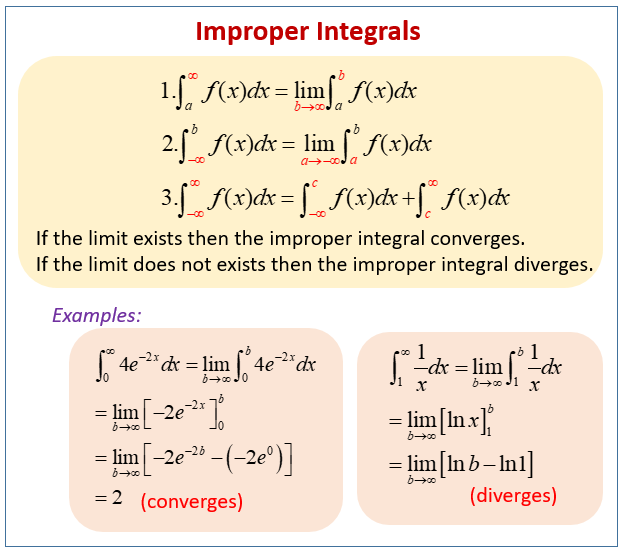
Improper Integrals Examples Solutions Videos

Comments are closed.