In Delta Abc The Bisector Of Angle B Meets Ac At D A Line Pq Ac
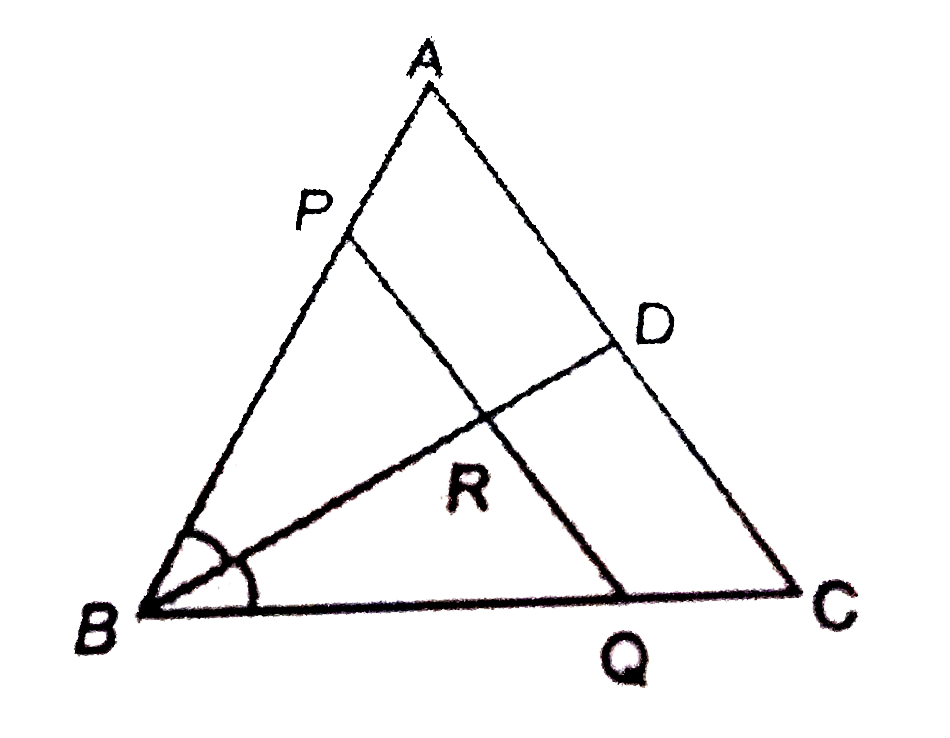
In Delta Abc The Bisector Of Angle B Meets Ac At D A Line Pq Ac Ab ac = bp pc , ap is the bisector of angle bac. q. ∆abc and ∆dbc lie on the same side of bc , as shown in the figure. from a point p on bc , pq ∥ ab and pr ∥ bd are drawn, meeting ac at q and cd at r , respectively. In ∆abc, the bisector of ∠b meets ac at d. a line oq║ac meets ab, bc and bd at o, q and r respectively. asked jun 28, 2021 in triangles by gavya ( 32.2k points).
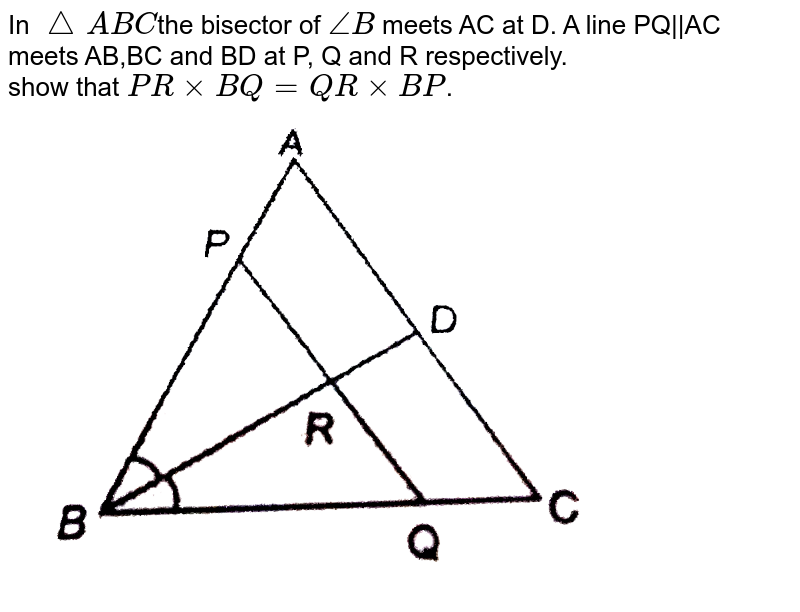
In тижюааabcюаб юааthe Bisectorюаб Of тиаюааbюаб юааmeetsюаб юааacюаб юааat Dюаб юааa Lineюаб Oqтхсю In triangle abc, p is the mid point of side bc. a line through p and parallel to ca meets ab at point q; and a line through q meets at s.qs parallel to bc meets median ap at point r. prove that : (i) ap = 2ar (ii) bc= 4qr. The angle bisector of an angle of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts that are proportional to the other two side of the triangle. calculation: the ac is. ⇒ ac = ad dc. ⇒ dc = 22.4 ad. using the concept. ⇒ a d d c = a b b c. ⇒ a d 22.4 − a d = 16 9.6. ⇒ 96ad = 3584 160ad. Solution: by the angle bisector theorem, or . plugging this into and solving for ac gives . we can plug this back in to find . in triangle abc, let p be a point on bc and let . find the value of . solution: first, we notice that . thus, ap is the angle bisector of angle a, making our answer 0. part (b), 1959 imo problems problem 5. Solution: a b = 6, b c = 3. also, bd is the angle bisector. according to the angle bisector theorem, bd divides ac in the ratio proportional to the ratio of the other two sides. thus, the ratio of ad to dc is the same as the ratio of ab to bc. a b b c = a d d c. ⇒ 6 3 = a d d c. ⇒ a d: d c = 6: 3.

In Triangleabc The Bisector Of Angleb Meets Ac At D A Line Pq ођ Solution: by the angle bisector theorem, or . plugging this into and solving for ac gives . we can plug this back in to find . in triangle abc, let p be a point on bc and let . find the value of . solution: first, we notice that . thus, ap is the angle bisector of angle a, making our answer 0. part (b), 1959 imo problems problem 5. Solution: a b = 6, b c = 3. also, bd is the angle bisector. according to the angle bisector theorem, bd divides ac in the ratio proportional to the ratio of the other two sides. thus, the ratio of ad to dc is the same as the ratio of ab to bc. a b b c = a d d c. ⇒ 6 3 = a d d c. ⇒ a d: d c = 6: 3. So the angle bisector theorem tells us that the ratio of 3 to 2 is going to be equal to 6 to x. and then we can just solve for x. so 3 to 2 is going to be equal to 6 to x. and then once again, you could just cross multiply, or you could multiply both sides by 2 and x. that kind of gives you the same result. Viewed 107 times. 1. internal angle bisector of ∠a ∠ a of triangle Δabc Δ a b c, meets side bc at d. a line drawn through d perpendicular to ad intersects the side ac at p and the side ab at q. if a, b, c represent the sides of ∆abc then. (a) ad = 2bc b ccos a2 a d = 2 b c b c cos a 2. (b) pq = 4bc b csin a 2 p q = 4 b c b c sin a 2.

Comments are closed.